Abstract
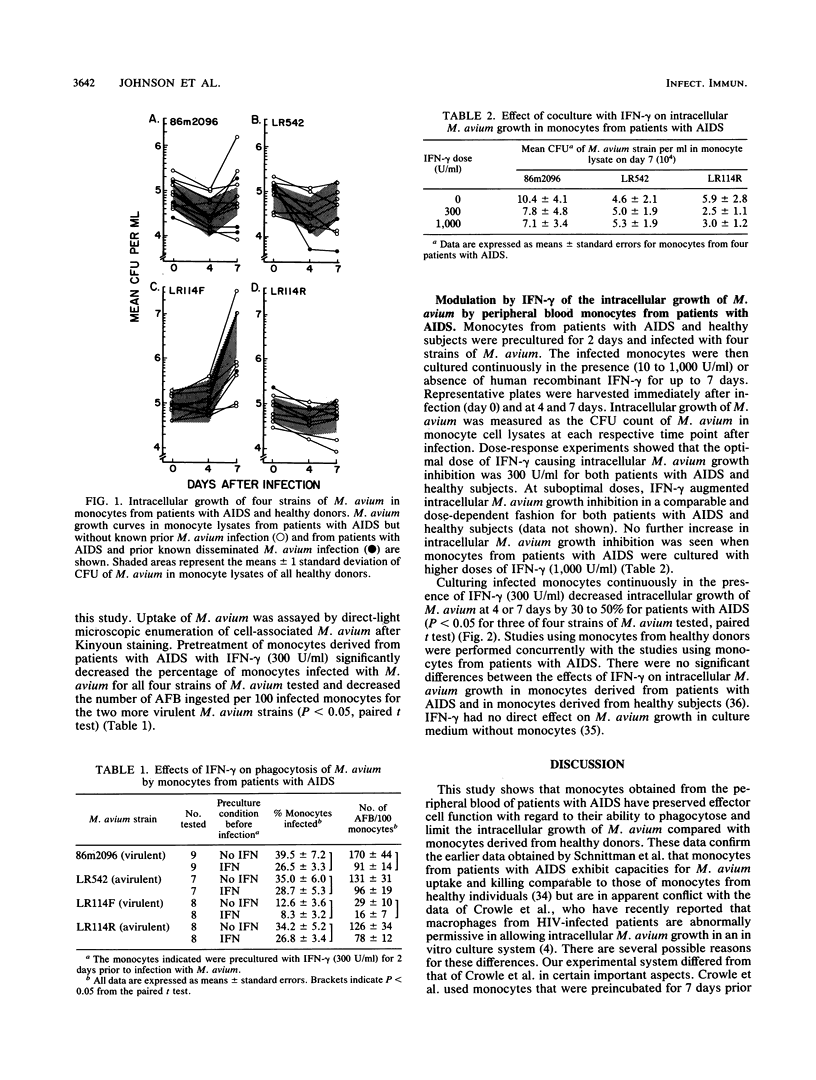
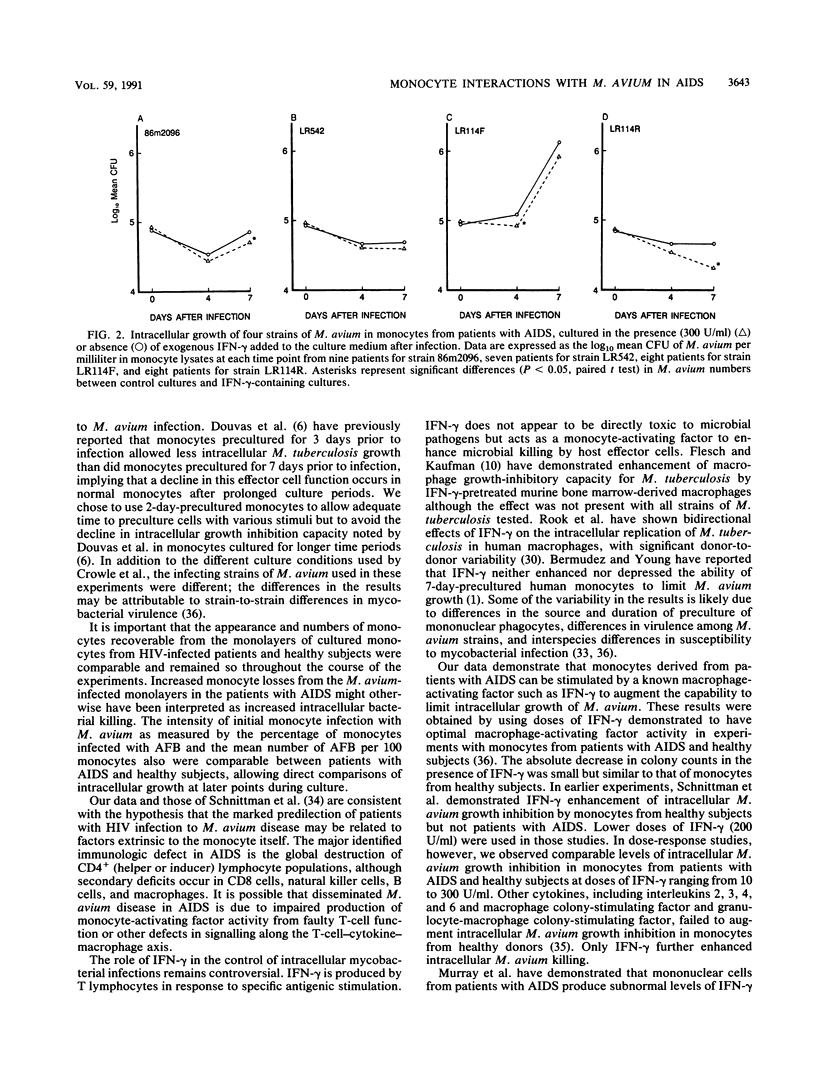
Mycobacterium avium-M. intracellulare is a frequent cause of late disseminated infection in patients with AIDS. The ability of human peripheral blood monocytes to phagocytose and kill M. avium was examined in an in vitro model. Monocytes were obtained from 13 healthy volunteers and 11 patients with AIDS, three of whom had documented disseminated M. avium infection. Monocytes were precultured for 2 days before infection with two AIDS-associated and two non-AIDS-associated strains of M. avium. Uptake of M. avium as measured by counting intracellular acid-fast bacilli did not differ among healthy subjects, patients with AIDS, or patients with AIDS and previously documented disseminated M. avium infection. Intracellular growth of M. avium was examined by a CFU assay of cell lysates from M. avium-infected monocytes after 0, 4, and 7 days of culture. Intracellular growth inhibition of M. avium at 7 days after infection was comparable between patients with AIDS and healthy donors for all M. avium strains tested. The effects of the addition of recombinant gamma interferon on M. avium uptake and intracellular growth in monocytes also were studied. Pretreatment of monocytes with gamma interferon prior to infection suppressed monocyte phagocytosis of M. avium. Continuously coculturing of monocytes with gamma interferon after infection augmented killing of M. avium among both patients with AIDS and healthy controls for three of the four strains of M. avium tested. The magnitude of this effect, however, was variable from donor to donor and strain to strain. No significant differences were noted between the growth-inhibiting abilities of gamma-interferon-treated monocytes obtained from healthy volunteers and those obtained from patients with AIDS.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bermudez L. E., Young L. S. Tumor necrosis factor, alone or in combination with IL-2, but not IFN-gamma, is associated with macrophage killing of Mycobacterium avium complex. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):3006–3013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhardwaj N., Nash T. W., Horwitz M. A. Interferon-gamma-activated human monocytes inhibit the intracellular multiplication of Legionella pneumophila. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 15;137(8):2662–2669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaisson R. E., Hopewell P. C. Mycobacteria and AIDS mortality. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Jan;139(1):1–3. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/139.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowle A. J., Cohn D. L., Poche P. Defects in sera from acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) patients and from non-AIDS patients with Mycobacterium avium infection which decrease macrophage resistance to M. avium. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1445–1451. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1445-1451.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowle A. J., Tsang A. Y., Vatter A. E., May M. H. Comparison of 15 laboratory and patient-derived strains of Mycobacterium avium for ability to infect and multiply in cultured human macrophages. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Nov;24(5):812–821. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.5.812-821.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douvas G. S., Berger E. M., Repine J. E., Crowle A. J. Natural mycobacteriostatic activity in human monocyte-derived adherent cells. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Jul;134(1):44–48. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.134.1.44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douvas G. S., Looker D. L., Vatter A. E., Crowle A. J. Gamma interferon activates human macrophages to become tumoricidal and leishmanicidal but enhances replication of macrophage-associated mycobacteria. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):1–8. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.1-8.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esparza I., Männel D., Ruppel A., Falk W., Krammer P. H. Interferon gamma and lymphotoxin or tumor necrosis factor act synergistically to induce macrophage killing of tumor cells and schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni. J Exp Med. 1987 Aug 1;166(2):589–594. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.2.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S., Macher A. M., Longo D. L., Lane H. C., Rook A. H., Masur H., Gelmann E. P. NIH conference. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: epidemiologic, clinical, immunologic, and therapeutic considerations. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Jan;100(1):92–106. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-100-1-92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flesch I. E., Kaufmann S. H. Attempts to characterize the mechanisms involved in mycobacterial growth inhibition by gamma-interferon-activated bone marrow macrophages. Infect Immun. 1988 Jun;56(6):1464–1469. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.6.1464-1469.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flesch I., Kaufmann S. H. Mycobacterial growth inhibition by interferon-gamma-activated bone marrow macrophages and differential susceptibility among strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4408–4413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene J. B., Sidhu G. S., Lewin S., Levine J. F., Masur H., Simberkoff M. S., Nicholas P., Good R. C., Zolla-Pazner S. B., Pollock A. A. Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare: a cause of disseminated life-threatening infection in homosexuals and drug abusers. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Oct;97(4):539–546. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-4-539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins C. C., Gold J. W., Whimbey E., Kiehn T. E., Brannon P., Cammarata R., Brown A. E., Armstrong D. Mycobacterium avium complex infections in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1986 Aug;105(2):184–188. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-105-2-184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. D., Rota T. R., Hirsch M. S. Infection of monocyte/macrophages by human T lymphotropic virus type III. J Clin Invest. 1986 May;77(5):1712–1715. doi: 10.1172/JCI112491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig S., Gendelman H. E., Orenstein J. M., Dal Canto M. C., Pezeshkpour G. H., Yungbluth M., Janotta F., Aksamit A., Martin M. A., Fauci A. S. Detection of AIDS virus in macrophages in brain tissue from AIDS patients with encephalopathy. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1089–1093. doi: 10.1126/science.3016903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau A. S., Read S. E., Williams B. R. Downregulation of interferon alpha but not gamma receptor expression in vivo in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1988 Oct;82(4):1415–1421. doi: 10.1172/JCI113746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macher A. M., Kovacs J. A., Gill V., Roberts G. D., Ames J., Park C. H., Straus S., Lane H. C., Parrillo J. E., Fauci A. S. Bacteremia due to Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Dec;99(6):782–785. