Abstract
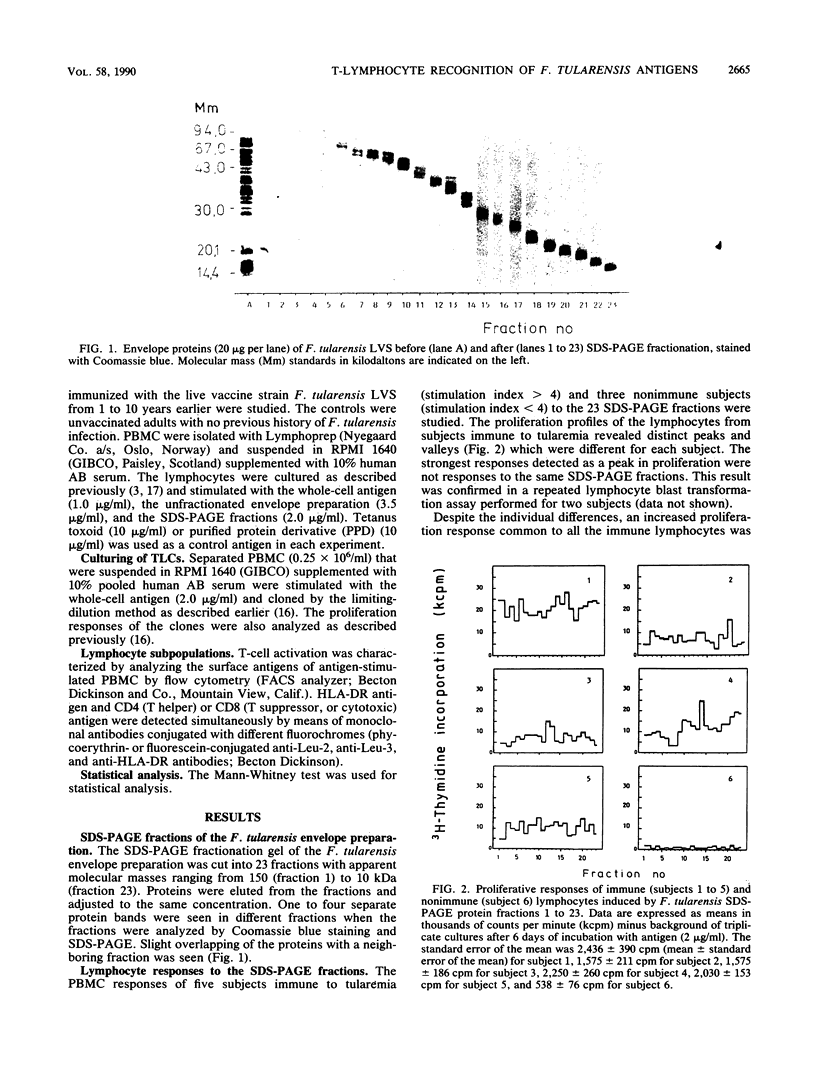
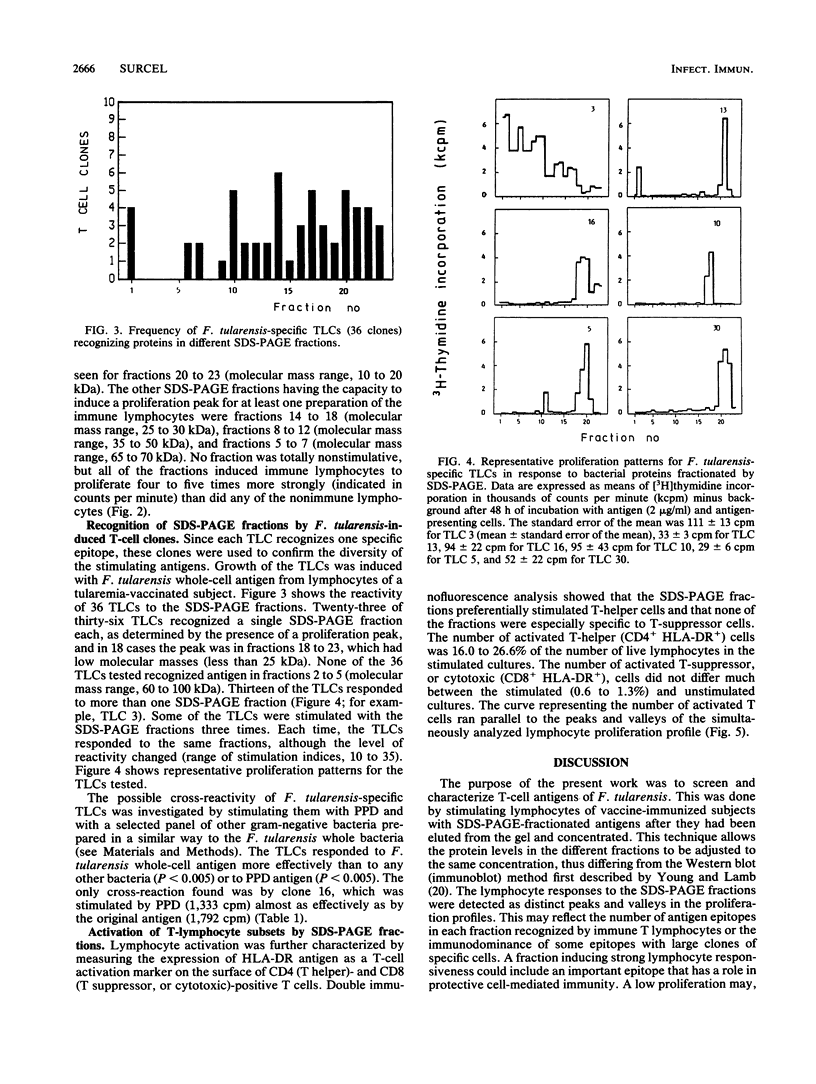
The Francisella tularensis T-lymphocyte antigens, which may have a role in protection against tularemia, were investigated with vaccine-immunized subjects. Preparative sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) was used to fractionate the bacterial envelope preparation. The 23 fractions obtained represented membrane proteins of different apparent molecular masses ranging from 10 to 150 kilodaltons. Different fractions contained one to four separate protein bands stained with Coomassie blue. The lymphocyte blast transformation responses of five tularemia vaccine-immunized and three nonimmunized subjects were tested against bacterial material eluted out of SDS-PAGE fractions. Every fraction stimulated lymphocytes from at least one of the subjects. No clearly immunodominant or inhibitory antigens were detected among the envelope fractions. Expression of the HLA-DR antigen at the surface of CD4- and CD8-positive lymphocytes was also studied as a measure of cell activation. The numbers of CD4+ DR+ cells varied directly with the lymphocyte proliferation profiles, and very few CD8+ cells were found in the preparations stimulated with the different fractions. The diversity of the antigens recognized by immune T lymphocytes was confirmed by using F. tularensis-specific T-lymphocyte clones obtained from vaccinated subjects. Most of the 36 T-lymphocyte clones tested were stimulated by one SDS-PAGE fraction only.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Converse P. J., Ottenhoff T. H., Gebre N., Ehrenberg J. P., Kiessling R. Cellular, humoral, and gamma interferon responses to Mycobacterium leprae and BCG antigens in healthy individuals exposed to leprosy. Scand J Immunol. 1988 May;27(5):515–525. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1988.tb02378.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmrich F., Kaufmann S. H. Human T-cell clones with reactivity to Mycobacterium leprae as tools for the characterization of potential vaccines against leprosy. Infect Immun. 1986 Mar;51(3):879–883. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.3.879-883.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koskela P., Herva E. Cell-mediated and humoral immunity induced by a live Francisella tularensis vaccine. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):983–989. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.983-989.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koskela P., Herva E. Cell-mediated immunity against Francisella tularensis after natural infection. Scand J Infect Dis. 1980;12(4):281–287. doi: 10.3109/inf.1980.12.issue-4.08. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb J. R., Rees A. D. Antigen specificity and function of human T lymphocyte clones reactive with mycobacteria. Br Med Bull. 1988 Jul;44(3):600–610. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. P., Stoker N. G., Grant K. A., Handzel Z. T., Hussain R., McAdam K. P., Dockrell H. M. Cellular immune responses of leprosy contacts to fractionated Mycobacterium leprae antigens. Infect Immun. 1989 Aug;57(8):2475–2480. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.8.2475-2480.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurelli A. T. Temperature regulation of virulence genes in pathogenic bacteria: a general strategy for human pathogens? Microb Pathog. 