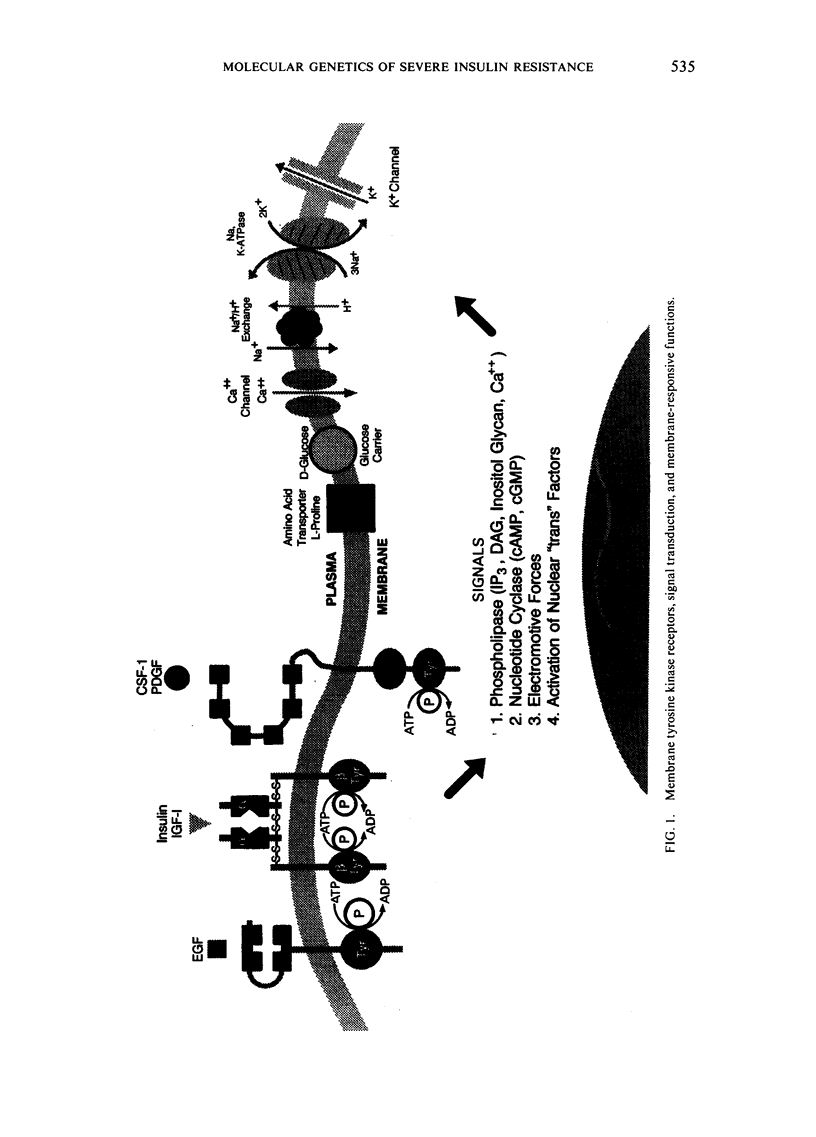
Abstract
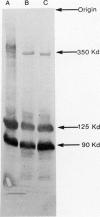
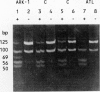
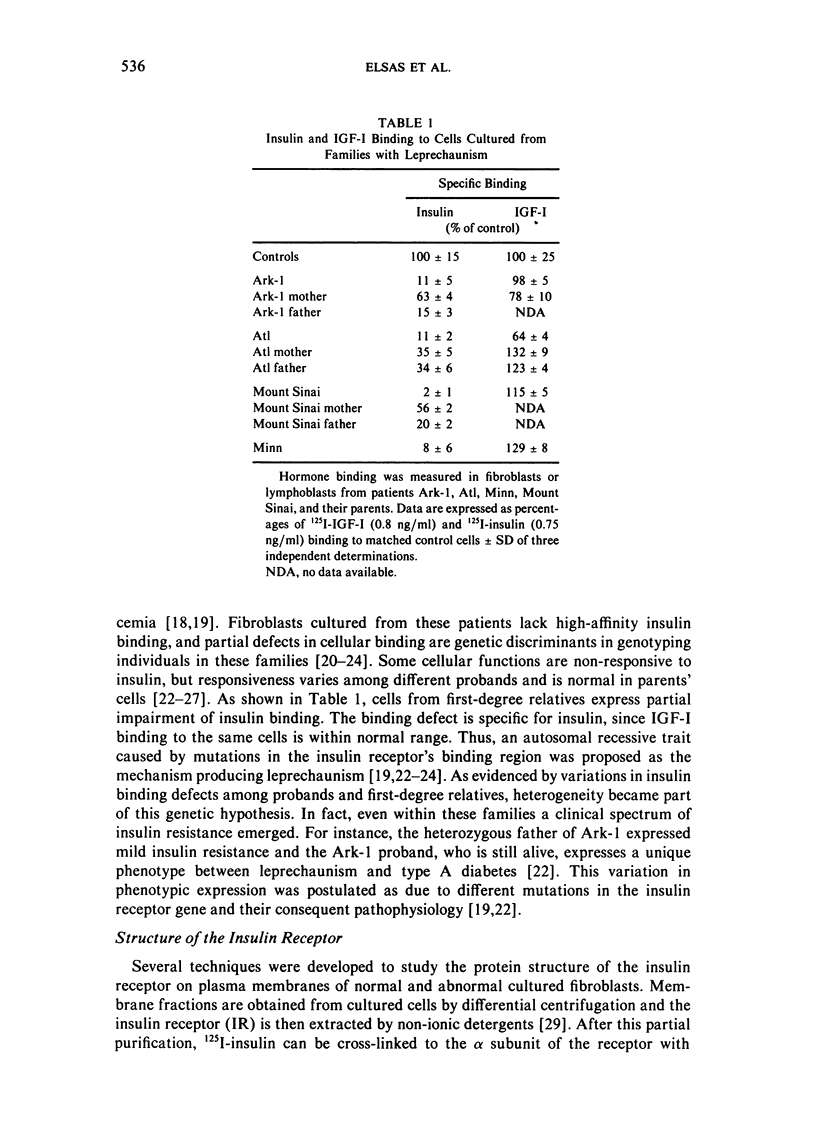
Leprechaunism and type A diabetes represent inborn errors of insulin resistance whose phenotypes suggested causation by mutations in the insulin receptor gene. Cells cultured from patients with leprechaunism specifically lacked high-affinity insulin binding. Partial but different degrees of impairment were observed in cells cultured from first-degree relatives. Different mutations in the insulin receptor's alpha subunit were proposed in different families (Ark-1, Atl, Minn, Mount Sinai) based on phenotype, cellular insulin binding, and insulin receptor structure. Molecular cloning and sequencing of mutant insulin receptor cDNA from family Ark-1 confirmed that the proband inherited a maternal missense and a paternal nonsense mutation in the alpha subunit and was a compound heterozygote. The insulin receptor was immunologically present on the plasma membrane of fibroblasts cultured from patients Ark-1 and Atl but was markedly reduced in cells from patients Minn and Mount Sinai. In cells from patient Minn, but not from patient Mount Sinai, the decreased number of insulin receptors was associated with reduced insulin receptor mRNA. In two families with the less severe form of insulin resistance, type A diabetes, mutations altered post-translational processing of the insulin receptor molecule. At a cellular level, these mutations of the alpha subunit of the insulin receptor shared defective binding and impaired stimulation of sugar transport by insulin. In family Atl, however, glucose uptake was constitutively increased. Thus, genetic variation in the insulin receptor gene causes a spectrum of inherited insulin-resistant syndromes and altered cellular signaling.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Araki E., Shimada F., Uzawa H., Mori M., Ebina Y. Characterization of the promoter region of the human insulin receptor gene. Evidence for promoter activity. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):16186–16191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou C. K., Dull T. J., Russell D. S., Gherzi R., Lebwohl D., Ullrich A., Rosen O. M. Human insulin receptors mutated at the ATP-binding site lack protein tyrosine kinase activity and fail to mediate postreceptor effects of insulin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1842–1847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coussens L., Van Beveren C., Smith D., Chen E., Mitchell R. L., Isacke C. M., Verma I. M., Ullrich A. Structural alteration of viral homologue of receptor proto-oncogene fms at carboxyl terminus. Nature. 1986 Mar 20;320(6059):277–280. doi: 10.1038/320277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman S. W., Wardzala L. J. Potential mechanism of insulin action on glucose transport in the isolated rat adipose cell. Apparent translocation of intracellular transport systems to the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4758–4762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina Y., Araki E., Taira M., Shimada F., Mori M., Craik C. S., Siddle K., Pierce S. B., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Replacement of lysine residue 1030 in the putative ATP-binding region of the insulin receptor abolishes insulin- and antibody-stimulated glucose uptake and receptor kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):704–708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina Y., Ellis L., Jarnagin K., Edery M., Graf L., Clauser E., Ou J. H., Masiarz F., Kan Y. W., Goldfine I. D. The human insulin receptor cDNA: the structural basis for hormone-activated transmembrane signalling. