Full text
PDF






















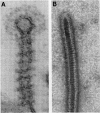
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahle S., Ungewickell E. Purification and properties of a new clathrin assembly protein. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3143–3149. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04621.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W., Tse F. W. Transmitter release from synapses: does a preassembled fusion pore initiate exocytosis? Neuron. 1990 Jun;4(6):813–818. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90134-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews J., Smith M., Merakovsky J., Coulson M., Hannan F., Kelly L. E. The stoned locus of Drosophila melanogaster produces a dicistronic transcript and encodes two distinct polypeptides. Genetics. 1996 Aug;143(4):1699–1711. doi: 10.1093/genetics/143.4.1699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. V. Electrical versus chemical neurotransmission. Res Publ Assoc Res Nerv Ment Dis. 1972;50:58–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. V. Gap junctions as electrical synapses. J Neurocytol. 1997 Jun;26(6):349–366. doi: 10.1023/a:1018560803261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. V. Physiology of electrotonic junctions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jul 14;137(2):509–539. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb50178.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson D. L., Colman D. R., Huntley G. W. Molecules, maps and synapse specificity. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2001 Dec;2(12):899–909. doi: 10.1038/35104078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz W. J., Bewick G. S. Optical analysis of synaptic vesicle recycling at the frog neuromuscular junction. Science. 1992 Jan 10;255(5041):200–203. doi: 10.1126/science.1553547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz W. J., Mao F., Bewick G. S. Activity-dependent fluorescent staining and destaining of living vertebrate motor nerve terminals. J Neurosci. 1992 Feb;12(2):363–375. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-02-00363.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz W. J., Mao F., Smith C. B. Imaging exocytosis and endocytosis. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1996 Jun;6(3):365–371. doi: 10.1016/s0959-4388(96)80121-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bommert K., Charlton M. P., DeBello W. M., Chin G. J., Betz H., Augustine G. J. Inhibition of neurotransmitter release by C2-domain peptides implicates synaptotagmin in exocytosis. Nature. 1993 May 13;363(6425):163–165. doi: 10.1038/363163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breckenridge L. J., Almers W. Currents through the fusion pore that forms during exocytosis of a secretory vesicle. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2Nature. 328(6133):814–817. doi: 10.1038/328814a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breckenridge L. J., Almers W. Final steps in exocytosis observed in a cell with giant secretory granules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1945–1949. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broadie K., Bellen H. J., DiAntonio A., Littleton J. T., Schwarz T. L. Absence of synaptotagmin disrupts excitation-secretion coupling during synaptic transmission. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 25;91(22):10727–10731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.22.10727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky F. M., Chen C. Y., Knuehl C., Towler M. C., Wakeham D. E. Biological basket weaving: formation and function of clathrin-coated vesicles. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2001;17:517–568. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.17.1.517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky F. M. Clathrin structure characterized with monoclonal antibodies. II. Identification of in vivo forms of clathrin. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2055–2062. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky F. M., Hill B. L., Acton S. L., Näthke I., Wong D. H., Ponnambalam S., Parham P. Clathrin light chains: arrays of protein motifs that regulate coated-vesicle dynamics. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Jun;16(6):208–213. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90087-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky F. M. Living with clathrin: its role in intracellular membrane traffic. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1396–1402. doi: 10.1126/science.2904698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunger A. T. Structure of proteins involved in synaptic vesicle fusion in neurons. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2001;30:157–171. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.30.1.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger K. N. Greasing membrane fusion and fission machineries. Traffic. 2000 Aug;1(8):605–613. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0854.2000.010804.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bähler M., Benfenati F., Valtorta F., Greengard P. The synapsins and the regulation of synaptic function. Bioessays. 1990 Jun;12(6):259–263. doi: 10.1002/bies.950120603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceccarelli B., Hurlbut W. P., Mauro A. Turnover of transmitter and synaptic vesicles at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Cell Biol. 1973 May;57(2):499–524. doi: 10.1083/jcb.57.2.