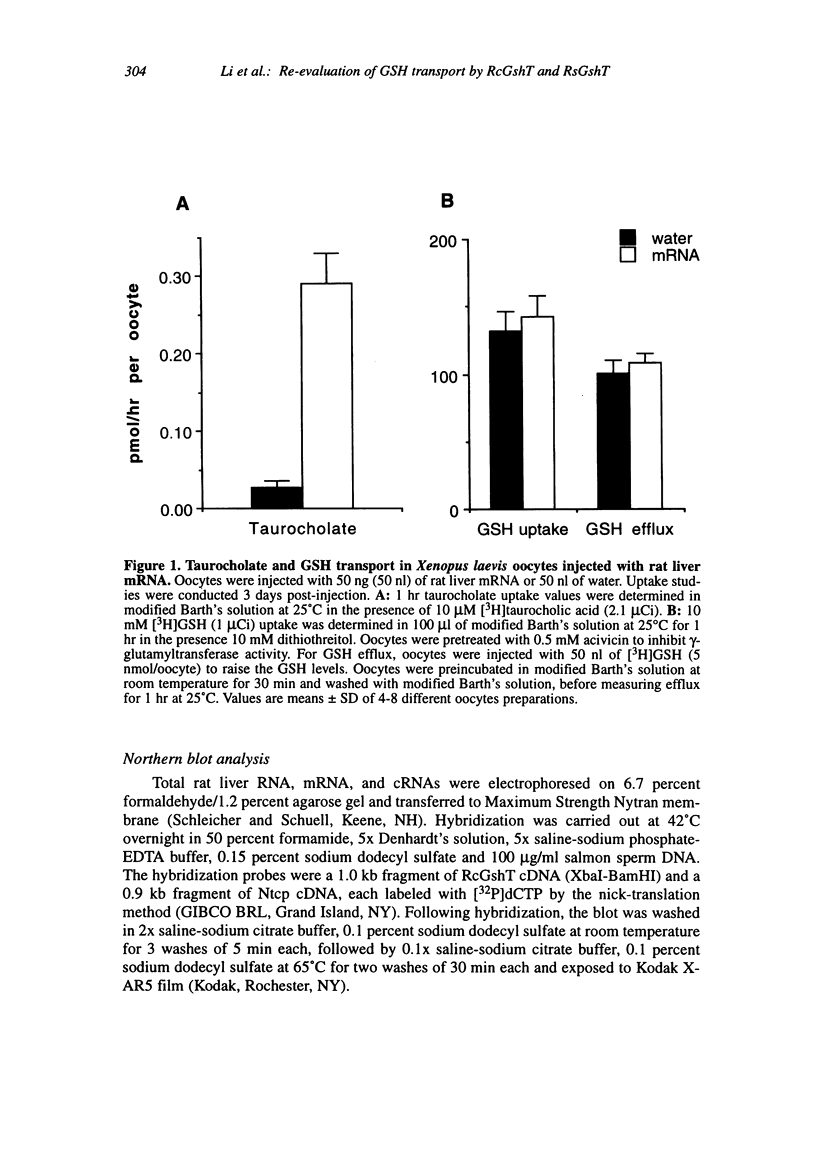
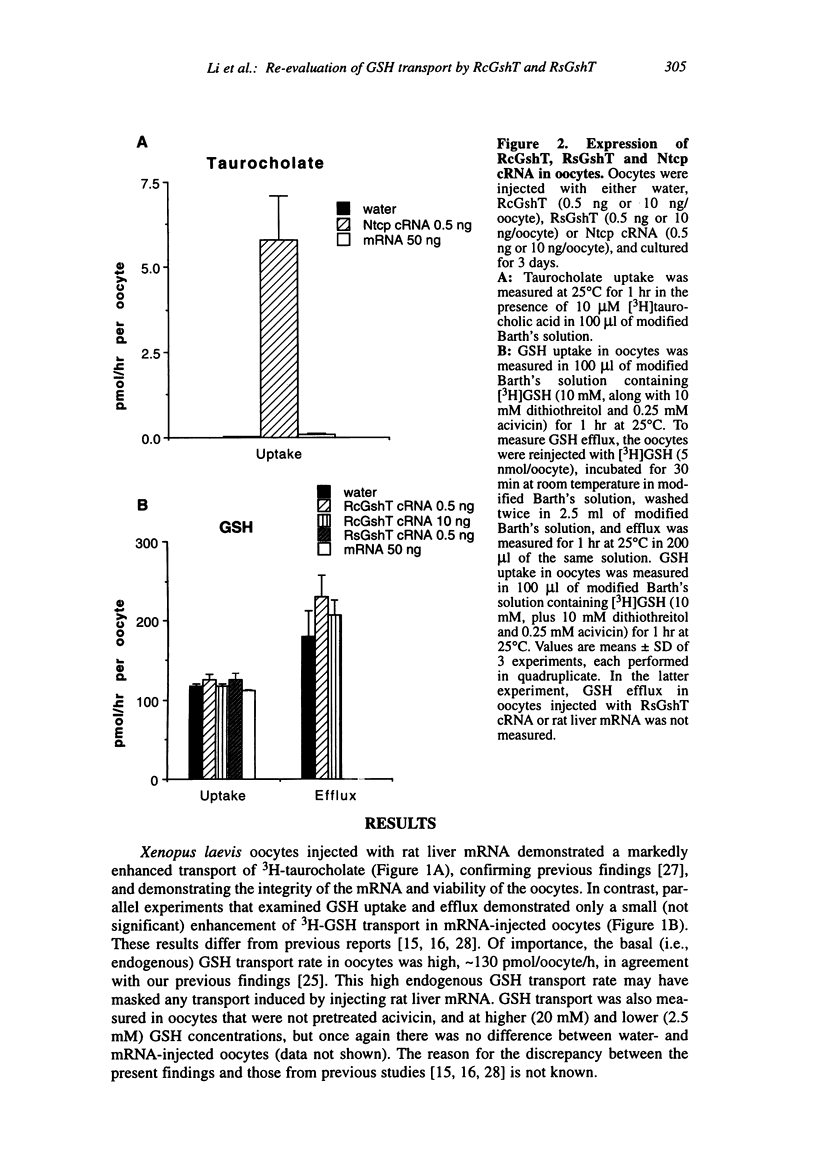
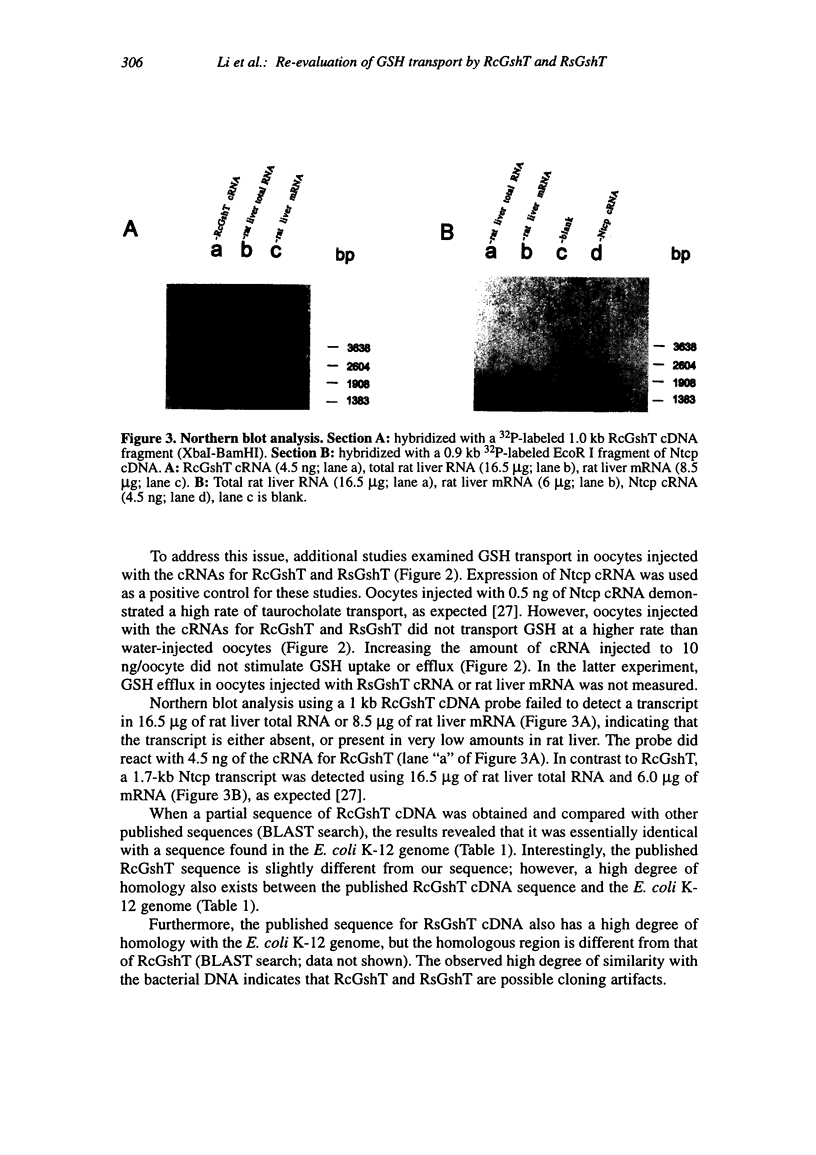
Abstract
Transport systems that mediate glutathione (GSH) efflux from hepatocytes into blood plasma and bile have been characterized extensively in sinusoidal and canalicular membrane vesicles, and recent reports describe two candidate GSH transport proteins: the rat sinusoidal GSH transporter (RsGshT) and rat canalicular GSH transporter (RcGshT). However, studies in our laboratory have been unable to confirm the function of these gene products. Xenopus laevis oocytes injected with either rat liver mRNA, the cRNA for RcGshT or the cRNA for RsGshT did not transport GSH at a higher rate than water-injected oocytes, when measured either as 3H-GSH uptake or efflux, at low or high GSH concentrations, or in the presence or absence of acivicin to inhibit gamma-glutamyltransferase activity. In contrast, transport of 3H-taurocholate was markedly accelerated in oocytes injected with rat liver mRNA or the cRNA for the Na(+)-taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (Ntcp), confirming the integrity of the mRNA and the viability of the oocytes. Northern blot analysis failed to detect an RcGshT transcript in rat liver total RNA or rat liver mRNA. Of significance, the RcGshT and RsGshT cDNA sequences are similar to those found in the Escherichia coli K-12 genome, indicating possible cloning artifacts. Further studies are needed to resolve this discrepancy, and to isolate and characterize hepatic GSH transport proteins.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aw T. Y., Ookhtens M., Kaplowitz N. Inhibition of glutathione efflux from isolated rat hepatocytes by methionine. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9355–9358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aw T. Y., Ookhtens M., Kaplowitz N. Mechanism of inhibition of glutathione efflux by methionine from isolated rat hepatocytes. Am J Physiol. 1986 Sep;251(3 Pt 1):G354–G361. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1986.251.3.G354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballatori N., Dutczak W. J. Identification and characterization of high and low affinity transport systems for reduced glutathione in liver cell canalicular membranes. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 5;269(31):19731–19737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballatori N. Glutathione mercaptides as transport forms of metals. Adv Pharmacol. 1994;27:271–298. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)61036-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballatori N., Jacob R., Boyer J. L. Intrabiliary glutathione hydrolysis. A source of glutamate in bile. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7860–7865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballatori N., Truong A. T. Glutathione as a primary osmotic driving force in hepatic bile formation. Am J Physiol. 1992 Nov;263(5 Pt 1):G617–G624. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.263.5.G617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballatori N., Truong A. T. Multiple canalicular transport mechanisms for glutathione S-conjugates. Transport on both ATP- and voltage-dependent carriers. J Biol Chem. 1995 Feb 24;270(8):3594–3601. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.8.3594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballatori N., Truong A. T. Relation between biliary glutathione excretion and bile acid-independent bile flow. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jan;256(1 Pt 1):G22–G30. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1989.256.1.G22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutczak W. J., Ballatori N. Transport of the glutathione-methylmercury complex across liver canalicular membranes on reduced glutathione carriers. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 1;269(13):9746–9751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Checa J. C., Maddatu T., Ookhtens M., Kaplowitz N. Inhibition of GSH efflux from rat liver by methionine: effects of GSH synthesis in cells and perfused organ. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jun;258(6 Pt 1):G967–G973. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1990.258.6.G967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Checa J. C., García-Ruiz C., Colell A., Yi J. R., Kaplowitz N. Inhibition of rat sinusoidal GSH transporter by thioethers: specificity, sidedness, and kinetics. Am J Physiol. 1996 Jun;270(6 Pt 1):G969–G975. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1996.270.6.G969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Checa J. C., Ookhtens M., Kaplowitz N. Selective induction by phenobarbital of the electrogenic transport of glutathione and organic anions in rat liver canalicular membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):10836–10841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Checa J. C., Yi J. R., Garcia-Ruiz C., Knezic Z., Tahara S. M., Kaplowitz N. Expression of rat liver reduced glutathione transport in Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2324–2328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Ruiz C., Fernández-Checa J. C., Kaplowitz N. Bidirectional mechanism of plasma membrane transport of reduced glutathione in intact rat hepatocytes and membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22256–22264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldin A. L. Maintenance of Xenopus laevis and oocyte injection. Methods Enzymol. 1992;207:266–279. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)07017-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbuch B., Stieger B., Foguet M., Lübbert H., Meier P. J. Functional expression cloning and characterization of the hepatocyte Na+/bile acid cotransport system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10629–10633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinchman C. A., Ballatori N. Glutathione conjugation and conversion to mercapturic acids can occur as an intrahepatic process. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1994 Apr;41(4):387–409. doi: 10.1080/15287399409531852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplowitz N., Aw T. Y., Ookhtens M. The regulation of hepatic glutathione. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1985;25:715–744. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.25.040185.003435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplowitz N., Eberle D. E., Petrini J., Touloukian J., Corvasce M. C., Kuhlenkamp J. Factors influencing the efflux of hepatic glutathione into bile in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Jan;224(1):141–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplowitz N., Fernández-Checa J. C., Kannan R., Garcia-Ruiz C., Ookhtens M., Yi J. R. GSH transporters: molecular characterization and role in GSH homeostasis. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1996 May;377(5):267–273. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1996.377.5.