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-6-782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Gellene R. A., Libby D. M., Rothermel C. D., Rubin B. Y. Activation of tissue macrophages from AIDS patients: in vitro response of AIDS alveolar macrophages to lymphokines and interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2374–2377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Rubin B. Y., Masur H., Roberts R. B. Impaired production of lymphokines and immune (gamma) interferon in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1984 Apr 5;310(14):883–889. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198404053101404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Scavuzzo D. A., Chaparas S. D., Roberts R. B. T lymphocyte responses to mycobacterial antigen in AIDS patients with disseminated Mycobacterium avium-Mycobacterium intracellulare infection. Chest. 1988 May;93(5):922–925. doi: 10.1378/chest.93.5.922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Scavuzzo D., Jacobs J. L., Kaplan M. H., Libby D. M., Schindler J., Roberts R. B. In vitro and in vivo activation of human mononuclear phagocytes by interferon-gamma. Studies with normal and AIDS monocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 15;138(8):2457–2462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mycobacterioses and the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Joint Position Paper of the American Thoracic Society and the Centers for Disease Control. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Aug;136(2):492–496. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.2.492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawara A., Nathan C. F. A simple method for counting adherent cells: application to cultured human monocytes, macrophages and multinucleated giant cells. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Jan 28;56(2):261–268. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90418-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Murray H. W., Wiebe M. E., Rubin B. Y. Identification of interferon-gamma as the lymphokine that activates human macrophage oxidative metabolism and antimicrobial activity. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):670–689. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson J. K., Cross G. D., Callaway C. S., McDougal J. S. In vitro infection of human monocytes with human T lymphotropic virus type III/lymphadenopathy-associated virus (HTLV-III/LAV). J Immunol. 1986 Jul 1;137(1):323–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passwell J. H., Shor R., Shoham J. The enhancing effect of interferon-beta and -gamma on the killing of Leishmania tropica major in human mononuclear phagocytes in vitro. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 15;136(8):3062–3066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli G., Bottazzi B., Acero R., Bersani L., Rossi V., Introna M., Lazzarin A., Galli M., Mantovani A. Monocyte function in intravenous drug abusers with lymphadenopathy syndrome and in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: selective impairment of chemotaxis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Oct;62(1):136–142. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovic M., Gartner S. Isolation of HIV-1 from monocytes but not T lymphocytes. Lancet. 1987 Oct 17;2(8564):916–916. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91403-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince H. E., Moody D. J., Shubin B. I., Fahey J. L. Defective monocyte function in acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS): evidence from a monocyte-dependent T-cell proliferative system. J Clin Immunol. 