1989 Jul;7(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90106-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modlin R. L., Brenner M. B., Krangel M. S., Duby A. D., Bloom B. R. T-cell receptors of human suppressor cells. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):541–545. doi: 10.1038/329541a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa A. S., Oftung F., Deggerdal A., Gill H. K., Young R. A., Godal T. Gene isolation with human T lymphocyte probes. Isolation of a gene that expresses an epitope recognized by T cells specific for Mycobacterium bovis BCG and pathogenic mycobacteria. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 15;141(8):2729–2733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottenhoff T. H., Klatser P. R., Ivanyi J., Elferink D. G., de Wit M. Y., de Vries R. R. Mycobacterium leprae-specific protein antigens defined by cloned human helper T cells. Nature. 1986 Jan 2;319(6048):66–68. doi: 10.1038/319066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pink J. R., Rijnbeek A. M., Reber-Liske R., Sinigaglia F. Plasmodium falciparum-specific human T cell clones: recognition of different parasite antigens. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Feb;17(2):193–196. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees A., Scoging A., Mehlert A., Young D. B., Ivanyi J. Specificity of proliferative response of human CD8 clones to mycobacterial antigens. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Dec;18(12):1881–1887. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830181203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandström G., Tärnvik A., Wolf-Watz H. Immunospecific T-lymphocyte stimulation by membrane proteins from Francisella tularensis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Apr;25(4):641–644. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.4.641-644.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöstedt A., Sandström G., Tärnvik A., Jaurin B. Molecular cloning and expression of a T-cell stimulating membrane protein of Francisella tularensis. Microb Pathog. 1989 Jun;6(6):403–414. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90082-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surcel H. M., Ilonen J., Poikonen K., Herva E. Francisella tularensis-specific T-cell clones are human leukocyte antigen class II restricted, secrete interleukin-2 and gamma interferon, and induce immunoglobulin production. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2906–2908. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2906-2908.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syrjälä H., Herva E., Ilonen J., Saukkonen K., Salminen A. A whole-blood lymphocyte stimulation test for the diagnosis of human tularemia. J Infect Dis. 1984 Dec;150(6):912–915. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.6.912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tärnvik A. Nature of protective immunity to Francisella tularensis. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 May-Jun;11(3):440–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. B., Lamb J. R. T lymphocytes respond to solid-phase antigen: a novel approach to the molecular analysis of cellular immunity. Immunology. 1986 Oct;59(2):167–171. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]