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauterburg B. H., Adams J. D., Mitchell J. R. Hepatic glutathione homeostasis in the rat: efflux accounts for glutathione turnover. Hepatology. 1984 Jul-Aug;4(4):586–590. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840040402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. K., Li L., Ballatori N. Hepatic glutathione and glutathione S-conjugate transport mechanisms. Yale J Biol Med. 1997 Jul-Aug;70(4):287–300. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu S. C., Garcia-Ruiz C., Kuhlenkamp J., Ookhtens M., Salas-Prato M., Kaplowitz N. Hormonal regulation of glutathione efflux. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16088–16095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu S. C., Kuhlenkamp J., Wu H., Sun W. M., Stone L., Kaplowitz N. Progressive defect in biliary GSH secretion in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Am J Physiol. 1997 Feb;272(2 Pt 1):G374–G382. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1997.272.2.G374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ookhtens M., Lyon I., Fernandez-Checa J., Kaplowitz N. Inhibition of glutathione efflux in the perfused rat liver and isolated hepatocytes by organic anions and bilirubin. Kinetics, sidedness, and molecular forms. J Clin Invest. 1988 Aug;82(2):608–616. doi: 10.1172/JCI113639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snutch T. P., Mandel G. Tissue RNA as source of ion channels and receptors. Methods Enzymol. 1992;207:297–309. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)07019-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yi J. R., Lu S., Fernandez-Checa J., Kaplowitz N. Expression cloning of a rat hepatic reduced glutathione transporter with canalicular characteristics. J Clin Invest. 1994 Apr;93(4):1841–1845. doi: 10.1172/JCI117170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yi J. R., Lu S., Fernández-Checa J., Kaplowitz N. Expression cloning of the cDNA for a polypeptide associated with rat hepatic sinusoidal reduced glutathione transport: characteristics and comparison with the canalicular transporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 28;92(5):1495–1499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.5.1495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]