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman E. R., Hanson P. I., An S., Jahn R. Ca2+ regulates the interaction between synaptotagmin and syntaxin 1. J Biol Chem. 1995 Oct 6;270(40):23667–23671. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.40.23667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman Edwin R. Synaptotagmin: a Ca(2+) sensor that triggers exocytosis? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Jul;3(7):498–508. doi: 10.1038/nrm855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chi P., Greengard P., Ryan T. A. Synapsin dispersion and reclustering during synaptic activity. Nat Neurosci. 2001 Dec;4(12):1187–1193. doi: 10.1038/nn756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu D. S., Pishvaee B., Payne G. S. A modulatory role for clathrin light chain phosphorylation in Golgi membrane protein localization during vegetative growth and during the mating response of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Biol Cell. 1999 Mar;10(3):713–726. doi: 10.1091/mbc.10.3.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couteaux R., Pécot-Dechavassine M. Vésicules synaptiques et poches au niveau des "zones actives" de la jonction neuromusculaire. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1970 Dec 21;271(25):2346–2349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremona O., De Camilli P. Phosphoinositides in membrane traffic at the synapse. J Cell Sci. 2001 Mar;114(Pt 6):1041–1052. doi: 10.1242/jcs.114.6.1041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremona O., Di Paolo G., Wenk M. R., Lüthi A., Kim W. T., Takei K., Daniell L., Nemoto Y., Shears S. B., Flavell R. A. Essential role of phosphoinositide metabolism in synaptic vesicle recycling. Cell. 1999 Oct 15;99(2):179–188. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81649-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech Michael P. Dynamics of phosphoinositides in membrane retrieval and insertion. Annu Rev Physiol. 2002 Oct 28;65:791–815. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physiol.65.092101.142522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE ROBERTIS E. D., BENNETT H. S. Some features of the submicroscopic morphology of synapses in frog and earthworm. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1955 Jan;1(1):47–58. doi: 10.1083/jcb.1.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Quantal components of the end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):560–573. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damke H., Baba T., Warnock D. E., Schmid S. L. Induction of mutant dynamin specifically blocks endocytic coated vesicle formation. J Cell Biol. 1994 Nov;127(4):915–934. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.4.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danino D., Hinshaw J. E. Dynamin family of mechanoenzymes. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001 Aug;13(4):454–460. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(00)00236-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David C., McPherson P. S., Mundigl O., de Camilli P. A role of amphiphysin in synaptic vesicle endocytosis suggested by its binding to dynamin in nerve terminals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Jan 9;93(1):331–335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.1.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Camilli P., Benfenati F., Valtorta F., Greengard P. The synapsins. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:433–460. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.002245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Camilli P., Cameron R., Greengard P. Synapsin I (protein I), a nerve terminal-specific phosphoprotein. I. Its general distribution in synapses of the central and peripheral nervous system demonstrated by immunofluorescence in frozen and plastic sections. J Cell Biol. 1983 May;96(5):1337–1354. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.5.1337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Camilli P., Harris S. M., Jr, Huttner W. B., Greengard P. Synapsin I (Protein I), a nerve terminal-specific phosphoprotein. II. Its specific association with synaptic vesicles demonstrated by immunocytochemistry in agarose-embedded synaptosomes. J Cell Biol. 1983 May;96(5):1355–1373. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.5.1355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Camilli P., Takei K. Molecular mechanisms in synaptic vesicle endocytosis and recycling. Neuron. 1996 Mar;16(3):481–486. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80068-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Paolo Gilbert, Sankaranarayanan Sethuraman, Wenk Markus R., Daniell Laurie, Perucco Ezio, Caldarone Barbara J., Flavell Richard, Picciotto Marina R., Ryan Timothy A., Cremona Ottavio. Decreased synaptic vesicle recycling efficiency and cognitive deficits in amphiphysin 1 knockout mice. Neuron. 2002 Feb 28;33(5):789–804. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(02)00601-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmqvist D., Quastel D. M. A quantitative study of end-plate potentials in isolated human muscle. J Physiol. 1965 Jun;178(3):505–529. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., KATZ B. An analysis of the end-plate potential recorded with an intracellular electrode. J Physiol. 1951 Nov 28;115(3):320–370. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., KATZ B. Spontaneous subthreshold activity at motor nerve endings. J Physiol. 1952 May;117(1):109–128. