Abstract
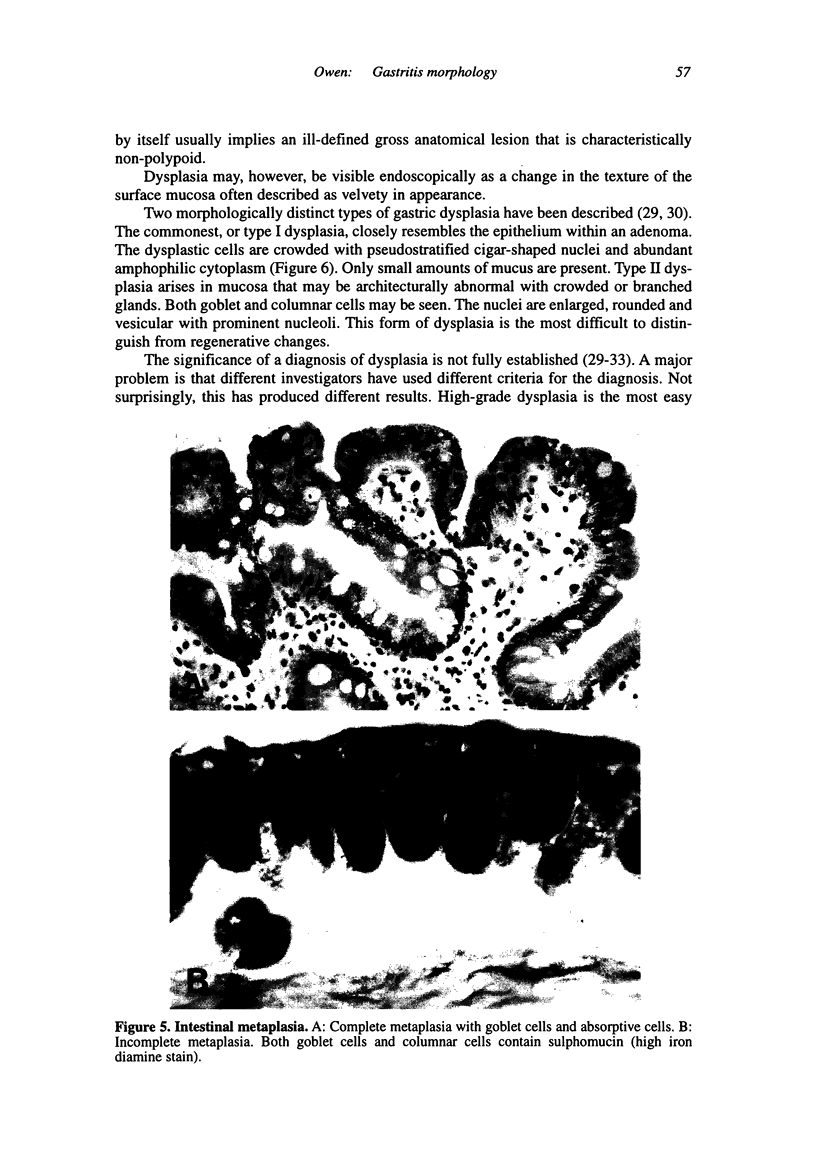
Gastritis is a histopathologic diagnosis, which correlates poorly with both clinical symptoms of non-ulcer dyspepsia and endoscopic abnormalities. Worldwide, most cases of gastritis are due to Helicobacter pylori and are characterized by a diffuse superficial antral gastritis. Chronic inflammatory cells and lymphoid follicles are present in the lamina propria. Neutrophils are present in the surface and pit-lining epithelium. In North America and Western Europe, reactive gastropathy due to duodenal reflux or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents is also common. In this condition, there is no increase in inflammatory cells, but the pit-lining cells become hyperplastic, and the pits have a corkscrew appearance. Most examples of multifocal atrophic gastritis are the result of long standing Helicobacter gastritis, although there may be other causes as well. It is characterized by loss of glands in both pyloric and corpus mucosae with intestinal metaplasia of the surface epithelium. A subtype of intestinal metaplasia, in which sulphomucin (large bowel mucin) is present, has been associated with the development of distal gastric cancer. However, this association is relatively weak and is not considered useful for screening purposes. Gastric dysplasia may develop in areas of the stomach affected by intestinal metaplasia. High-grade dysplasia is a significant finding, with up to 60 percent of cases having coincident carcinoma and a further 25 percent of cases likely to develop an invasive malignancy within fifteen months.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayerdörffer E., Lehn N., Hatz R., Mannes G. A., Oertel H., Sauerbruch T., Stolte M. Difference in expression of Helicobacter pylori gastritis in antrum and body. Gastroenterology. 1992 May;102(5):1575–1582. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)91716-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J. Gastric Campylobacter-like organisms, gastritis, and peptic ulcer disease. Gastroenterology. 1987 Aug;93(2):371–383. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)91028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J. Hypotheses on the pathogenesis and natural history of Helicobacter pylori-induced inflammation. Gastroenterology. 1992 Feb;102(2):720–727. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90126-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter H. A., Talley N. J. Gastroscopy is incomplete without biopsy: clinical relevance of distinguishing gastropathy from gastritis. Gastroenterology. 1995 Mar;108(3):917–924. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90468-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Correa P. Chronic gastritis: a clinico-pathological classification. Am J Gastroenterol. 1988 May;83(5):504–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Correa P., Fox J., Fontham E., Ruiz B., Lin Y. P., Zavala D., Taylor N., Mackinley D., de Lima E., Portilla H. Helicobacter pylori and gastric carcinoma. Serum antibody prevalence in populations with contrasting cancer risks. Cancer. 1990 Dec 15;66(12):2569–2574. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19901215)66:12<2569::aid-cncr2820661220>3.0.co;2-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Correa P., Yardley J. H. Grading and classification of chronic gastritis: one American response to the Sydney system. Gastroenterology. 1992 Jan;102(1):355–359. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)91820-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuello C., López J., Correa P., Murray J., Zarama G., Gordillo G. Histopathology of gastric dysplasias: correlations with gastric juice chemistry. Am J Surg Pathol. 1979 Dec;3(6):491–500. doi: 10.1097/00000478-197912000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler A. F., Havstad S., Ma C. K., Blaser M. J., Perez-Perez G. I., Schubert T. T. Accuracy of invasive and noninvasive tests to diagnose Helicobacter pylori infection. Gastroenterology. 1995 Jul;109(1):136–141. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90278-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon M. F., O'Connor H. J., Axon A. T., King R. F., Johnston D. Reflux gastritis: distinct histopathological entity? J Clin Pathol. 1986 May;39(5):524–530. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.5.524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drumm B., Sherman P., Cutz E., Karmali M. Association of Campylobacter pylori on the gastric mucosa with antral gastritis in children. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jun 18;316(25):1557–1561. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198706183162501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ectors N., Dixon M. F. The prognostic value of sulphomucin positive intestinal metaplasia in the development of gastric cancer. Histopathology. 1986 Dec;10(12):1271–1277. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1986.tb02570.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falck V. G., Novelli M. R., Wright N. A., Alexander N. Gastric dysplasia: inter-observer variation, sulphomucin staining and nucleolar organizer region counting. Histopathology. 