1985 Jan;5(1):21–25. doi: 10.1007/BF00915164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich E. A., Toossi Z., Fujiwara H., Hanigosky R., Lederman M. M., Ellner J. J. Defective accessory function of monocytes in human immunodeficiency virus-related disease syndromes. J Lab Clin Med. 1988 Aug;112(2):174–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rook G. A., Steele J., Ainsworth M., Champion B. R. Activation of macrophages to inhibit proliferation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis: comparison of the effects of recombinant gamma-interferon on human monocytes and murine peritoneal macrophages. Immunology. 1986 Nov;59(3):333–338. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothermel C. D., Rubin B. Y., Murray H. W. Gamma-interferon is the factor in lymphokine that activates human macrophages to inhibit intracellular Chlamydia psittaci replication. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2542–2544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salahuddin S. Z., Rose R. M., Groopman J. E., Markham P. D., Gallo R. C. Human T lymphotropic virus type III infection of human alveolar macrophages. Blood. 1986 Jul;68(1):281–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer W. B., Davis C. L., Cohn M. L. Pathogenicity of transparent, opaque, and rough variants of Mycobacterium avium in chickens and mice. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1970 Oct;102(4):499–506. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1970.102.4.499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnittman S., Lane H. C., Witebsky F. G., Gosey L. L., Hoggan M. D., Fauci A. S. Host defense against Mycobacterium-avium complex. J Clin Immunol. 1988 Jul;8(4):234–243. doi: 10.1007/BF00916551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiratsuchi H., Johnson J. L., Ellner J. J. Bidirectional effects of cytokines on the growth of Mycobacterium avium within human monocytes. J Immunol. 1991 May 1;146(9):3165–3170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiratsuchi H., Johnson J. L., Toba H., Ellner J. J. Strain- and donor-related differences in the interaction of Mycobacterium avium with human monocytes and its modulation by interferon-gamma. J Infect Dis. 1990 Oct;162(4):932–938. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.4.932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. D., Ohura K., Masur H., Lane H. C., Fauci A. S., Wahl S. M. Monocyte function in the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Defective chemotaxis. J Clin Invest. 1984 Dec;74(6):2121–2128. doi: 10.1172/JCI111637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires K. E., Murphy W. F., Madoff L. C., Murray H. W. Interferon-gamma and Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare infection. J Infect Dis. 1989 Mar;159(3):599–600. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.3.599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toba H., Crawford J. T., Ellner J. J. Pathogenicity of Mycobacterium avium for human monocytes: absence of macrophage-activating factor activity of gamma interferon. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):239–244. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.239-244.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace J. M., Hannah J. B. Mycobacterium avium complex infection in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. A clinicopathologic study. Chest. 1988 May;93(5):926–932. doi: 10.1378/chest.93.5.926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washburn R. G., Tuazon C. U., Bennett J. E. Phagocytic and fungicidal activity of monocytes from patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1985 Mar;151(3):565–566. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.3.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