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk M. M. Biosynthesis and structural composition of gap junction intercellular membrane channels. Eur J Cell Biol. 2000 Aug;79(8):564–574. doi: 10.1078/0171-9335-00080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farsad K., Ringstad N., Takei K., Floyd S. R., Rose K., De Camilli P. Generation of high curvature membranes mediated by direct endophilin bilayer interactions. J Cell Biol. 2001 Oct 15;155(2):193–200. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200107075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fergestad T., Broadie K. Interaction of stoned and synaptotagmin in synaptic vesicle endocytosis. J Neurosci. 2001 Feb 15;21(4):1218–1227. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-04-01218.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fergestad T., Davis W. S., Broadie K. The stoned proteins regulate synaptic vesicle recycling in the presynaptic terminal. J Neurosci. 1999 Jul 15;19(14):5847–5860. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-14-05847.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fesce R., Grohovaz F., Valtorta F., Meldolesi J. Neurotransmitter release: fusion or 'kiss-and-run'? Trends Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;4(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(94)90025-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford M. G., Pearse B. M., Higgins M. K., Vallis Y., Owen D. J., Gibson A., Hopkins C. R., Evans P. R., McMahon H. T. Simultaneous binding of PtdIns(4,5)P2 and clathrin by AP180 in the nucleation of clathrin lattices on membranes. Science. 2001 Feb 9;291(5506):1051–1055. doi: 10.1126/science.291.5506.1051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford Marijn G. J., Mills Ian G., Peter Brian J., Vallis Yvonne, Praefcke Gerrit J. K., Evans Philip R., McMahon Harvey T. Curvature of clathrin-coated pits driven by epsin. Nature. 2002 Sep 26;419(6905):361–366. doi: 10.1038/nature01020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gad H., Löw P., Zotova E., Brodin L., Shupliakov O. Dissociation between Ca2+-triggered synaptic vesicle exocytosis and clathrin-mediated endocytosis at a central synapse. Neuron. 1998 Sep;21(3):607–616. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80570-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gad H., Ringstad N., Löw P., Kjaerulff O., Gustafsson J., Wenk M., Di Paolo G., Nemoto Y., Crun J., Ellisman M. H. Fission and uncoating of synaptic clathrin-coated vesicles are perturbed by disruption of interactions with the SH3 domain of endophilin. Neuron. 2000 Aug;27(2):301–312. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)00038-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geppert M., Goda Y., Hammer R. E., Li C., Rosahl T. W., Stevens C. F., Südhof T. C. Synaptotagmin I: a major Ca2+ sensor for transmitter release at a central synapse. Cell. 1994 Nov 18;79(4):717–727. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90556-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González-Gaitán M., Jäckle H. Role of Drosophila alpha-adaptin in presynaptic vesicle recycling. Cell. 1997 Mar 21;88(6):767–776. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81923-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guichet Antoine, Wucherpfennig Tanja, Dudu Veronica, Etter Sylvain, Wilsch-Bräuniger Michaela, Hellwig Andrea, González-Gaitán Marcos, Huttner Wieland B., Schmidt Anne A. Essential role of endophilin A in synaptic vesicle budding at the Drosophila neuromuscular junction. EMBO J. 2002 Apr 2;21(7):1661–1672. doi: 10.1093/emboj/21.7.1661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haffner C., Takei K., Chen H., Ringstad N., Hudson A., Butler M. H., Salcini A. E., Di Fiore P. P., De Camilli P. Synaptojanin 1: localization on coated endocytic intermediates in nerve terminals and interaction of its 170 kDa isoform with Eps15. FEBS Lett. 1997 Dec 15;419(2-3):175–180. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(97)01451-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haimann C., Torri-Tarelli F., Fesce R., Ceccarelli B. Measurement of quantal secretion induced by ouabain and its correlation with depletion of synaptic vesicles. J Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;101(5 Pt 1):1953–1965. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.5.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannah M. J., Schmidt A. A., Huttner W. B. Synaptic vesicle biogenesis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1999;15:733–798. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.15.1.733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haucke V., De Camilli P. AP-2 recruitment to synaptotagmin stimulated by tyrosine-based endocytic motifs. Science. 1999 Aug 20;285(5431):1268–1271. doi: 10.1126/science.285.5431.1268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haucke V., Wenk M. R., Chapman E. R., Farsad K., De Camilli P. Dual interaction of synaptotagmin with mu2- and alpha-adaptin facilitates clathrin-coated pit nucleation. EMBO J. 2000 Nov 15;19(22):6011–6019. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.22.6011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuser J. E., Reese T. S., Dennis M. J., Jan Y., Jan L., Evans L. Synaptic vesicle exocytosis captured by quick freezing and correlated with quantal transmitter release. J Cell Biol. 1979 May;81(2):275–300. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuser J. E., Reese T. S. Evidence for recycling of synaptic vesicle membrane during transmitter release at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Cell Biol. 1973 May;57(2):315–344. doi: 10.1083/jcb.57.2.