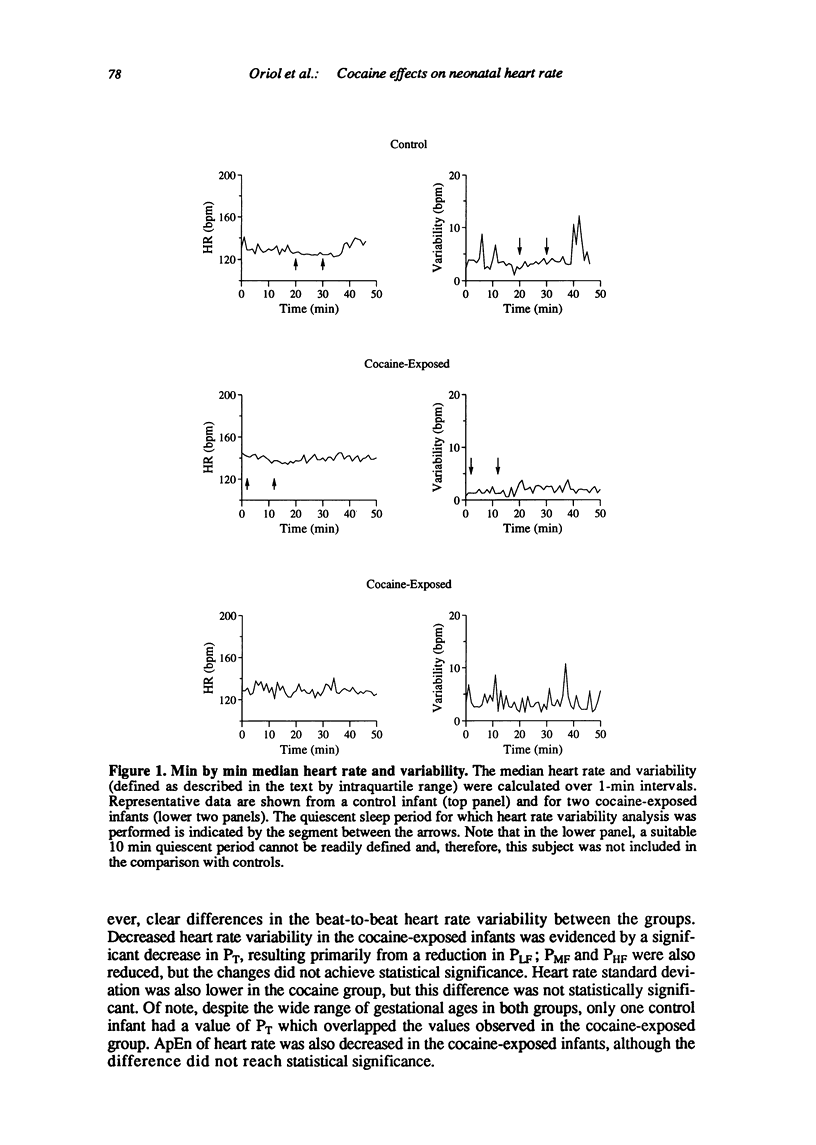
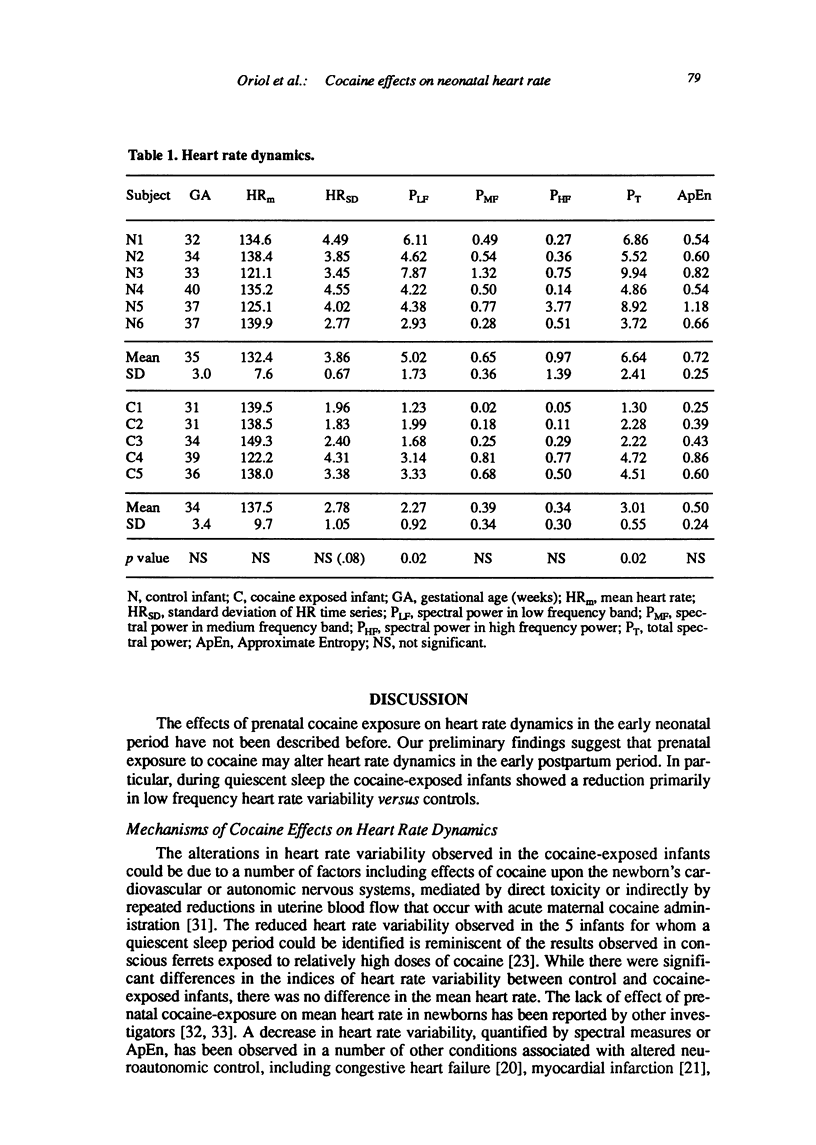
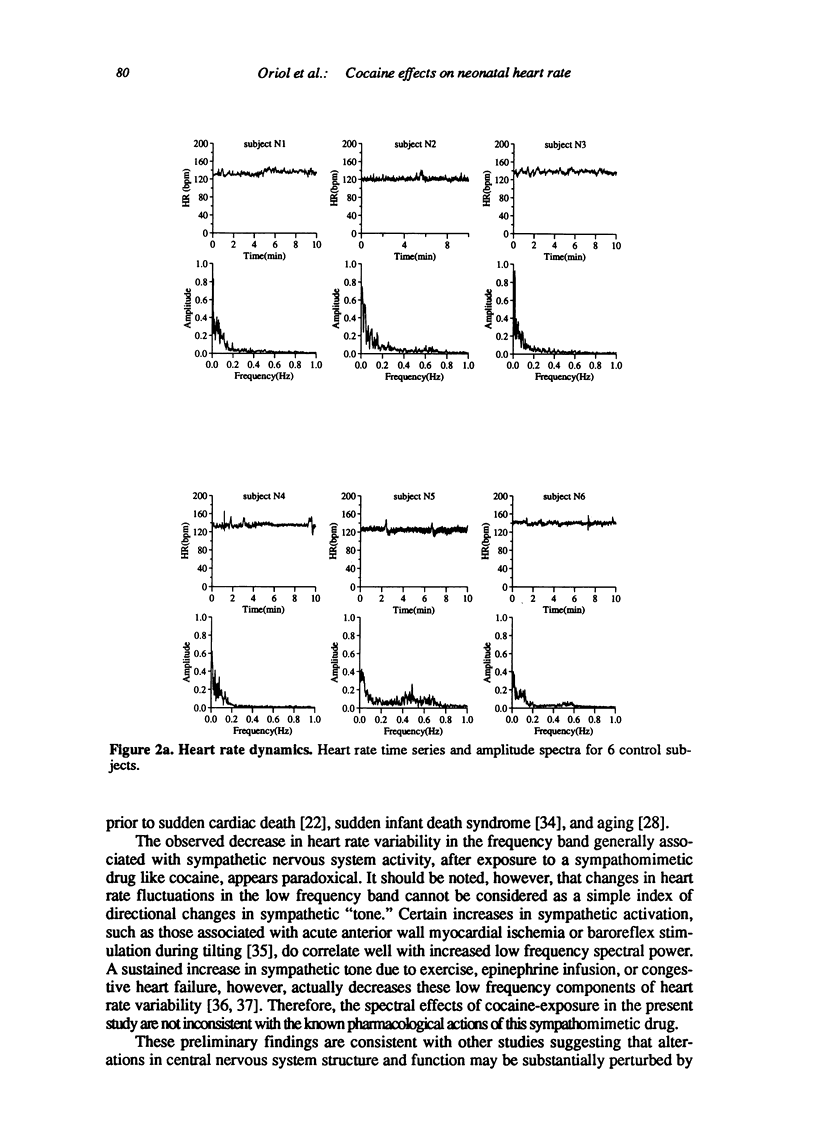
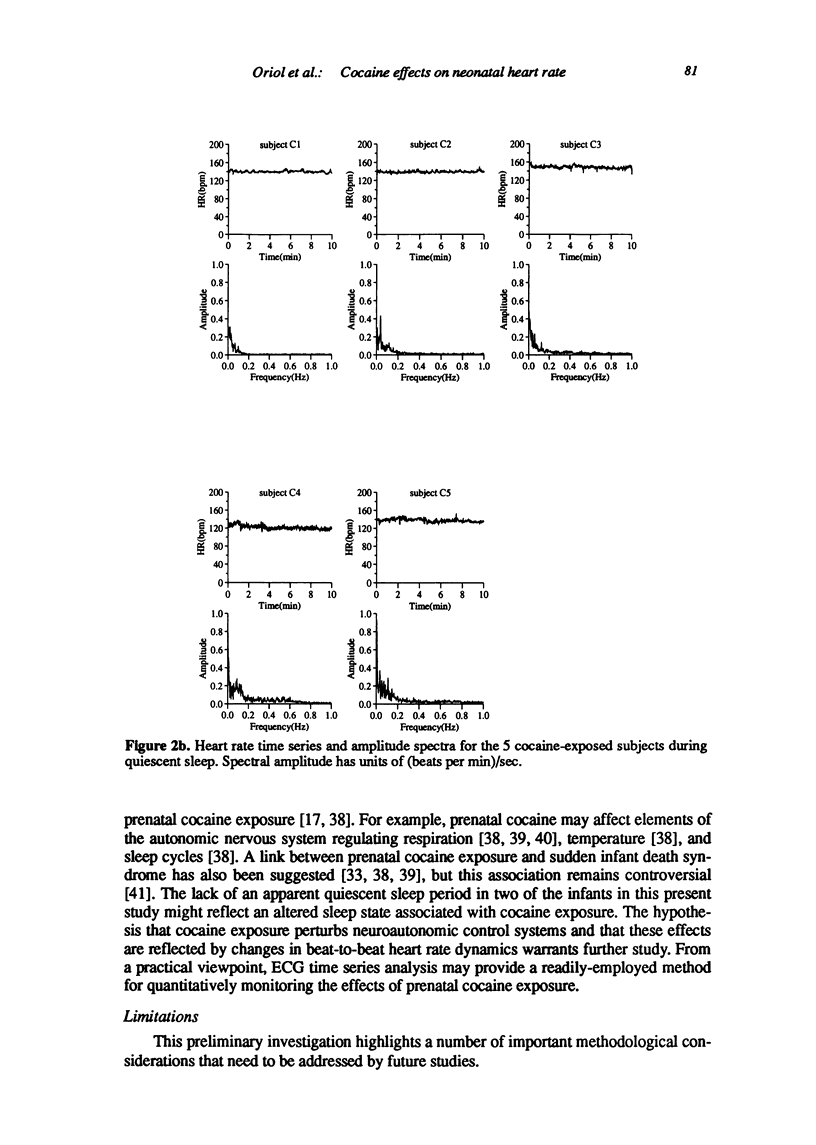
Abstract
Cocaine use by pregnant women has been reported to cause fetal and neonatal morbidity and mortality. We hypothesized that human neonates exposed to cocaine via maternal use during pregnancy might manifest changes in beat-to-beat heart rate variability, similar to those described in experimental animals. In this preliminary report, we present findings from the first systematic analysis of heart rate dynamics in a small group of (n = 5) neonates exposed in utero to cocaine compared to gestationally age matched controls (n = 6) without known drug exposure. Overall heart rate spectral power during ten minute periods of quiescent sleep was significantly reduced (p < 0.01) in the cocaine-exposed group, reminiscent of the changes recently reported in an animal model. In two other cocaine-exposed newborns, a quiescent sleep period could not be found. We discuss the special methodological problems associated with collection and interpretation of such data.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arai Y., Saul J. P., Albrecht P., Hartley L. H., Lilly L. S., Cohen R. J., Colucci W. S. Modulation of cardiac autonomic activity during and immediately after exercise. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jan;256(1 Pt 2):H132–H141. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.256.1.H132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandstra E. S., Burkett G. Maternal-fetal and neonatal effects of in utero cocaine exposure. Semin Perinatol. 1991 Aug;15(4):288–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauchner H., Zuckerman B., McClain M., Frank D., Fried L. E., Kayne H. Risk of sudden infant death syndrome among infants with in utero exposure to cocaine. J Pediatr. 1988 Nov;113(5):831–834. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(88)80009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bingol N., Fuchs M., Diaz V., Stone R. K., Gromisch D. S. Teratogenicity of cocaine in humans. J Pediatr. 