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):747–758. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90334-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbein S. C., Borecki I., Corsetti L., Fajans S. S., Hansen A. T., Nerup J., Province M., Permutt M. A. Linkage analysis of the human insulin receptor gene and maturity onset diabetes of the young. Diabetologia. 1987 Aug;30(8):641–647. doi: 10.1007/BF00277322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis L., Clauser E., Morgan D. O., Edery M., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Replacement of insulin receptor tyrosine residues 1162 and 1163 compromises insulin-stimulated kinase activity and uptake of 2-deoxyglucose. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90786-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis L., Morgan D. O., Clauser E., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. A membrane-anchored cytoplasmic domain of the human insulin receptor mediates a constitutively elevated insulin-independent uptake of 2-deoxyglucose. Mol Endocrinol. 1987 Jan;1(1):15–24. doi: 10.1210/mend-1-1-15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsas L. J., 2nd, MacDonell R. C., Jr, Rosenberg L. E. Influence of age on insulin stimulation of amino acid uptake in rat diaphragm. J Biol Chem. 1971 Nov;246(21):6452–6459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsas L. J., Albrecht I., Koehne W., Rosenberg L. E. Effect of puromycin on insulin-stimulated amino-acid transport in muscle. Nature. 1967 May 27;214(5091):916–917. doi: 10.1038/214916b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsas L. J., Albrecht I., Rosenberg L. E. Insulin stimulation of amino acid uptake in rat diaphragm. Relationship to protein sythesis. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 25;243(8):1846–1853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsas L. J., Endo F., Strumlauf E., Elders J., Priest J. H. Leprechaunism: an inherited defect in a high-affinity insulin receptor. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Jan;37(1):73–88. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsas L. J., Longo N. Impaired insulin binding and excess glucose transport in fibroblasts from a patient with leprechaunism. Enzyme. 1987;38(1-4):184–193. doi: 10.1159/000469204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo F., Nagata N., Priest J. H., Longo N., Elsas L. J., 2nd Structural analysis of normal and mutant insulin receptors in fibroblasts cultured from families with leprechaunism. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Sep;41(3):402–417. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espinal J. Mechanism of insulin action. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):574–575. doi: 10.1038/328574a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espinal J. What is the role of the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase? Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Oct;13(10):367–368. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90170-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsayeth J. R., Caro J. F., Sinha M. K., Maddux B. A., Goldfine I. D. Monoclonal antibodies to the human insulin receptor that activate glucose transport but not insulin receptor kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3448–3451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germinario R. J., Oliveira M. Stimulation of hexose transport in cultured human skin fibroblasts by insulin. J Cell Physiol. 