Abstract
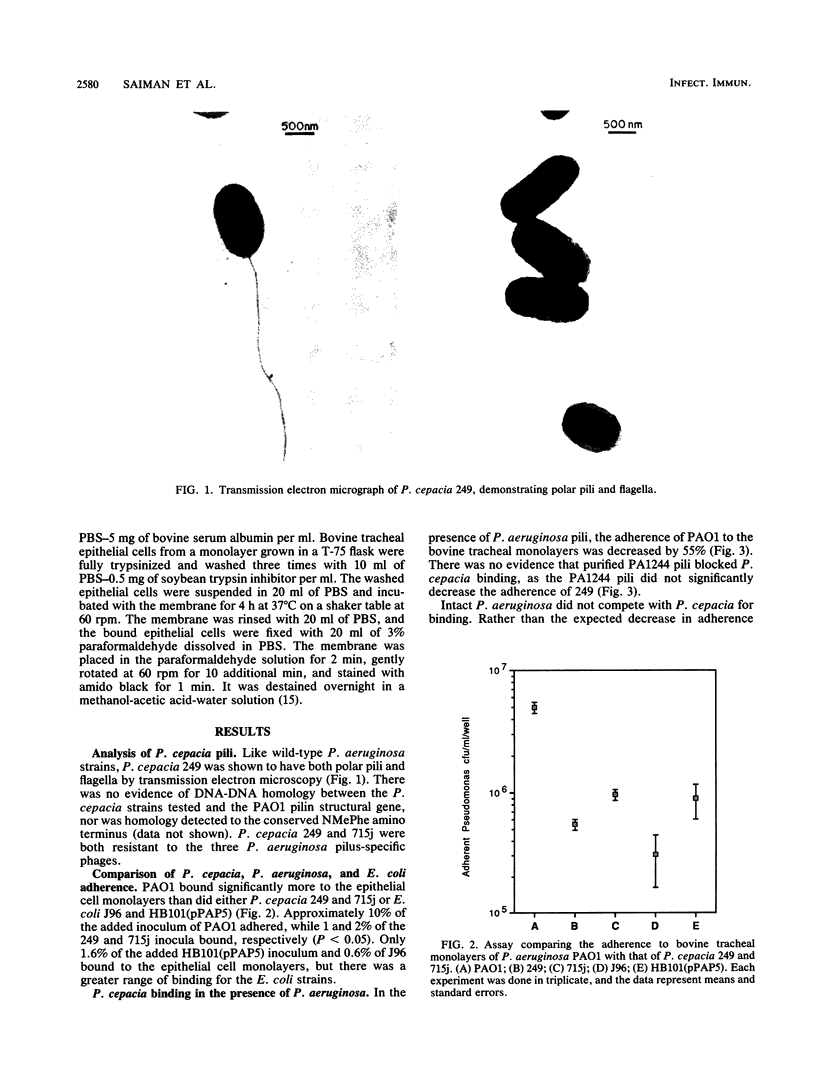
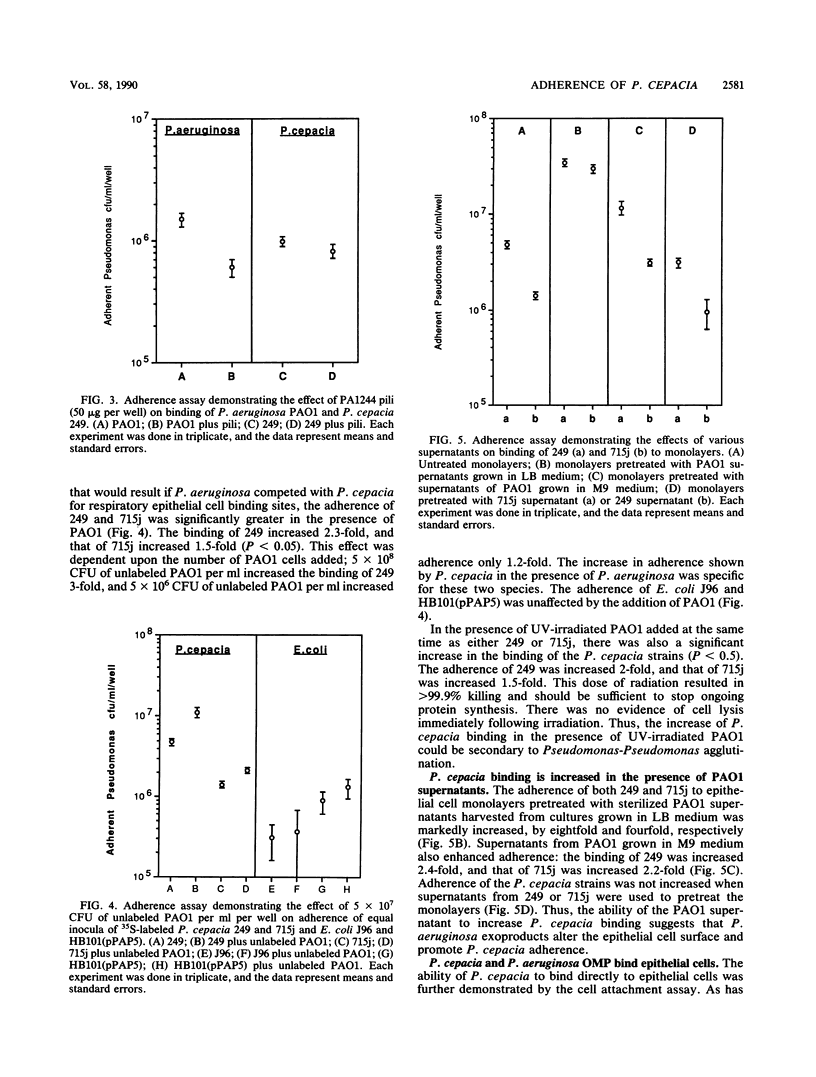
Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Pseudomonas cepacia are both opportunistic pathogens of patients with cystic fibrosis. The binding characteristics of these two species were compared to determine if they use similar mechanisms to adhere to respiratory epithelial cells. P. cepacia 249 was shown to be piliated, but there was no detectable homology between P. aeruginosa pilin gene probes and P. cepacia genomic DNA. P. cepacia and P. aeruginosa did not appear to compete for epithelial receptors. In the presence of purified P. aeruginosa pili, the adherence of 35S-labeled strain 249 to respiratory epithelial monolayers was unaffected, while that of P. aeruginosa PAO1 was decreased by 55%. The binding of P. cepacia 249 and 715j was increased by 2.4-fold and 1.5-fold, respectively, in the presence of an equal inoculum of PAO1. Interbacterial agglutination contributed to the increased adherence of P. cepacia, as the binding of 249 was increased twofold in the presence of irradiated PAO1. PAO1 exoproducts had a marked effect in enhancing the ability of the P. cepacia strains to adhere to the epithelial monolayers. A PAO1 supernatant increased the binding of 249 by eightfold and that of 715j by fourfold. Thus, there appears to be a synergistic relationship between P. aeruginosa and P. cepacia in which PAO1 exoproducts modify the epithelial cell surface, exposing receptors and facilitating increased P. cepacia attachment.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballard R. W., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M., Stanier R. Y., Mandel M. Taxonomy of the aerobic pseudomonads: Pseudomonas cepacia, P. marginata, P. alliicola and P. caryophylli. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Feb;60(2):199–214. doi: 10.1099/00221287-60-2-199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckman W., Lessie T. G. Response of Pseudomonas cepacia to beta-Lactam antibiotics: utilization of penicillin G as the carbon source. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):1126–1128. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.1126-1128.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkelman R. L., Lewin S., Allen J. R., Anderson R. L., Budnick L. D., Shapiro S., Friedman S. M., Nicholas P., Holzman R. S., Haley R. W. Pseudobacteremia attributed to contamination of povidone-iodine with Pseudomonas cepacia. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Jul;95(1):32–36. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-95-1-32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E., Pitt T. L. An immunological study of the pili of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Hyg (Lond) 1975 Jun;74(3):419–430. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400046933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E., Pitt T. L. Pilus-dependence of four Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteriophages with non-contractile tails. J Gen Virol. 1974 Jul;24(1):1–15. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-24-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns J. L., Hedin L. A., Lien D. M. Chloramphenicol resistance in Pseudomonas cepacia because of decreased permeability. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Feb;33(2):136–141. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.2.136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson L. A., Favero M. S., Bond W. W., Petersen N. J. Morphological, biochemical, and growth characteristics of pseudomonas cepacia from distilled water. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Mar;25(3):476–483. doi: 10.1128/am.25.3.476-483.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corey M., Allison L., Prober C., Levison H. Sputum bacteriology in patients with cystic fibrosis in a Toronto hospital during 1970-1981. J Infect Dis. 1984 Feb;149(2):283–283. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.2.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. E., Kaslow R. A., Mackel D. C., Fulkerson C. C., Mallison G. F. Aqueous quaternary ammonium antiseptics and disinfectants. Use and misuse. JAMA. 1976 Nov 22;236(21):2415–2417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doig P., Todd T., Sastry P. A., Lee K. K., Hodges R. S., Paranchych W., Irvin R. T. Role of pili in adhesion of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to human respiratory epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1988 Jun;56(6):1641–1646. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.6.1641-1646.