1990 Feb;16(2):141–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1990.tb01082.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filipe M. I. Mucins in the human gastrointestinal epithelium: a review. Invest Cell Pathol. 1979 Jul-Sep;2(3):195–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filipe M. I., Potet F., Bogomoletz W. V., Dawson P. A., Fabiani B., Chauveinc P., Fenzy A., Gazzard B., Goldfain D., Zeegen R. Incomplete sulphomucin-secreting intestinal metaplasia for gastric cancer. Preliminary data from a prospective study from three centres. Gut. 1985 Dec;26(12):1319–1326. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.12.1319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freilich R. J., Thompson S. J., Walker R. W., Rosenblum M. K. Adenocarcinomatous transformation of intracranial germ cell tumors. Am J Surg Pathol. 1995 May;19(5):537–544. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199505000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genta R. M., Lew G. M., Graham D. Y. Changes in the gastric mucosa following eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Mod Pathol. 1993 May;6(3):281–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genta R. M., Robason G. O., Graham D. Y. Simultaneous visualization of Helicobacter pylori and gastric morphology: a new stain. Hum Pathol. 1994 Mar;25(3):221–226. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(94)90191-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson L. R., Engstrand L., Nyrén O., Lindgren A. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection in subtypes of gastric cancer. Gastroenterology. 1995 Sep;109(3):885–888. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90398-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jass J. R. A classification of gastric dysplasia. Histopathology. 1983 Mar;7(2):181–193. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1983.tb02234.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jass J. R., Filipe M. I. The mucin profiles of normal gastric mucosa, intestinal metaplasia and its variants and gastric carcinoma. Histochem J. 1981 Nov;13(6):931–939. doi: 10.1007/BF01002633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalish R. J., Clancy P. E., Orringer M. B., Appelman H. D. Clinical, epidemiologic, and morphologic comparison between adenocarcinomas arising in Barrett's esophageal mucosa and in the gastric cardia. Gastroenterology. 1984 Mar;86(3):461–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lansdown M., Quirke P., Dixon M. F., Axon A. T., Johnston D. High grade dysplasia of the gastric mucosa: a marker for gastric carcinoma. Gut. 1990 Sep;31(9):977–983. doi: 10.1136/gut.31.9.977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin K. J., Dowling F., Wright J. P., Taylor K. B. Gastric morphology and serum gastrin levels in pernicious anaemia. Gut. 1976 Jul;17(7):551–560. doi: 10.1136/gut.17.7.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mégraud F., Brassens-Rabbé M. P., Denis F., Belbouri A., Hoa D. Q. Seroepidemiology of Campylobacter pylori infection in various populations. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Aug;27(8):1870–1873. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.8.1870-1873.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price A. B. The Sydney System: histological division. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1991 May-Jun;6(3):209–222. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.1991.tb01468.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rugge M., Farinati F., Baffa R., Sonego F., Di Mario F., Leandro G., Valiante F. Gastric epithelial dysplasia in the natural history of gastric cancer: a multicenter prospective follow-up study. Interdisciplinary Group on Gastric Epithelial Dysplasia. Gastroenterology. 1994 Nov;107(5):1288–1296. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90529-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siurala M., Sipponen P., Kekki M. Campylobacter pylori in a sample of Finnish population: relations to morphology and functions of the gastric mucosa. Gut. 1988 Jul;29(7):909–915. doi: 10.1136/gut.29.7.909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolte M., Baumann K., Bethke B., Ritter M., Lauer E., Eidt H. Active autoimmune gastritis without total atrophy of the glands. Z Gastroenterol. 1992 Oct;30(10):729–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland R. G., Mackay I. R. A reappraisal of the nature and significance of chronic atrophic gastritis. Am J Dig Dis. 1973 May;18(5):426–440. doi: 10.1007/BF01071995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabo S., Goldberg I. Experimental pathogenesis: drugs and chemical lesions in the gastric mucosa. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1990;174:1–8. doi: 10.3109/00365529009091924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein W. M., Goldstein N. S. Gastric dysplasia and its management. Gastroenterology. 1994 Nov;107(5):1543–1545. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90561-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]