1979 Jun;99(3):313–318. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040990305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigorescu F., Flier J. S., Kahn C. R. Defect in insulin receptor phosphorylation in erythrocytes and fibroblasts associated with severe insulin resistance. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15003–15006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunberger G., Zick Y., Gorden P. Defect in phosphorylation of insulin receptors in cells from an insulin-resistant patient with normal insulin binding. Science. 1984 Mar 2;223(4639):932–934. doi: 10.1126/science.6141638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg M. D., Cuatrecasas P. Insulin and epidermal growth factor. Human fibroblast receptors related to deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis and amino acid uptake. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):3845–3853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Brown R., Navarro J., Pilch P. F. Insulin-regulatable tissues express a unique insulin-sensitive glucose transport protein. Nature. 1988 May 12;333(6169):183–185. doi: 10.1038/333183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Strube M., Mueckler M. Molecular cloning and characterization of an insulin-regulatable glucose transporter. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):83–87. doi: 10.1038/338083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas H. A., Newman J. D., Harrison L. C. An atypical insulin receptor with high affinity for insulin-like growth factors copurified with placental insulin receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4124–4128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki T., Bevins C. L., Cama A., Ojamaa K., Marcus-Samuels B., Kadowaki H., Beitz L., McKeon C., Taylor S. I. Two mutant alleles of the insulin receptor gene in a patient with extreme insulin resistance. Science. 1988 May 6;240(4853):787–790. doi: 10.1126/science.2834824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Karlsson F. A., Kahn C. R. Insulin stimulates the phosphorylation of the 95,000-dalton subunit of its own receptor. Science. 1982 Jan 8;215(4529):185–187. doi: 10.1126/science.7031900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight A. B., Rechler M. M., Romanus J. A., Van Obberghen-Schilling E. E., Nissley S. P. Stimulation of glucose incorporation and amino acid transport by insulin and an insulin-like growth factor in fibroblasts with defective insulin receptors cultured from a patient with leprechaunism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2554–2558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lantz R. C., Elsas L. J., DeHaan R. L. Ouabain-resistant hyperpolarization induced by insulin in aggregates of embryonic heart cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):3062–3066. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.3062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longo N., Franchi-Gazzola R., Bussolati O., Dall'Asta V., Foà P. P., Guidotti G. G., Gazzola G. C. Effect of insulin on the activity of amino acid transport systems in cultured human fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Feb 21;844(2):216–223. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(85)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longo N., Griffin L. D., Shuster R. C., Langley S., Elsas L. J. Increased glucose transport by human fibroblasts with a heritable defect in insulin binding. Metabolism. 1989 Jul;38(7):690–697. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(89)90109-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller-Wieland D., Taub R., Tewari D. S., Kriauciunas K. M., Sethu S., Reddy K., Kahn C. R. Insulin-receptor gene and its expression in patients with insulin resistance. Diabetes. 1989 Jan;38(1):31–38. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.1.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odawara M., Kadowaki T., Yamamoto R., Shibasaki Y., Tobe K., Accili D., Bevins C., Mikami Y., Matsuura N., Akanuma Y. Human diabetes associated with a mutation in the tyrosine kinase domain of the insulin receptor. Science. 1989 Jul 7;245(4913):66–68. doi: 10.1126/science.2544998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojamaa K., Hedo J. A., Roberts C. T., Jr, Moncada V. Y., Gorden P., Ullrich A., Taylor S. I. Defects in human insulin receptor gene expression. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Mar;2(3):242–247. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-3-242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilch P. F., Czech M. P. Interaction of cross-linking agents with the insulin effector system of isolated fat cells. Covalent linkage of 125I-insulin to a plasma membrane receptor protein of 140,000 daltons. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3375–3381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podskalny J. M., Kahn C. R. Cell culture studies on patients with extreme insulin resistance. I. Receptor defects on cultured fibroblasts. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Feb;54(2):261–268. doi: 10.1210/jcem-54-2-261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podskalny J. M., Kahn C. R. Cell culture studies on patients with extreme insulin resistance. II. Abnormal biological responses in cultured fibroblasts. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Feb;54(2):269–275. doi: 10.1210/jcem-54-2-269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen O. M. After insulin binds. Science. 1987 Sep 18;237(4821):1452–1458. doi: 10.1126/science.2442814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg A. M., Haworth J. C., Degroot G. W., Trevenen C. L., Rechler M. M. A case of leprechaunism with severe hyperinsulinemia. Am J Dis Child. 1980 Feb;134(2):170–175. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1980.02130140044014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schilling E. E., Rechler M. M., Grunfeld C., Rosenberg A. M. Primary defect of insulin receptors in skin fibroblasts cultured from an infant with leprechaunism and insulin resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5877–5881. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seino S., Bell G. I. Alternative splicing of human insulin receptor messenger RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Feb 28;159(1):312–316. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92439-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seino S., Seino M., Nishi S., Bell G. I. Structure of the human insulin receptor gene and characterization of its promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):114–118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J., Rettenmier C. W., Sacca R., Roussel M. F., Look A. T., Stanley E. R. The c-fms proto-oncogene product is related to the receptor for the mononuclear phagocyte growth factor, CSF-1. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):665–676. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taira M., Taira M., Hashimoto N., Shimada F., Suzuki Y., Kanatsuka A., Nakamura F., Ebina Y., Tatibana M., Makino H. Human diabetes associated with a deletion of the tyrosine kinase domain of the insulin receptor. Science. 1989 Jul 7;245(4913):63–66. doi: 10.1126/science.2544997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R., Soos M. A., Wells A., Argyraki M., Siddle K. Insulin-like and insulin-inhibitory effects of monoclonal antibodies for different epitopes on the human insulin receptor. Biochem J. 1987 Feb 15;242(1):123–129. doi: 10.1042/bj2420123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trischitta V., Wong K. Y., Brunetti A., Scalisi R., Vigneri R., Goldfine I. D. Endocytosis, recycling, and degradation of the insulin receptor. Studies with monoclonal antireceptor antibodies that do not activate receptor kinase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):5041–5046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Bell J. R., Chen E. Y., Herrera R., Petruzzelli L. M., Dull T. J., Gray A., Coussens L., Liao Y. C., Tsubokawa M. Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):756–761. doi: 10.1038/313756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Coussens L., Hayflick J. S., Dull T. J., Gray A., Tam A. W., Lee J., Yarden Y., Libermann T. A., Schlessinger J. Human epidermal growth factor receptor cDNA sequence and aberrant expression of the amplified gene in A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):418–425. doi: 10.1038/309418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Gray A., Tam A. W., Yang-Feng T., Tsubokawa M., Collins C., Henzel W., Le Bon T., Kathuria S., Chen E. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor primary structure: comparison with insulin receptor suggests structural determinants that define functional specificity. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2503–2512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler F. B., Santora A. C., 2nd, Elsas L. J., 2nd Evidence supporting a two-receptor model for insulin binding by cultured embryonic heart cells. Endocrinology. 1980 Jul;107(1):195–207. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-1-195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiang K. S., Cox N. J., Sanz N., Huang P., Karam J. H., Bell G. I. Insulin-receptor and apolipoprotein genes contribute to development of NIDDM in Chinese Americans. Diabetes. 1989 Jan;38(1):17–23. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.1.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Feng T. L., Francke U., Ullrich A. Gene for human insulin receptor: localization to site on chromosome 19 involved in pre-B-cell leukemia. Science. 1985 May 10;228(4700):728–731. doi: 10.1126/science.3873110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Escobedo J. A., Kuang W. J., Yang-Feng T. L., Daniel T. O., Tremble P. M., Chen E. Y., Ando M. E., Harkins R. N., Francke U. Structure of the receptor for platelet-derived growth factor helps define a family of closely related growth factor receptors. Nature. 1986 Sep 18;323(6085):226–232. doi: 10.1038/323226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Ullrich A. Growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:443–478. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]