Abstract
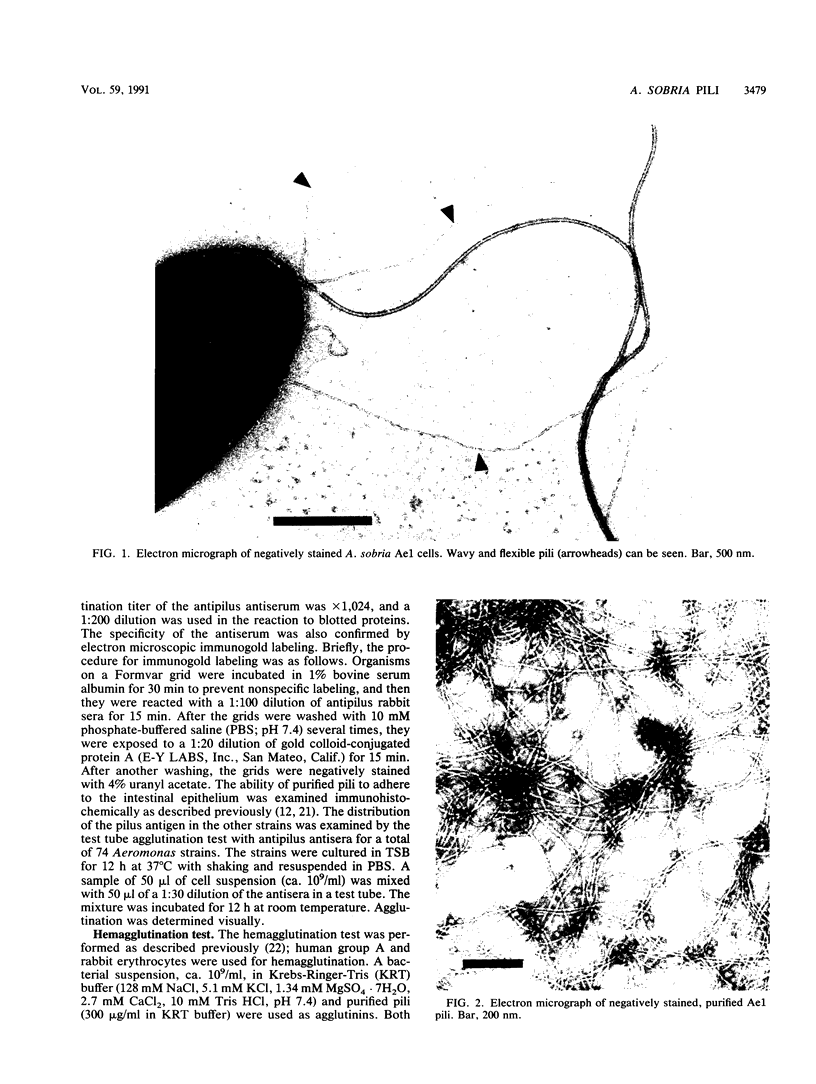
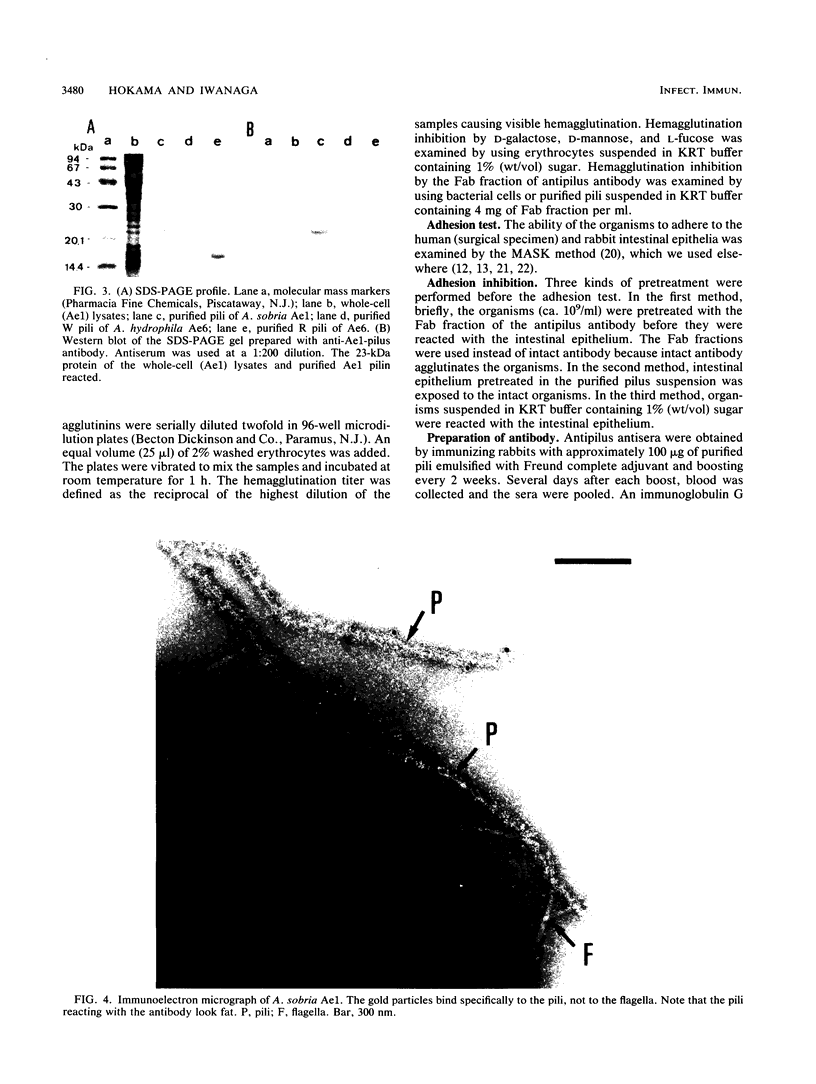
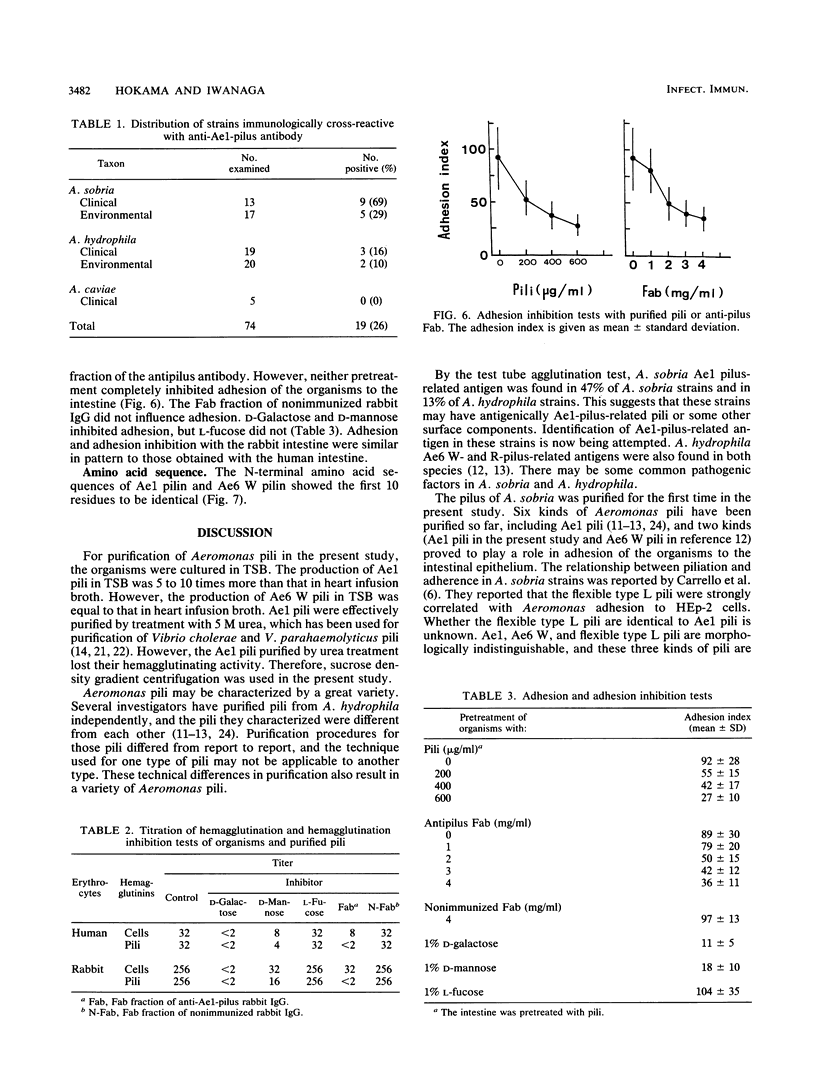
Pili of Aeromonas sobria Ae1 were purified and characterized. The molecular mass of the pilin was estimated to be about 23 kDa by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The Ae1 pili were electrophoretically and immunologically distinguishable from the W pili of A. hydrophila Ae6, although the two pili were morphologically indistinguishable. The N-terminal amino acid sequences of the two pilins were identical in the first 10 residues. Strain Ae1 and its purified pili adhered to human and rabbit intestines and agglutinated human and rabbit erythrocytes. Hemagglutination was inhibited by D-galactose and D-mannose, but not by L-fucose. Organisms pretreated with the Fab fraction of the antipilus antibody failed to adhere to the intestines. Organisms did not adhere to intestines pretreated with the purified pili. These findings suggest that the pili are a colonization factor of A. sobria Ae1.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D., Atkinson H. M., Woods W. H. Aeromonas hydrophila typing scheme based on patterns of agglutination with erythrocytes and yeast cells. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Mar;17(3):422–427. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.3.422-427.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson H. M., Trust T. J. Hemagglutination properties and adherence ability of Aeromonas hydrophila. Infect Immun. 1980 Mar;27(3):938–946. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.3.938-946.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke V., Cooper M., Robinson J. Haemagglutination patterns of Aeromonas spp. related to species and source of strains. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1986 Dec;64(Pt 6):563–570. doi: 10.1038/icb.1986.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill M. M. Virulence factors in motile Aeromonas species. J Appl Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;69(1):1–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1990.tb02905.