1987 Jan;110(1):93–96. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(87)80297-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasnoff I. J., Burns K. A., Burns W. J. Cocaine use in pregnancy: perinatal morbidity and mortality. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 1987 Jul-Aug;9(4):291–293. doi: 10.1016/0892-0362(87)90017-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasnoff I. J., Burns W. J., Schnoll S. H., Burns K. A. Cocaine use in pregnancy. N Engl J Med. 1985 Sep 12;313(11):666–669. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198509123131105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasnoff I. J., Hunt C. E., Kletter R., Kaplan D. Prenatal cocaine exposure is associated with respiratory pattern abnormalities. Am J Dis Child. 1989 May;143(5):583–587. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1989.02150170085028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doberczak T. M., Shanzer S., Senie R. T., Kandall S. R. Neonatal neurologic and electroencephalographic effects of intrauterine cocaine exposure. J Pediatr. 1988 Aug;113(2):354–358. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(88)80283-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen L. N., Field T. M., Bandstra E. S., Roberts J. P., Morrow C., Larson S. K., Steele B. M. Perinatal cocaine effects on neonatal stress behavior and performance on the Brazelton Scale. Pediatrics. 1991 Sep;88(3):477–480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberger A. L., Rigney D. R., Mietus J., Antman E. M., Greenwald S. Nonlinear dynamics in sudden cardiac death syndrome: heartrate oscillations and bifurcations. Experientia. 1988 Dec 1;44(11-12):983–987. doi: 10.1007/BF01939894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadeed A. J., Siegel S. R. Maternal cocaine use during pregnancy: effect on the newborn infant. Pediatrics. 1989 Aug;84(2):205–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper R. M., Hoppenbrouwers T., Sterman M. B., McGinty D. J., Hodgman J. Polygraphic studies of normal infants during the first six months of life. I. Heart rate and variability as a function of state. Pediatr Res. 1976 Nov;10(11):945–948. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197611000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper R. M. Postnatal development of cardiac and respiratory control following prenatal drug exposure. NIDA Res Monogr. 1991;114:187–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. T., Furman M. I., Pincus S. M., Ryan S. M., Lipsitz L. A., Goldberger A. L. Aging and the complexity of cardiovascular dynamics. Biophys J. 1991 Apr;59(4):945–949. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82309-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipshultz S. E., Frassica J. J., Orav E. J. Cardiovascular abnormalities in infants prenatally exposed to cocaine. J Pediatr. 1991 Jan;118(1):44–51. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)81842-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little B. B., Snell L. M., Klein V. R., Gilstrap L. C., 3rd Cocaine abuse during pregnancy: maternal and fetal implications. Obstet Gynecol. 1989 Feb;73(2):157–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardi F., Sandrone G., Pernpruner S., Sala R., Garimoldi M., Cerutti S., Baselli G., Pagani M., Malliani A. Heart rate variability as an index of sympathovagal interaction after acute myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol. 1987 Dec 1;60(16):1239–1245. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(87)90601-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor S. N., Keith L. G., Chasnoff I. J., Rosner M. A., Chisum G. M., Shaw P., Minogue J. P. Cocaine use during pregnancy: adverse perinatal outcome. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1987 Sep;157(3):686–690. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(87)80029-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malliani A., Pagani M., Lombardi F., Cerutti S. Cardiovascular neural regulation explored in the frequency domain. Circulation. 1991 Aug;84(2):482–492. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.84.2.482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirochnick M., Meyer J., Cole J., Herren T., Zuckerman B. Circulating catecholamine concentrations in cocaine-exposed neonates: a pilot study. Pediatrics. 1991 Sep;88(3):481–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oro A. S., Dixon S. D. Perinatal cocaine and methamphetamine exposure: maternal and neonatal correlates. J Pediatr. 1987 Oct;111(4):571–578. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(87)80125-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus S. M. Approximate entropy as a measure of system complexity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2297–2301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus S. M., Gladstone I. M., Ehrenkranz R. A. A regularity statistic for medical data analysis. J Clin Monit. 1991 Oct;7(4):335–345. doi: 10.1007/BF01619355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus S. M., Viscarello R. R. Approximate entropy: a regularity measure for fetal heart rate analysis. Obstet Gynecol. 1992 Feb;79(2):249–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan L., Ehrlich S., Finnegan L. Cocaine abuse in pregnancy: effects on the fetus and newborn. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 1987 Jul-Aug;9(4):295–299. doi: 10.1016/0892-0362(87)90018-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saul J. P., Arai Y., Berger R. D., Lilly L. S., Colucci W. S., Cohen R. J. Assessment of autonomic regulation in chronic congestive heart failure by heart rate spectral analysis. Am J Cardiol. 1988 Jun 1;61(15):1292–1299. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(88)91172-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechtman V. L., Harper R. M., Kluge K. A. Development of heart rate variation over the first 6 months of life in normal infants. Pediatr Res. 1989 Oct;26(4):343–346. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198910000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J. W., Chasnoff I. J. Motor assessment of cocaine/polydrug exposed infants at age 4 months. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 1992 Mar-Apr;14(2):97–101. doi: 10.1016/0892-0362(92)90057-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G. M., Malcoe L. H., Lammer E. J., Swan S. H. Maternal use of cocaine during pregnancy and congenital cardiac anomalies. J Pediatr. 1991 Jan;118(1):167–168. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)81888-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvestri J. M., Long J. M., Weese-Mayer D. E., Barkov G. A. Effect of prenatal cocaine on respiration, heart rate, and sudden infant death syndrome. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1991;11(4):328–334. doi: 10.1002/ppul.1950110409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer L. T., Garber R., Kliegman R. Neurobehavioral sequelae of fetal cocaine exposure. J Pediatr. 1991 Oct;119(4):667–672. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)82426-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slutsker L. Risks associated with cocaine use during pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 1992 May;79(5 ):778–789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stambler B. S., Morgan J. P., Mietus J., Moody G. B., Goldberger A. L. Cocaine alters heart rate dynamics in conscious ferrets. Yale J Biol Med. 1991 Mar-Apr;64(2):143–153. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward S. L., Schuetz S., Kirshna V., Bean X., Wingert W., Wachsman L., Keens T. G. Abnormal sleeping ventilatory pattern in infants of substance-abusing mothers. Am J Dis Child. 1986 Oct;140(10):1015–1020. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1986.02140240061028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods J. R., Jr, Plessinger M. A., Clark K. E. Effect of cocaine on uterine blood flow and fetal oxygenation. JAMA. 1987 Feb 20;257(7):957–961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods J. R., Jr, Plessinger M. A. Maternal-fetal cardiovascular system: a target of cocaine. NIDA Res Monogr. 1991;108:7–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Bor M., Walther F. J., Ebrahimi M. Decreased cardiac output in infants of mothers who abused cocaine. Pediatrics. 1990 Jan;85(1):30–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


