Abstract
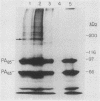
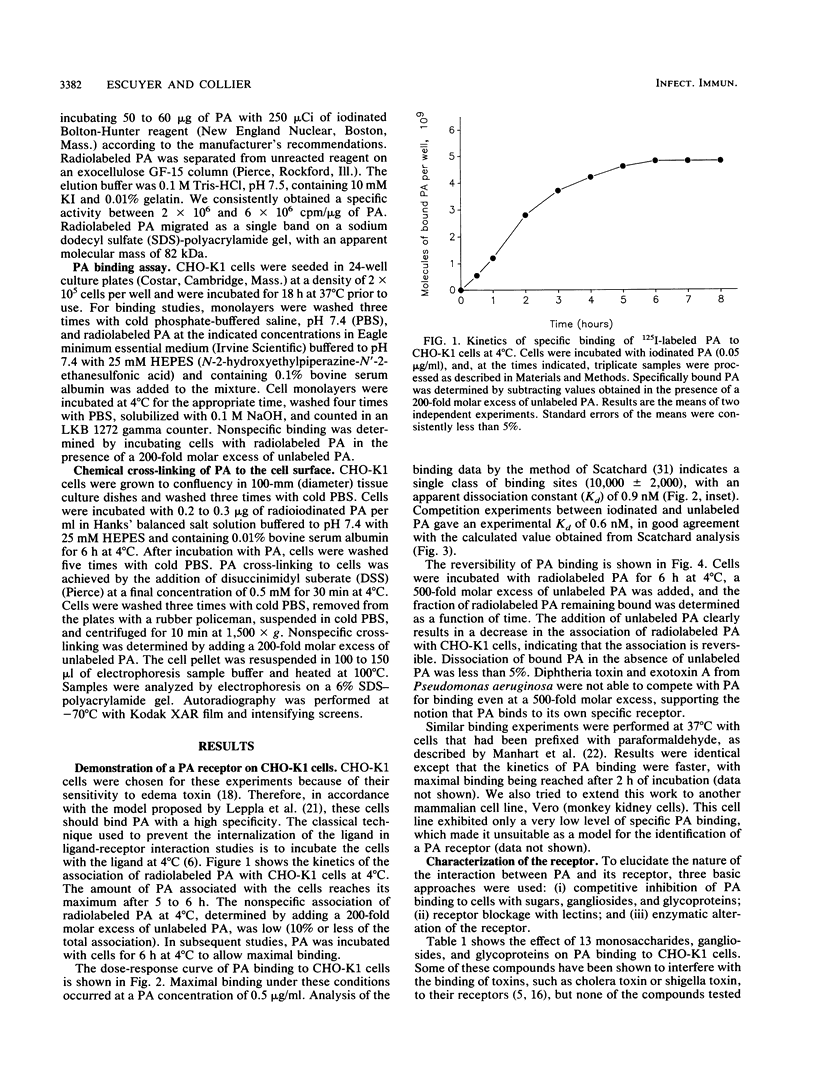
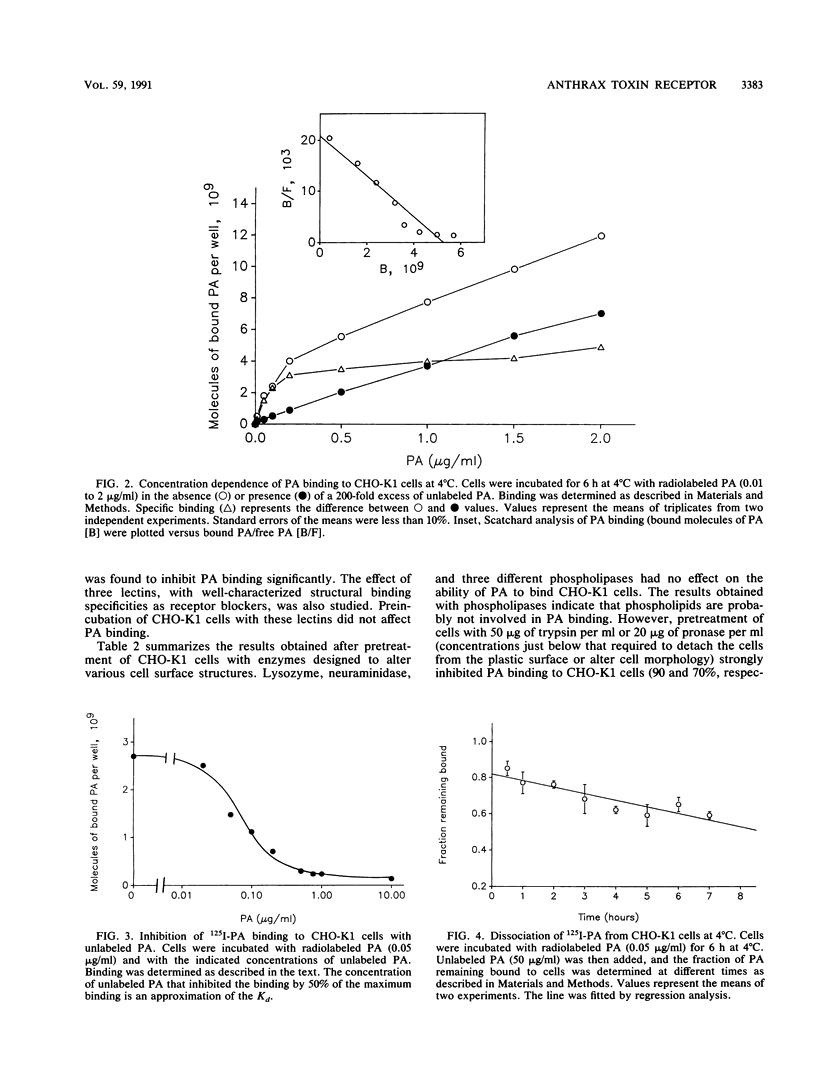
The interaction of protective antigen (PA), a component of the anthrax toxin, with receptors on the Chinese hamster ovary cell line CHO-K1 was characterized. Protective antigen binding at 4 degrees C is highly specific, concentration dependent, saturable (Kd = 0.9 nM), and reversible. Scatchard analysis indicates the presence of a single class of PA binding sites at a concentration of 10,000 +/- 2,000 per cell. Pretreatment of cells with a number of different proteases strongly inhibits PA binding, suggesting that the receptor may be at least partially proteinaceous. Direct chemical cross-linking of radioiodinated PA to the cell surface results in the appearance of a major band exhibiting an apparent molecular mass of 170 kDa, as estimated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The appearance of this band is completely inhibited by a 200-fold molar excess of unlabeled PA, indicating a high specificity for this interaction. Our results suggest that a cell surface protein(s) of 85 to 90 kDa is, or constitutes a portion of, a specific receptor for the PA.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEALL F. A., TAYLOR M. J., THORNE C. B. Rapid lethal effect in rats of a third component found upon fractionating the toxin of Bacillus anthracis. J Bacteriol. 1962 Jun;83:1274–1280. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.6.1274-1280.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein R. O., Koehler T. M., Collier R. J., Finkelstein A. Anthrax toxin: channel-forming activity of protective antigen in planar phospholipid bilayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2209–2213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cieplak W., Gaudin H. M., Eidels L. Diphtheria toxin receptor. Identification of specific diphtheria toxin-binding proteins on the surface of Vero and BS-C-1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 25;262(27):13246–13253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Commentary. Insulin receptors, cell membranes and hormone action. Biochem Pharmacol. 1974 Sep 1;23(17):2353–2361. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(74)90224-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Gangliosides and membrane receptors for cholera toxin. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 28;12(18):3558–3566. doi: 10.1021/bi00742a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eidels L., Proia R. L., Hart D. A. Membrane receptors for bacterial toxins. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Dec;47(4):596–620. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.4.596-620.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escuyer V., Duflot E., Sezer O., Danchin A., Mock M. Structural homology between virulence-associated bacterial adenylate cyclases. Gene. 1988 Nov 30;71(2):293–298. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90045-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish D. C., Klein F., Lincoln R. E., Walker J. S., Dobbs J. P. Pathophysiological changes in the rat associated with anthrax toxin. J Infect Dis. 1968 Feb;118(1):114–124. doi: 10.1093/infdis/118.1.114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FitzGerald D., Morris R. E., Saelinger C. B. Receptor-mediated internalization of Pseudomonas toxin by mouse fibroblasts. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):867–873. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90450-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedlander A. M. Macrophages are sensitive to anthrax lethal toxin through an acid-dependent process. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 5;261(16):7123–7126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon V. M., Leppla S. H., Hewlett E. L. Inhibitors of receptor-mediated endocytosis block the entry of Bacillus anthracis adenylate cyclase toxin but not that of Bordetella pertussis adenylate cyclase toxin. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1066–1069. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1066-1069.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hranitzky K. W., Durham D. L., Hart D. A., Eidels L. Role of glycosylation in expression of functional diphtheria toxin receptors. Infect Immun. 1985 Aug;49(2):336–343. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.2.336-343.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen J. H., Maxfield F. R., Hardegree M. C., Habig W. H. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of diphtheria toxin by cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2912–2916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keusch G. T., Jacewicz M. Pathogenesis of Shigella diarrhea. VII. Evidence for a cell membrane toxin receptor involving beta1 leads to 4-linked N-acetyl-D-glucosamine oligomers. J Exp Med. 1977 Aug 1;146(2):535–546. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.2.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koehler T. M., Collier R. J. Anthrax toxin protective antigen: low-pH-induced hydrophobicity and channel formation in liposomes. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jun;5(6):1501–1506. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00796.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppla S. H. Anthrax toxin edema factor: a bacterial adenylate cyclase that increases cyclic AMP concentrations of eukaryotic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3162–3166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppla S. H. Bacillus anthracis calmodulin-dependent adenylate cyclase: chemical and enzymatic properties and interactions with eucaryotic cells. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphorylation Res. 1984;17:189–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppla S. H. Production and purification of anthrax toxin. Methods Enzymol. 1988;165:103–116. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(88)65019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manhart M. D., Morris R. E., Bonventre P. F., Leppla S., Saelinger C. B. Evidence for pseudomonas exotoxin A receptors on plasma membrane of toxin-sensitive lm fibroblasts. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):596–603. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.596-603.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekada E., Okada Y., Uchida T. Identification of diphtheria toxin receptor and a nonproteinous diphtheria toxin-binding molecule in Vero cell membrane. J Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;107(2):511–519. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.2.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlebrook J. L., Dorland R. B. Bacterial toxins: cellular mechanisms of action. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Sep;48(3):199–221. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.3.199-221.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mock M., Labruyère E., Glaser P., Danchin A., Ullmann A. Cloning and expression of the calmodulin-sensitive Bacillus anthracis adenylate cyclase in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1988 Apr 29;64(2):277–284. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90342-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick D., Orchansky P., Revel M., Rubinstein M. The human interferon-gamma receptor. Purification, characterization, and preparation of antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8483–8487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilch P. F., Czech M. P. Interaction of cross-linking agents with the insulin effector system of isolated fat cells. Covalent linkage of 125I-insulin to a plasma membrane receptor protein of 140,000 daltons. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3375–3381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proia R. L., Eidels L., Hart D. A. Diphtheria toxin-binding glycoproteins on hamster cells: candidates for diphtheria toxin receptors. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):786–791. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.786-791.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson D. L., Leppla S. H. Molecular cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the lethal factor gene of Bacillus anthracis. Gene. 1986;44(1):71–78. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90044-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson D. L., Tippetts M. T., Leppla S. H. Nucleotide sequence of the Bacillus anthracis edema factor gene (cya): a calmodulin-dependent adenylate cyclase. Gene. 1988 Dec 20;73(2):363–371. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90501-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STANLEY J. L., SMITH H. Purification of factor I and recognition of a third factor of the anthrax toxin. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Sep;26:49–63. doi: 10.1099/00221287-26-1-49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh Y., Chaudhary V. K., Leppla S. H. A deleted variant of Bacillus anthracis protective antigen is non-toxic and blocks anthrax toxin action in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):19103–19107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh Y., Leppla S. H., Bhatnagar R., Friedlander A. M. Internalization and processing of Bacillus anthracis lethal toxin by toxin-sensitive and -resistant cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 5;264(19):11099–11102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenmark H., Olsnes S., Sandvig K. Requirement of specific receptors for efficient translocation of diphtheria toxin A fragment across the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):13449–13455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takatsuki A., Tamura G. Effect of tunicamycin on the synthesis of macromolecules in cultures of chick embryo fibroblasts infected with Newcastle disease virus. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1971 Nov;24(11):785–794. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.24.785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson M. R., Forristal J., Kauffmann P., Madden T., Kozak K., Morris R. E., Saelinger C. B. Isolation and characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A binding glycoprotein from mouse LM cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2390–2396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vodkin M. H., Leppla S. H. Cloning of the protective antigen gene of Bacillus anthracis. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):693–697. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90402-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welkos S. L., Lowe J. R., Eden-McCutchan F., Vodkin M., Leppla S. H., Schmidt J. J. Sequence and analysis of the DNA encoding protective antigen of Bacillus anthracis. Gene. 1988 Sep 30;69(2):287–300. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90439-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood C. L., O'Dorisio M. S. Covalent cross-linking of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide to its receptors on intact human lymphoblasts. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):1243–1247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]