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrello A., Silburn K. A., Budden J. R., Chang B. J. Adhesion of clinical and environmental Aeromonas isolates to HEp-2 cells. J Med Microbiol. 1988 May;26(1):19–27. doi: 10.1099/00222615-26-1-19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daily O. P., Joseph S. W., Coolbaugh J. C., Walker R. I., Merrell B. R., Rollins D. M., Seidler R. J., Colwell R. R., Lissner C. R. Association of Aeromonas sobria with human infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Apr;13(4):769–777. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.4.769-777.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbashir A. M., Millership S. E. Haemagglutinating activity of Aeromonas spp. from different sources; attempted use as a typing system. Epidemiol Infect. 1989 Apr;102(2):221–229. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800029897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Common themes in microbial pathogenicity. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jun;53(2):210–230. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.2.210-230.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gracey M., Burke V., Robinson J. Aeromonas-associated gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1982 Dec 11;2(8311):1304–1306. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91510-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho A. S., Mietzner T. A., Smith A. J., Schoolnik G. K. The pili of Aeromonas hydrophila: identification of an environmentally regulated "mini pilin". J Exp Med. 1990 Sep 1;172(3):795–806. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.3.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hokama A., Honma Y., Nakasone N. Pili of an Aeromonas hydrophila strain as a possible colonization factor. Microbiol Immunol. 1990;34(11):901–915. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1990.tb01069.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honma Y., Nakasone N. Pili of Aeromonas hydrophila: purification, characterization, and biological role. Microbiol Immunol. 1990;34(2):83–98. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1990.tb00995.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwanaga M., Nakasone N., Ehara M. Pili of Vibrio cholerae O1 biotype E1 Tor: a comparative study on adhesive and non-adhesive strains. Microbiol Immunol. 