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuser J. The role of coated vesicles in recycling of synaptic vesicle membrane. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1989 Dec;13(12):1063–1076. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(89)90020-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinshaw J. E. Dynamin and its role in membrane fission. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2000;16:483–519. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.16.1.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinshaw J. E., Schmid S. L. Dynamin self-assembles into rings suggesting a mechanism for coated vesicle budding. Nature. 1995 Mar 9;374(6518):190–192. doi: 10.1038/374190a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt J. M., Bommert K., Charlton M. P., Kistner A., Habermann E., Augustine G. J., Betz H. A post-docking role for synaptobrevin in synaptic vesicle fusion. Neuron. 1994 Jun;12(6):1269–1279. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90443-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttner W. B., Schiebler W., Greengard P., De Camilli P. Synapsin I (protein I), a nerve terminal-specific phosphoprotein. III. Its association with synaptic vesicles studied in a highly purified synaptic vesicle preparation. J Cell Biol. 1983 May;96(5):1374–1388. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.5.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttner W. B., Schmidt A. Lipids, lipid modification and lipid-protein interaction in membrane budding and fission--insights from the roles of endophilin A1 and synaptophysin in synaptic vesicle endocytosis. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2000 Oct;10(5):543–551. doi: 10.1016/s0959-4388(00)00126-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn R., Hell J., Maycox P. R. Synaptic vesicles: key organelles involved in neurotransmission. J Physiol (Paris) 1990;84(1):128–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarousse N., Kelly R. B. Endocytotic mechanisms in synapses. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001 Aug;13(4):461–469. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(00)00237-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Warren T., Chang Sunghoe, Daniell Laurie, Cremona Ottavio, Di Paolo Gilbert, De Camilli Pietro. Delayed reentry of recycling vesicles into the fusion-competent synaptic vesicle pool in synaptojanin 1 knockout mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Dec 12;99(26):17143–17148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.222657399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchhausen T. Clathrin. Annu Rev Biochem. 2000;69:699–727. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.69.1.699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein D. E., Lee A., Frank D. W., Marks M. S., Lemmon M. A. The pleckstrin homology domains of dynamin isoforms require oligomerization for high affinity phosphoinositide binding. J Biol Chem. 1998 Oct 16;273(42):27725–27733. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.42.27725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klingauf J., Kavalali E. T., Tsien R. W. Kinetics and regulation of fast endocytosis at hippocampal synapses. Nature. 1998 Aug 6;394(6693):581–585. doi: 10.1038/29079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klockow Boris, Tichelaar Willem, Madden Dean R., Niemann Hartmut H., Akiba Toshihiko, Hirose Keiko, Manstein Dietmar J. The dynamin A ring complex: molecular organization and nucleotide-dependent conformational changes. EMBO J. 2002 Feb 1;21(3):240–250. doi: 10.1093/emboj/21.3.240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig J. H., Ikeda K. Disappearance and reformation of synaptic vesicle membrane upon transmitter release observed under reversible blockage of membrane retrieval. J Neurosci. 1989 Nov;9(11):3844–3860. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-11-03844.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig J. H., Ikeda K. Synaptic vesicles have two distinct recycling pathways. J Cell Biol. 1996 Nov;135(3):797–808. doi: 10.1083/jcb.135.3.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuffler S. W., Yoshikami D. The number of transmitter molecules in a quantum: an estimate from iontophoretic application of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular synapse. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;251(2):465–482. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C., Kim S. R., Chung J. K., Frohman M. A., Kilimann M. W., Rhee S. G. Inhibition of phospholipase D by amphiphysins. J Biol Chem. 2000 Jun 23;275(25):18751–18758. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M001695200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Eunkyung, Marcucci Melissa, Daniell Laurie, Pypaert Marc, Weisz Ora A., Ochoa Gian-Carlo, Farsad Khashayar, Wenk Markus R., De Camilli Pietro. Amphiphysin 2 (Bin1) and T-tubule biogenesis in muscle. Science. 2002 Aug 16;297(5584):1193–1196. doi: 10.1126/science.1071362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C., Ullrich B., Zhang J. Z., Anderson R. G., Brose N., Südhof T. C. Ca(2+)-dependent and -independent activities of neural and non-neural synaptotagmins. Nature. 1995 Jun 15;375(6532):594–599. doi: 10.1038/375594a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin R. C., Scheller R. H. Mechanisms of synaptic vesicle exocytosis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2000;16:19–49. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.16.1.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littleton J. T., Stern M., Perin M., Bellen H. J. Calcium dependence of neurotransmitter release and rate of spontaneous vesicle fusions are altered in Drosophila synaptotagmin mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 8;91(23):10888–10892. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.23.10888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littleton J. T., Stern M., Schulze K., Perin M., Bellen H. J. Mutational analysis of Drosophila synaptotagmin demonstrates its essential role in Ca(2+)-activated neurotransmitter release. Cell. 1993 Sep 24;74(6):1125–1134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90733-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu G., Tsien R. W. Properties of synaptic transmission at single hippocampal synaptic boutons. Nature. 1995 Jun 1;375(6530):404–408. doi: 10.1038/375404a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S. H., Wong M. L., Craik C. S., Brodsky F. M. Regulation of clathrin assembly and trimerization defined using recombinant triskelion hubs. Cell. 1995 Oct 20;83(2):257–267. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90167-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao Y., Chen J., Maynard J. A., Zhang B., Quiocho F. A. A novel all helix fold of the AP180 amino-terminal domain for phosphoinositide binding and clathrin assembly in synaptic vesicle endocytosis. Cell. 2001 Feb 9;104(3):433–440. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00230-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks B., McMahon H. T. Calcium triggers calcineurin-dependent synaptic vesicle recycling in mammalian nerve terminals. Curr Biol. 1998 Jun 18;8(13):740–749. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(98)70297-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks B., Stowell M. H., Vallis Y., Mills I. G., Gibson A., Hopkins C. R., McMahon H. T. GTPase activity of dynamin and resulting conformation change are essential for endocytosis. Nature. 2001 Mar 8;410(6825):231–235. doi: 10.1038/35065645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martina J. A., Bonangelino C. J., Aguilar R. C., Bonifacino J. S. Stonin 2: an adaptor-like protein that interacts with components of the endocytic machinery. J Cell Biol. 2001 May 28;153(5):1111–1120. doi: 10.1083/jcb.153.5.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maycox P. R., Link E., Reetz A., Morris S. A., Jahn R. Clathrin-coated vesicles in nervous tissue are involved primarily in synaptic vesicle recycling. J Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;118(6):1379–1388. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.6.1379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon H. T. Endocytosis: an assembly protein for clathrin cages. Curr Biol. 1999 May 6;9(9):R332–R335. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(99)80206-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNew J. A., Parlati F., Fukuda R., Johnston R. J., Paz K., Paumet F., Söllner T. H., Rothman J. E. Compartmental specificity of cellular membrane fusion encoded in SNARE proteins. Nature. 2000 Sep 14;407(6801):153–159. doi: 10.1038/35025000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNiven M. A., Cao H., Pitts K. R., Yoon Y. The dynamin family of mechanoenzymes: pinching in new places. Trends Biochem Sci. 2000 Mar;25(3):115–120. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(99)01538-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson P. S., Garcia E. P., Slepnev V. I., David C., Zhang X., Grabs D., Sossin W. S., Bauerfeind R., Nemoto Y., De Camilli P. A presynaptic inositol-5-phosphatase. Nature. 1996 Jan 25;379(6563):353–357. doi: 10.1038/379353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikoshiba K., Fukuda M., Moreira J. E., Lewis F. M., Sugimori M., Niinobe M., Llinás R. Role of the C2A domain of synaptotagmin in transmitter release as determined by specific antibody injection into the squid giant synapse preterminal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Nov 7;92(23):10703–10707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.23.10703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musacchio A., Smith C. J., Roseman A. M., Harrison S. C., Kirchhausen T., Pearse B. M. Functional organization of clathrin in coats: combining electron cryomicroscopy and X-ray crystallography. Mol Cell. 1999 Jun;3(6):761–770. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(01)80008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E. Cell physiology. Secretion without full fusion. Nature. 1993 Jun 10;363(6429):497–498. doi: 10.1038/363497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonet M. L., Grundahl K., Meyer B. J., Rand J. B. Synaptic function is impaired but not eliminated in C. elegans mutants lacking synaptotagmin. Cell. 1993 Jul 2;73(7):1291–1305. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90357-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonet M. L., Holgado A. M., Brewer F., Serpe C. J., Norbeck B. A., Holleran J., Wei L., Hartwieg E., Jorgensen E. M., Alfonso A. UNC-11, a Caenorhabditis elegans AP180 homologue, regulates the size and protein composition of synaptic vesicles. Mol Biol Cell. 1999 Jul;10(7):2343–2360. doi: 10.1091/mbc.10.7.2343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Näthke I. S., Heuser J., Lupas A., Stock J., Turck C. W., Brodsky F. M. Folding and trimerization of clathrin subunits at the triskelion hub. Cell. 1992 Mar 6;68(5):899–910. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90033-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada Y., Yamazaki H., Sekine-Aizawa Y., Hirokawa N. The neuron-specific kinesin superfamily protein KIF1A is a unique monomeric motor for anterograde axonal transport of synaptic vesicle precursors. Cell. 1995 Jun 2;81(5):769–780. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90538-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PALAY S. L., PALADE G. E. The fine structure of neurons. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1955 Jan;1(1):69–88. doi: 10.1083/jcb.1.1.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parlati F., McNew J. A., Fukuda R., Miller R., Söllner T. H., Rothman J. E. Topological restriction of SNARE-dependent membrane fusion. Nature. 2000 Sep 14;407(6801):194–198. doi: 10.1038/35025076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellizzari R., Rossetto O., Schiavo G., Montecucco C. Tetanus and botulinum neurotoxins: mechanism of action and therapeutic uses. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1999 Feb 28;354(1381):259–268. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1999.0377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips A. M., Smith M., Ramaswami M., Kelly L. E. The products of the Drosophila stoned locus interact with synaptic vesicles via synaptotagmin. J Neurosci. 2000 Nov 15;20(22):8254–8261. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-22-08254.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramjaun A. R., Micheva K. D., Bouchelet I., McPherson P. S. Identification and characterization of a nerve terminal-enriched amphiphysin isoform. J Biol Chem. 1997 Jun 27;272(26):16700–16706. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.26.16700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rikhy Richa, Kumar Vimlesh, Mittal Rohit, Krishnan K. S. Endophilin is critically required for synapse formation and function in Drosophila melanogaster. J Neurosci. 2002 Sep 1;22(17):7478–7484. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-17-07478.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringstad N., Gad H., Löw P., Di Paolo G., Brodin L., Shupliakov O., De Camilli P. Endophilin/SH3p4 is required for the transition from early to late stages in clathrin-mediated synaptic vesicle endocytosis. Neuron. 1999 Sep;24(1):143–154. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80828-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson P. J., Liu J. P., Powell K. A., Fykse E. M., Südhof T. C. Phosphorylation of dynamin I and synaptic-vesicle recycling. Trends Neurosci. 1994 Aug;17(8):348–353. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(94)90179-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodal S. K., Skretting G., Garred O., Vilhardt F., van Deurs B., Sandvig K. Extraction of cholesterol with methyl-beta-cyclodextrin perturbs formation of clathrin-coated endocytic vesicles. Mol Biol Cell. 1999 Apr;10(4):961–974. doi: 10.1091/mbc.10.4.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos J., Kelly R. B. The endocytic machinery in nerve terminals surrounds sites of exocytosis. Curr Biol. 1999 Dec 2;9(23):1411–1414. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)80087-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenmund C., Stevens C. F. Definition of the readily releasable pool of vesicles at hippocampal synapses. Neuron. 1996 Jun;16(6):1197–1207. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80146-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E. Mechanisms of intracellular protein transport. Nature. 1994 Nov 3;372(6501):55–63. doi: 10.1038/372055a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan T. A., Reuter H., Wendland B., Schweizer F. E., Tsien R. W., Smith S. J. The kinetics of synaptic vesicle recycling measured at single presynaptic boutons. Neuron. 1993 Oct;11(4):713–724. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90081-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan T. A., Smith S. J., Reuter H. The timing of synaptic vesicle endocytosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 May 28;93(11):5567–5571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.11.5567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan T. A., Smith S. J. Vesicle pool mobilization during action potential firing at hippocampal synapses. Neuron. 1995 May;14(5):983–989. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90336-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salim K., Bottomley M. J., Querfurth E., Zvelebil M. J., Gout I., Scaife R., Margolis R. L., Gigg R., Smith C. I., Driscoll P. C. Distinct specificity in the recognition of phosphoinositides by the pleckstrin homology domains of dynamin and Bruton's tyrosine kinase. EMBO J. 1996 Nov 15;15(22):6241–6250. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiavo G., Stenbeck G., Rothman J. E., Söllner T. H. Binding of the synaptic vesicle v-SNARE, synaptotagmin, to the plasma membrane t-SNARE, SNAP-25, can explain docked vesicles at neurotoxin-treated synapses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Feb 4;94(3):997–1001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.3.997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schikorski T., Stevens C. F. Quantitative ultrastructural analysis of hippocampal excitatory synapses. J Neurosci. 1997 Aug 1;17(15):5858–5867. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-15-05858.