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Nikaido H. Outer membranes of gram-negative bacteria. XIX. Isolation from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 and use in reconstitution and definition of the permeability barrier. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):381–390. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.381-390.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway B. W., Krishnapillai V., Morgan A. F. Chromosomal genetics of Pseudomonas. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Mar;43(1):73–102. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.1.73-102.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull R. A., Gill R. E., Hsu P., Minshew B. H., Falkow S. Construction and expression of recombinant plasmids encoding type 1 or D-mannose-resistant pili from a urinary tract infection Escherichia coli isolate. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):933–938. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.933-938.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Leong J. M. Cultured mammalian cells attach to the invasin protein of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6682–6686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krivan H. C., Ginsburg V., Roberts D. D. Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Pseudomonas cepacia isolated from cystic fibrosis patients bind specifically to gangliotetraosylceramide (asialo GM1) and gangliotriaosylceramide (asialo GM2). Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Jan;260(1):493–496. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90473-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. K., Doig P., Irvin R. T., Paranchych W., Hodges R. S. Mapping the surface regions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAK pilin: the importance of the C-terminal region for adherence to human buccal epithelial cells. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Nov;3(11):1493–1499. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00135.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leffler H., Svanborg-Edén C. Glycolipid receptors for uropathogenic Escherichia coli on human erythrocytes and uroepithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):920–929. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.920-929.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg F. P., Lund B., Normark S. Genes of pyelonephritogenic E. coli required for digalactoside-specific agglutination of human cells. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1167–1173. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01946.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonon M. K., Woods D. E., Straus D. C. Production of lipase by clinical isolates of Pseudomonas cepacia. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 May;26(5):979–984. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.5.979-984.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martone W. J., Osterman C. A., Fisher K. A., Wenzel R. P. Pseudomonas cepacia: implications and control of epidemic nosocomial colonization. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Jul-Aug;3(4):708–715. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.4.708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKevitt A. I., Bajaksouzian S., Klinger J. D., Woods D. E. Purification and characterization of an extracellular protease from Pseudomonas cepacia. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):771–778. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.771-778.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKevitt A. I., Woods D. E. Characterization of Pseudomonas cepacia isolates from patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):291–293. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.291-293.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa T., Yamada Y., Ishibashi M. Characterization of hemolysin in extracellular products of Pseudomonas cepacia. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Feb;25(2):195–198. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.2.195-198.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paranchych W., Frost L. S. The physiology and biochemistry of pili. Adv Microb Physiol. 1988;29:53–114. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60346-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pemberton J. M. F116: a DNA bacteriophage specific for the pili of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAO. Virology. 1973 Oct;55(2):558–560. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90203-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramphal R., Pier G. B. Role of Pseudomonas aeruginosa mucoid exopolysaccharide in adherence to tracheal cells. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):1–4. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.1-4.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramphal R., Sadoff J. C., Pyle M., Silipigni J. D. Role of pili in the adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to injured tracheal epithelium. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):38–40. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.38-40.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivera M., Nicotra M. B. Pseudomonas aeruginosa mucoid strain. Its significance in adult chest diseases. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Nov;126(5):833–836. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.126.5.833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenstein B. J., Hall D. E. Pneumonia and septicemia due to Pseudomonas cepacia in a patient with cystic fibrosis. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1980 Nov;147(5):188–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiman L., Ishimoto K., Lory S., Prince A. The effect of piliation and exoproduct expression on the adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to respiratory epithelial monolayers. J Infect Dis. 1990 Mar;161(3):541–548. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.3.541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiman L., Sadoff J., Prince A. Cross-reactivity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa antipilin monoclonal antibodies with heterogeneous strains of P. aeruginosa and Pseudomonas cepacia. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2764–2770. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2764-2770.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sastry P. A., Finlay B. B., Pasloske B. L., Paranchych W., Pearlstone J. R., Smillie L. B. Comparative studies of the amino acid and nucleotide sequences of pilin derived from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAK and PAO. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):571–577. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.571-577.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke J. R., Edwards M. S., Langston C., Baker C. J. A mouse model of chronic pulmonary infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Pseudomonas cepacia. Pediatr Res. 1987 Dec;22(6):698–702. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198712000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Tenney J. H., Mackel D. C., Snyder M. J., Polakavetz S., Dunne M. E., Dixon R. Pseudomonas species bacteremia caused by contaminated normal human serum albumin. J Infect Dis. 1977 May;135(5):729–735. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.5.729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stover G. B., Drake D. R., Montie T. C. Virulence of different Pseudomonas species in a burned mouse model: tissue colonization by Pseudomonas cepacia. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1099–1104. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1099-1104.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. XIV. Cell wall protein differences among color/opacity colony variants of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):292–302. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.292-302.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tablan O. C., Chorba T. L., Schidlow D. V., White J. W., Hardy K. A., Gilligan P. H., Morgan W. M., Carson L. A., Martone W. J., Jason J. M. Pseudomonas cepacia colonization in patients with cystic fibrosis: risk factors and clinical outcome. J Pediatr. 1985 Sep;107(3):382–387. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(85)80511-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Straus D. C., Johanson W. G., Jr, Bass J. A. Role of salivary protease activity in adherence of gram-negative bacilli to mammalian buccal epithelial cells in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1981 Dec;68(6):1435–1440. doi: 10.1172/JCI110395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Straus D. C., Johanson W. G., Jr, Berry V. K., Bass J. A. Role of pili in adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to mammalian buccal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):1146–1151. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.1146-1151.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeitlin P. L., Loughlin G. M., Guggino W. B. Ion transport in cultured fetal and adult rabbit tracheal epithelia. Am J Physiol. 1988 May;254(5 Pt 1):C691–C698. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.254.5.C691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]