Abstract
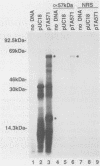
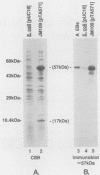
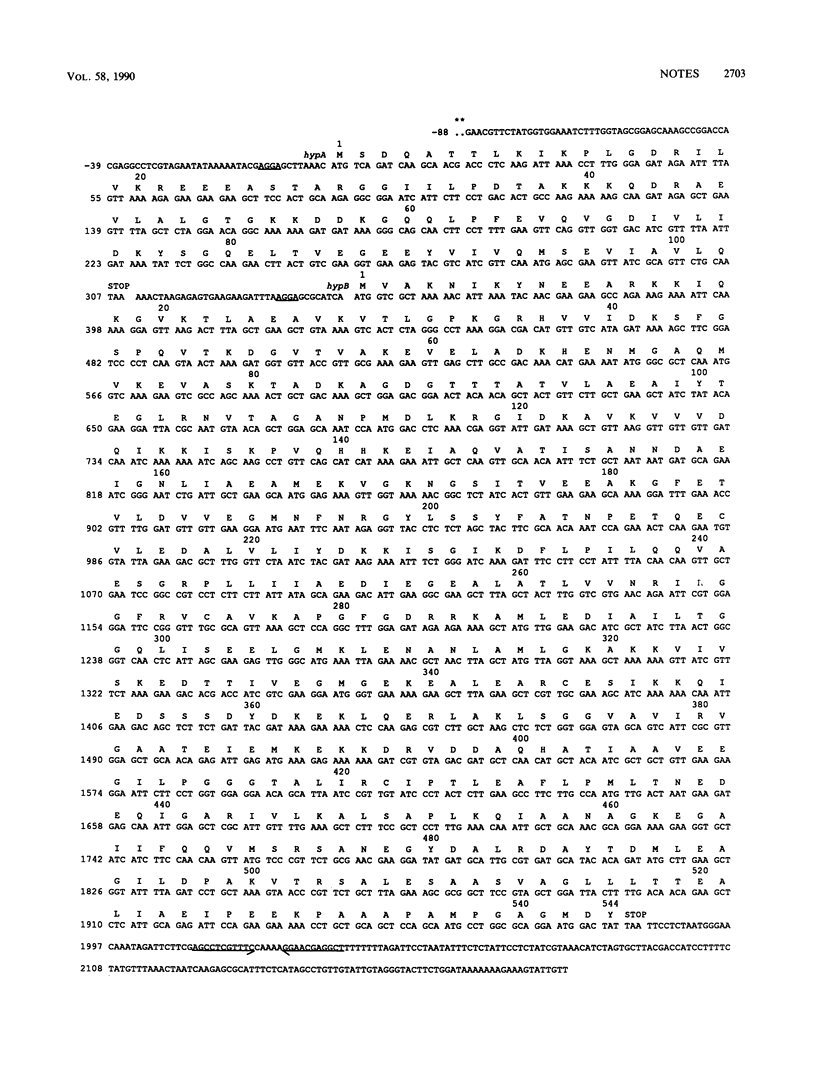
The Chlamydia trachomatis serovar A hyp operon was cloned, sequenced, and expressed in Escherichia coli. Two cotranscribed open reading frames, hypA and hypB, encoded polypeptides of 17 and 57 kilodaltons, respectively. The deduced amino acid sequences of serovar A HypA and HypB proteins were (respectively) 85 and 94% identical with HypA and HypB proteins of Chlamydia psittaci GPIC, and HypB was greater than 50% identical to 60-kilodalton stress response proteins from other procaryotes and eucaryotes. The sequence should be useful in defining the antigenic structure of the Chlamydia trachomatis HypB protein, a necessary step toward understanding the relationship between the immune response to this protein and the pathogenesis of human chlamydial diseases.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caldwell H. D., Kromhout J., Schachter J. Purification and partial characterization of the major outer membrane protein of Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1161–1176. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1161-1176.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier L. H. The immunopathology of trachoma: some facts and fancies. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1967;22(1):280–293. doi: 10.1007/BF01240523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G., Adam S. A., Choi Y. D. Physical change in cytoplasmic messenger ribonucleoproteins in cells treated with inhibitors of mRNA transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):415–423. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grayston J. T., Wang S. P., Yeh L. J., Kuo C. C. Importance of reinfection in the pathogenesis of trachoma. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Nov-Dec;7(6):717–725. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.6.717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmingsen S. M., Woolford C., van der Vies S. M., Tilly K., Dennis D. T., Georgopoulos C. P., Hendrix R. W., Ellis R. J. Homologous plant and bacterial proteins chaperone oligomeric protein assembly. Nature. 1988 May 26;333(6171):330–334. doi: 10.1038/333330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison R. P., Belland R. J., Lyng K., Caldwell H. D. Chlamydial disease pathogenesis. The 57-kD chlamydial hypersensitivity antigen is a stress response protein. J Exp Med. 1989 Oct 1;170(4):1271–1283. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.4.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison R. P., Lyng K., Caldwell H. D. Chlamydial disease pathogenesis. Ocular hypersensitivity elicited by a genus-specific 57-kD protein. J Exp Med. 1989 Mar 1;169(3):663–675. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.3.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Møller B. R., Weström L., Ahrons S., Ripa K. T., Svensson L., von Mecklenburg C., Henrikson H., Mårdh P. A. Chlamydia trachomatis infection of the Fallopian tubes. Histological findings in two patients. Br J Vener Dis. 1979 Dec;55(6):422–428. doi: 10.1136/sti.55.6.422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor H. R., Johnson S. L., Schachter J., Caldwell H. D., Prendergast R. A. Pathogenesis of trachoma: the stimulus for inflammation. J Immunol. 1987 May 1;138(9):3023–3027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins N. G., Hadlow W. J., Moos A. B., Caldwell H. D. Ocular delayed hypersensitivity: a pathogenetic mechanism of chlamydial-conjunctivitis in guinea pigs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7480–7484. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan Y., Zhang Y. X., Watkins N. G., Caldwell H. D. Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences for the four variable domains of the major outer membrane proteins of the 15 Chlamydia trachomatis serovars. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1040–1049. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1040-1049.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. X., Stewart S., Joseph T., Taylor H. R., Caldwell H. D. Protective monoclonal antibodies recognize epitopes located on the major outer membrane protein of Chlamydia trachomatis. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 15;138(2):575–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Asrar A. M., Van den Oord J. J., Geboes K., Missotten L., Emarah M. H., Desmet V. Immunopathology of trachomatous conjunctivitis. Br J Ophthalmol. 1989 Apr;73(4):276–282. doi: 10.1136/bjo.73.4.276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]