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid S. L. Clathrin-coated vesicle formation and protein sorting: an integrated process. Annu Rev Biochem. 1997;66:511–548. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.66.1.511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt A., Wolde M., Thiele C., Fest W., Kratzin H., Podtelejnikov A. V., Witke W., Huttner W. B., Söling H. D. Endophilin I mediates synaptic vesicle formation by transfer of arachidonate to lysophosphatidic acid. Nature. 1999 Sep 9;401(6749):133–141. doi: 10.1038/43613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sever S., Muhlberg A. B., Schmid S. L. Impairment of dynamin's GAP domain stimulates receptor-mediated endocytosis. Nature. 1999 Apr 8;398(6727):481–486. doi: 10.1038/19024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shpetner H. S., Vallee R. B. Identification of dynamin, a novel mechanochemical enzyme that mediates interactions between microtubules. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):421–432. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90027-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shupliakov O., Löw P., Grabs D., Gad H., Chen H., David C., Takei K., De Camilli P., Brodin L. Synaptic vesicle endocytosis impaired by disruption of dynamin-SH3 domain interactions. Science. 1997 Apr 11;276(5310):259–263. doi: 10.1126/science.276.5310.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slepnev V. I., De Camilli P. Accessory factors in clathrin-dependent synaptic vesicle endocytosis. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2000 Dec;1(3):161–172. doi: 10.1038/35044540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slepnev V. I., Ochoa G. C., Butler M. H., De Camilli P. Tandem arrangement of the clathrin and AP-2 binding domains in amphiphysin 1 and disruption of clathrin coat function by amphiphysin fragments comprising these sites. J Biol Chem. 2000 Jun 9;275(23):17583–17589. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M910430199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slepnev V. I., Ochoa G. C., Butler M. H., Grabs D., De Camilli P. Role of phosphorylation in regulation of the assembly of endocytic coat complexes. Science. 1998 Aug 7;281(5378):821–824. doi: 10.1126/science.281.5378.821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. J., Grigorieff N., Pearse B. M. Clathrin coats at 21 A resolution: a cellular assembly designed to recycle multiple membrane receptors. EMBO J. 1998 Sep 1;17(17):4943–4953. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.17.4943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spruce A. E., Breckenridge L. J., Lee A. K., Almers W. Properties of the fusion pore that forms during exocytosis of a mast cell secretory vesicle. Neuron. 1990 May;4(5):643–654. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90192-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens C. F., Tsujimoto T. Estimates for the pool size of releasable quanta at a single central synapse and for the time required to refill the pool. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jan 31;92(3):846–849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.3.846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stimson D. T., Estes P. S., Rao S., Krishnan K. S., Kelly L. E., Ramaswami M. Drosophila stoned proteins regulate the rate and fidelity of synaptic vesicle internalization. J Neurosci. 2001 May 1;21(9):3034–3044. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-09-03034.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subtil A., Gaidarov I., Kobylarz K., Lampson M. A., Keen J. H., McGraw T. E. Acute cholesterol depletion inhibits clathrin-coated pit budding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Jun 8;96(12):6775–6780. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.12.6775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweitzer S. M., Hinshaw J. E. Dynamin undergoes a GTP-dependent conformational change causing vesiculation. Cell. 1998 Jun 12;93(6):1021–1029. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81207-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takei K., Haucke V., Slepnev V., Farsad K., Salazar M., Chen H., De Camilli P. Generation of coated intermediates of clathrin-mediated endocytosis on protein-free liposomes. Cell. 1998 Jul 10;94(1):131–141. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81228-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takei K., McPherson P. S., Schmid S. L., De Camilli P. Tubular membrane invaginations coated by dynamin rings are induced by GTP-gamma S in nerve terminals. Nature. 1995 Mar 9;374(6518):186–190. doi: 10.1038/374186a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takei K., Mundigl O., Daniell L., De Camilli P. The synaptic vesicle cycle: a single vesicle budding step involving clathrin and dynamin. J Cell Biol. 1996 Jun;133(6):1237–1250. doi: 10.1083/jcb.133.6.1237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takei K., Slepnev V. I., Haucke V., De Camilli P. Functional partnership between amphiphysin and dynamin in clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Nat Cell Biol. 1999 May;1(1):33–39. doi: 10.1038/9004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takenawa T., Itoh T. Phosphoinositides, key molecules for regulation of actin cytoskeletal organization and membrane traffic from the plasma membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001 Oct 31;1533(3):190–206. doi: 10.1016/s1388-1981(01)00165-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teng H., Wilkinson R. S. Clathrin-mediated endocytosis near active zones in snake motor boutons. J Neurosci. 