Abstract
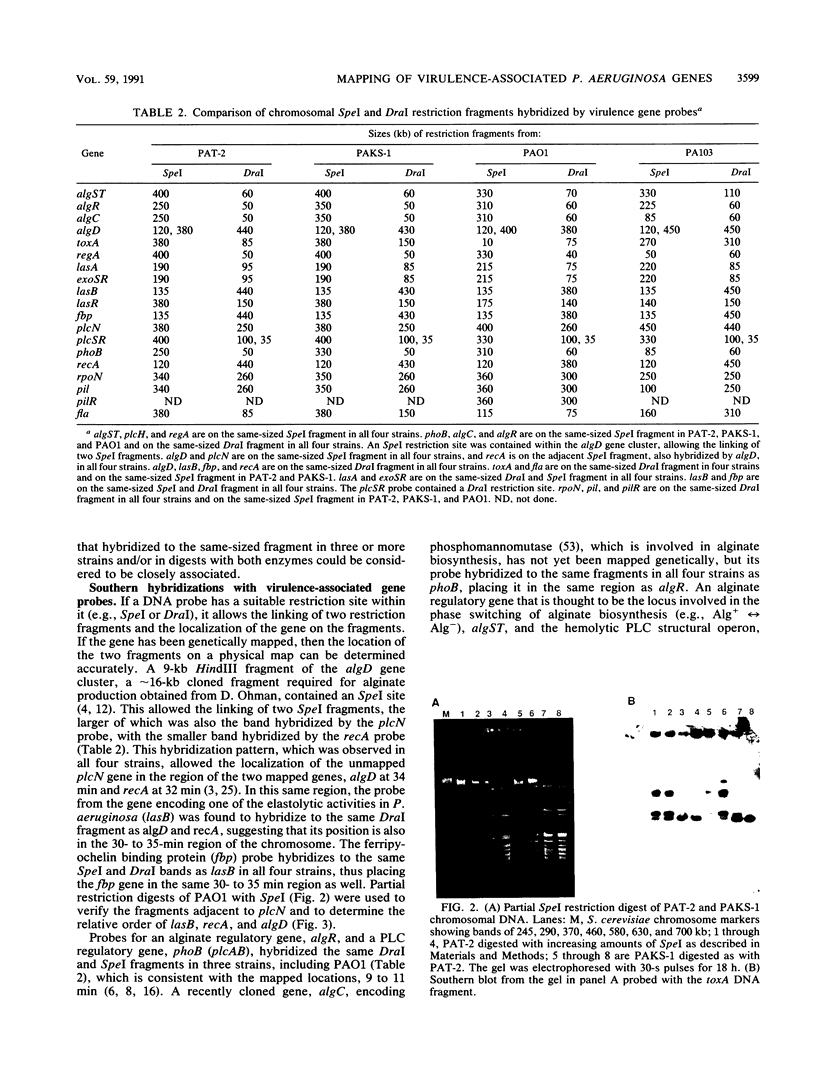
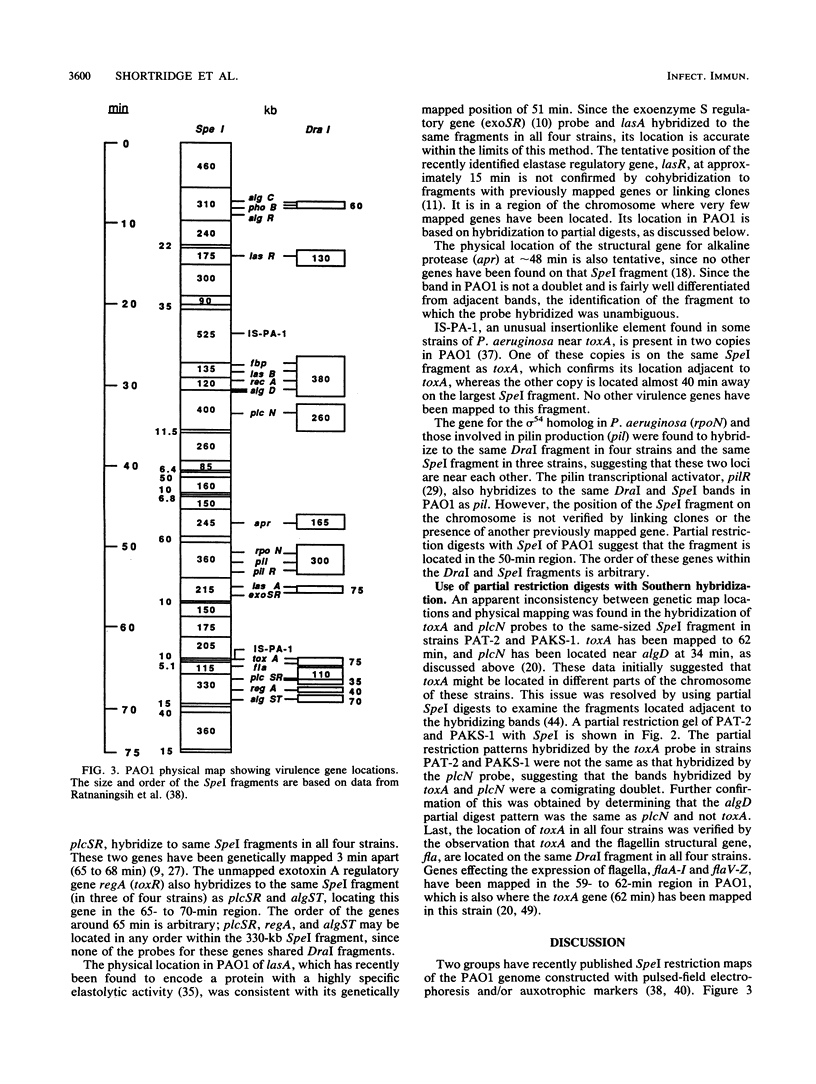
The relative chromosomal locations of 20 virulence-associated genes in four clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa were investigated by using transverse alternating-field electrophoresis. Each strain had a characteristic restriction pattern when digested with either SpeI or DraI and electrophoresed with 15-s pulses. All four strains had restriction fragments that hybridized with each of the gene probes used, although there were variations in fragment size. An SpeI physical map constructed by Ratnaningsih et al. (E. Ratnaningsih, S. Dharmsthiti, V. Krishnapillai, A. Morgan, M. Sinclair, and B. W. Holloway, J. Gen. Microbiol. 136:2351-2357, 1990) for one of these strains, PAO1, was used to identify the location of 11 previously unmapped genes. The physical locations of the remaining genes were found to be consistent with their genetically mapped loci. Whereas phospholipase C and alginate structural and regulatory genes were associated in three separate clusters in the early, middle, and late regions of the chromosome, no virulence cluster was identified. Our data suggest that the pathogenicity of P. aeruginosa results from the gradual acquisition of genes encoding various virulence determinants.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bever R. A., Iglewski B. H. Molecular characterization and nucleotide sequence of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa elastase structural gene. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4309–4314. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4309-4314.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canard B., Cole S. T. Genome organization of the anaerobic pathogen Clostridium perfringens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6676–6680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darzins A., Wang S. K., Vanags R. I., Chakrabarty A. M. Clustering of mutations affecting alginic acid biosynthesis in mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):516–524. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.516-524.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deretic V., Gill J. F., Chakrabarty A. M. Gene algD coding for GDPmannose dehydrogenase is transcriptionally activated in mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):351–358. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.351-358.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deretic V., Konyecsni W. M. Control of mucoidy in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: transcriptional regulation of algR and identification of the second regulatory gene, algQ. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):3680–3688. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.3680-3688.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filloux A., Bally M., Soscia C., Murgier M., Lazdunski A. Phosphate regulation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: cloning of the alkaline phosphatase gene and identification of phoB- and phoR-like genes. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Jun;212(3):510–513. doi: 10.1007/BF00330857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn J. L., Ohman D. E. Cloning of genes from mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa which control spontaneous conversion to the alginate production phenotype. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1452–1460. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1452-1460.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gambello M. J., Iglewski B. H. Cloning and characterization of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa lasR gene, a transcriptional activator of elastase expression. J Bacteriol. 1991 May;173(9):3000–3009. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.9.3000-3009.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg J. B., Ohman D. E. Cloning and expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa of a gene involved in the production of alginate. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):1115–1121. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.1115-1121.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg J. B., Ohman D. E. Cloning and transcriptional regulation of the elastase lasA gene in mucoid and nonmucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1349–1351. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1349-1351.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant C. C., Vasil M. L. Analysis of transcription of the exotoxin A gene of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1112–1119. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1112-1119.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray G. L., Smith D. H., Baldridge J. S., Harkins R. N., Vasil M. L., Chen E. Y., Heyneker H. L. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression in Escherichia coli of the exotoxin A structural gene of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2645–2649. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray G. L., Vasil M. L. Mapping of a gene controlling the production of phospholipase C and alkaline phosphatase in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;183(2):403–405. doi: 10.1007/BF00270648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grothues D., Koopmann U., von der Hardt H., Tümmler B. Genome fingerprinting of Pseudomonas aeruginosa indicates colonization of cystic fibrosis siblings with closely related strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Oct;26(10):1973–1977. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.10.1973-1977.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzzo J., Murgier M., Filloux A., Lazdunski A. Cloning of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa alkaline protease gene and secretion of the protease into the medium by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):942–948. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.942-948.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLOWAY B. W. Genetic recombination in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Gen Microbiol. 1955 Dec;13(3):572–581. doi: 10.1099/00221287-13-3-572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas D., Jann A., Reimmann C., Lüthi E., Leisinger T. Chromosome organization in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Clustering and scattering of genes specifying four arginine catabolic pathways. Antibiot Chemother (1971) 1987;39:256–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanne L. F., Howe T. R., Iglewski B. H. Locus of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin A gene. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):383–386. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.383-386.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi T., Kamio Y., Hishinuma F., Usami Y., Titani K., Terawaki Y. Pseudomonas aeruginosa cytotoxin: the nucleotide sequence of the gene and the mechanism of activation of the protoxin. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Jul;3(7):861–868. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00235.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway B. W., Morgan A. F. Genome organization in Pseudomonas. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:79–105. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.000455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn J. M., Ohman D. E. Transcriptional and translational analyses of recA mutant alleles in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1637–1650. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1637-1650.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. J., Smith H. O., Redfield R. J. Organization of the Haemophilus influenzae Rd genome. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3016–3024. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3016-3024.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindgren V., Ostroff R. M., Vasil M. L., Wretlind B. Genetic mapping of the structural gene for phospholipase C of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):1155–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.1155-1156.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V. The roles of various fractions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in its pathogenesis. 3. Identity of the lethal toxins produced in vitro and in vivo. J Infect Dis. 1966 Oct;116(4):481–489. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.4.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hoy K., Krishnapillai V. Recalibration of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAO chromosome map in time units using high-frequency-of-recombination donors. Genetics. 1987 Apr;115(4):611–618. doi: 10.1093/genetics/115.4.611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogle J. W., Janda J. M., Woods D. E., Vasil M. L. Characterization and use of a DNA probe as an epidemiological marker for Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jan;155(1):119–126. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.1.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostroff R. M., Vasil A. I., Vasil M. L. Molecular comparison of a nonhemolytic and a hemolytic phospholipase C from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;172(10):5915–5923. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.5915-5923.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostroff R. M., Vasil M. L. Identification of a new phospholipase C activity by analysis of an insertional mutation in the hemolytic phospholipase C structural gene of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1987 Oct;169(10):4597–4601. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.10.4597-4601.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostroff R. M., Wretlind B., Vasil M. L. Mutations in the hemolytic-phospholipase C operon result in decreased virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 grown under phosphate-limiting conditions. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1369–1373. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1369-1373.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters J. E., Galloway D. R. Purification and characterization of an active fragment of the LasA protein from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: enhancement of elastase activity. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2236–2240. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2236-2240.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard A. E., Vasil M. L. Nucleotide sequence and expression of a phosphate-regulated gene encoding a secreted hemolysin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):291–298. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.291-298.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard A. E., Vasil M. L. Possible insertion sequences in a mosaic genome organization upstream of the exotoxin A gene in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1990 Apr;172(4):2020–2028. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.4.2020-2028.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratnaningsih E., Dharmsthiti S., Krishnapillai V., Morgan A., Sinclair M., Holloway B. W. A combined physical and genetic map of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Dec;136(12):2351–2357. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-12-2351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley M., Anilionis A. Evolution of the bacterial genome. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1978;32:519–560. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.32.100178.002511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Römling U., Grothues D., Bautsch W., Tümmler B. A physical genome map of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4081–4089. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08592.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sastry P. A., Finlay B. B., Pasloske B. L., Paranchych W., Pearlstone J. R., Smillie L. B. Comparative studies of the amino acid and nucleotide sequences of pilin derived from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAK and PAO. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):571–577. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.571-577.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokol P. A. Surface expression of ferripyochelin-binding protein is required for virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2021–2025. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2021-2025.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terry J. M., Piña S. E., Mattingly S. J. Environmental conditions which influence mucoid conversion Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Infect Immun. 1991 Feb;59(2):471–477. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.2.471-477.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Totten P. A., Lara J. C., Lory S. The rpoN gene product of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is required for expression of diverse genes, including the flagellin gene. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jan;172(1):389–396. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.1.389-396.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Totten P. A., Lory S. Characterization of the type a flagellin gene from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAK. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):7188–7199. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.7188-7199.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda M., Oguchi T., Iino T. Analysis of flagellar genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by use of Rfla plasmids and conjugations. J Bacteriol. 1981 Sep;147(3):1008–1014. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.3.1008-1014.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasil M. L., Berka R. M., Gray G. L., Nakai H. Cloning of a phosphate-regulated hemolysin gene (phospholipase C) from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):431–440. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.431-440.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasil M. L., Chamberlain C., Grant C. C. Molecular studies of Pseudomonas exotoxin A gene. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):538–548. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.538-548.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J. M., Holloway B. W. Chromosome mapping in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAT. J Bacteriol. 1978 Mar;133(3):1113–1125. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.3.1113-1125.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zielinski N. A., Chakrabarty A. M., Berry A. Characterization and regulation of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa algC gene encoding phosphomannomutase. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9754–9763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]