1989;33(1):1–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1989.tb01492.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiwa S. F. Enterotoxigenicity, hemagglutination and cell-surface hydrophobicity in Aeromonas hydrophila, A. sobria and A. salmonicida. Vet Microbiol. 1983 Feb;8(1):17–34. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(83)90016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungh A., Wadström T. Aeromonas hydrophila--an accepted enterotoxigenic "neoenteropathogen"? J Infect Dis. 1985 May;151(5):972–973. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.5.972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakasone N., Iwanaga M. Pili of Vibrio cholerae non-O1. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1640–1646. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1640-1646.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakasone N., Iwanaga M. Pili of a Vibrio parahaemolyticus strain as a possible colonization factor. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):61–69. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.61-69.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakasone N., Iwanaga M. Quantitative evaluation of colonizing ability of Vibrio cholerae O1. Microbiol Immunol. 1987;31(8):753–761. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1987.tb03137.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nandapalan N., Chang B. J. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to Aeromonas sobria surface antigens. FEMS Microbiol Immunol. 1989 Dec;1(8-9):515–524. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1989.tb02444.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Research on Aeromonas and Plesiomonas. IV. Virulence factors. Experientia. 1987 Apr 15;43(4):367–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato M., Arita M., Honda T., Miwatani T. Characterization of a pilus produced by Aeromonas hydrophila. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Jun;50(3):325–329. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90440-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