2000 Nov 1;20(21):7986–7993. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-21-07986.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiele C., Hannah M. J., Fahrenholz F., Huttner W. B. Cholesterol binds to synaptophysin and is required for biogenesis of synaptic vesicles. Nat Cell Biol. 2000 Jan;2(1):42–49. doi: 10.1038/71366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukita S., Ishikawa H. The movement of membranous organelles in axons. Electron microscopic identification of anterogradely and retrogradely transported organelles. J Cell Biol. 1980 Mar;84(3):513–530. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.3.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger V. M., Kumar N. M., Gilula N. B., Yeager M. Three-dimensional structure of a recombinant gap junction membrane channel. Science. 1999 Feb 19;283(5405):1176–1180. doi: 10.1126/science.283.5405.1176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verstreken Patrik, Kjaerulff Ole, Lloyd Thomas E., Atkinson Richard, Zhou Yi, Meinertzhagen Ian A., Bellen Hugo J. Endophilin mutations block clathrin-mediated endocytosis but not neurotransmitter release. Cell. 2002 Apr 5;109(1):101–112. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00688-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walther K., Krauss M., Diril M. K., Lemke S., Ricotta D., Honing S., Kaiser S., Haucke V. Human stoned B interacts with AP-2 and synaptotagmin and facilitates clathrin-coated vesicle uncoating. EMBO Rep. 2001 Jul 3;2(7):634–640. doi: 10.1093/embo-reports/kve134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber T., Zemelman B. V., McNew J. A., Westermann B., Gmachl M., Parlati F., Söllner T. H., Rothman J. E. SNAREpins: minimal machinery for membrane fusion. Cell. 1998 Mar 20;92(6):759–772. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81404-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenk M. R., Pellegrini L., Klenchin V. A., Di Paolo G., Chang S., Daniell L., Arioka M., Martin T. F., De Camilli P. PIP kinase Igamma is the major PI(4,5)P(2) synthesizing enzyme at the synapse. Neuron. 2001 Oct 11;32(1):79–88. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(01)00456-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigge P., Köhler K., Vallis Y., Doyle C. A., Owen D., Hunt S. P., McMahon H. T. Amphiphysin heterodimers: potential role in clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Mol Biol Cell. 1997 Oct;8(10):2003–2015. doi: 10.1091/mbc.8.10.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigge P., Vallis Y., McMahon H. T. Inhibition of receptor-mediated endocytosis by the amphiphysin SH3 domain. Curr Biol. 1997 Aug 1;7(8):554–560. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(06)00254-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler F. K., Stanley K. K. Clathrin heavy chain, light chain interactions. EMBO J. 1983;2(8):1393–1400. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01597.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L. G., Betz W. J. Nerve activity but not intracellular calcium determines the time course of endocytosis at the frog neuromuscular junction. Neuron. 1996 Oct;17(4):769–779. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80208-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ybe J. A., Greene B., Liu S. H., Pley U., Parham P., Brodsky F. M. Clathrin self-assembly is regulated by three light-chain residues controlling the formation of critical salt bridges. EMBO J. 1998 Aug 10;17(5):1297–1303. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.5.1297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang B., Koh Y. H., Beckstead R. B., Budnik V., Ganetzky B., Bellen H. J. Synaptic vesicle size and number are regulated by a clathrin adaptor protein required for endocytosis. Neuron. 1998 Dec;21(6):1465–1475. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80664-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang P., Hinshaw J. E. Three-dimensional reconstruction of dynamin in the constricted state. Nat Cell Biol. 2001 Oct;3(10):922–926. doi: 10.1038/ncb1001-922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker R. S. Changes in the statistics of transmitter release during facilitation. J Physiol. 1973 Mar;229(3):787–810. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Heuvel E., Bell A. W., Ramjaun A. R., Wong K., Sossin W. S., McPherson P. S. Identification of the major synaptojanin-binding proteins in brain. J Biol Chem. 1997 Mar 28;272(13):8710–8716. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.13.8710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ter Haar E., Harrison S. C., Kirchhausen T. Peptide-in-groove interactions link target proteins to the beta-propeller of clathrin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Feb 1;97(3):1096–1100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.3.1096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Bliek A. M., Meyerowitz E. M. Dynamin-like protein encoded by the Drosophila shibire gene associated with vesicular traffic. Nature. 1991 May 30;351(6325):411–414. doi: 10.1038/351411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Bliek A. M., Redelmeier T. E., Damke H., Tisdale E. J., Meyerowitz E. M., Schmid S. L. Mutations in human dynamin block an intermediate stage in coated vesicle formation. J Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;122(3):553–563. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.3.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]