Abstract
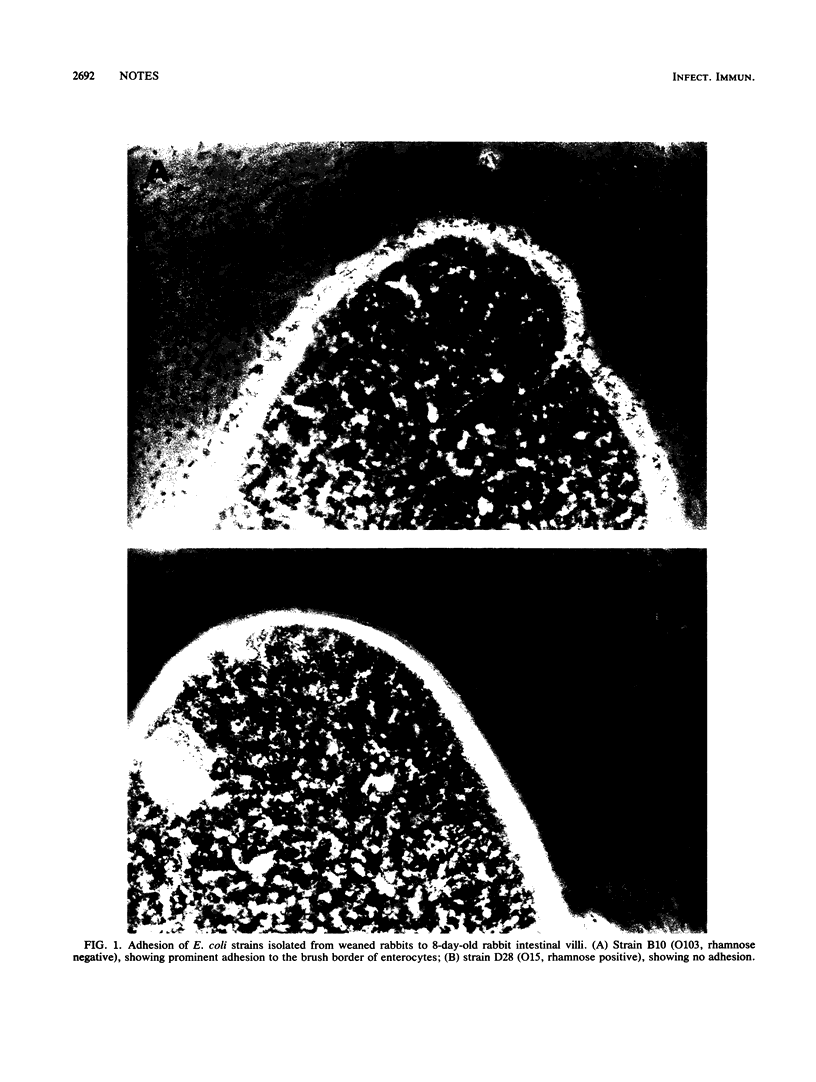
Thirty-eight strains, representative of 575 Escherichia coli isolates from weaned diarrheic rabbits, were tested for their ability to adhere in vitro to rabbit intestinal villi and to HeLa 229 cells. The O103 rhamnose-negative, highly pathogenic strains, which are epidemiologically predominant in France, attached to intestinal villi prepared from 8-day-old as well as 6-week-old rabbits and gave a diffuse adhesion pattern with HeLa cells. These adhesion properties were associated with the presence of a protein with a molecular weight of 32,000 in surface extracts of the strains. The expression of the adhesion was dependent on culture medium and temperature, and the adhesion was D-mannose resistant. Antisera raised against the 32,000-molecular-weight protein inhibited adhesion. This adhesion was not expressed in two nonpathogenic O103 strains, indicating its implication in virulence. However, the same adhesin was expressed by two O128 non- or moderately pathogenic strains. Therefore, adhesion to enterocytes is not the only factor involved in the pathogenicity of O103 strains.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berendson R., Cheney C. P., Schad P. A., Boedeker E. C. Species-specific binding of purified pili (AF/R1) from the Escherichia coli RDEC-1 to rabbit intestinal mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1983 Oct;85(4):837–845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camguilhem R., Lebas F., Labie C. Reproduction expérimentale chez le lapin en engraissement d'une diarrhée provoquée par une souche de Escherichia coli de sérogroupe O-103. Ann Rech Vet. 1986;17(4):409–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camguilhem R., Milon A. Biotypes and O serogroups of Escherichia coli involved in intestinal infections of weaned rabbits: clues to diagnosis of pathogenic strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Apr;27(4):743–747. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.4.743-747.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantey J. R., Blake R. K. Diarrhea due to Escherichia coli in the rabbit: a novel mechanism. J Infect Dis. 1977 Mar;135(3):454–462. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.3.454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheney C. P., Boedeker E. C. Rabbit mucosal receptors for an enteropathogenic Escherichia coli strain: appearance of bacterial receptor activity at weaning. Gastroenterology. 1984 Oct;87(4):821–826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheney C. P., Formal S. B., Schad P. A., Boedeker E. C. Genetic transfer of a mucosal adherence factor (R1) from an enteropathogenic Escherichia coli strain into a Shigella flexneri strain and the phenotypic suppression of this adherence factor. J Infect Dis. 1983 Apr;147(4):711–723. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.4.711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girardeau J. P. A new in vitro technique for attachment to intestinal villi using enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1980 Jul-Aug;131B(1):31–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M. Escherichia coli that cause diarrhea: enterotoxigenic, enteropathogenic, enteroinvasive, enterohemorrhagic, and enteroadherent. J Infect Dis. 1987 Mar;155(3):377–389. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.3.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W., Whipp S. C., Argenzio R. A., Levine M. M., Giannella R. A. Attaching and effacing activities of rabbit and human enteropathogenic Escherichia coli in pig and rabbit intestines. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1340–1351. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1340-1351.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okerman L., Devriese L. A. Biotypes of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli strains from rabbits. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Dec;22(6):955–958. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.6.955-958.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okerman L. Enteric infections caused by non-enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in animals: occurrence and pathogenicity mechanisms. A review. Vet Microbiol. 1987 May;14(1):33–46. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(87)90050-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeters J. E., Charlier G. J., Raeymaekers R. Scanning and transmission electron microscopy of attaching effacing Escherichia coli in weanling rabbits. Vet Pathol. 1985 Jan;22(1):54–59. doi: 10.1177/030098588502200109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeters J. E., Pohl P., Okerman L., Devriese L. A. Pathogenic properties of Escherichia coli strains isolated from diarrheic commercial rabbits. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jul;20(1):34–39. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.1.34-39.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scaletsky I. C., Silva M. L., Trabulsi L. R. Distinctive patterns of adherence of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to HeLa cells. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):534–536. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.534-536.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi A., Inman L. R., O'Hanley P. D., Cantey J. R., Lushbaugh W. B. Scanning and transmission electron microscopic study of Escherichia coli O15 (RDEC-1) enteric infection in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):686–694. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.686-694.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Graaf F. K., Klemm P., Gaastra W. Purification, characterization, and partial covalent structure of Escherichia coli adhesive antigen K99. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):877–883. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.877-883.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]