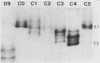
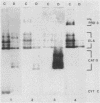
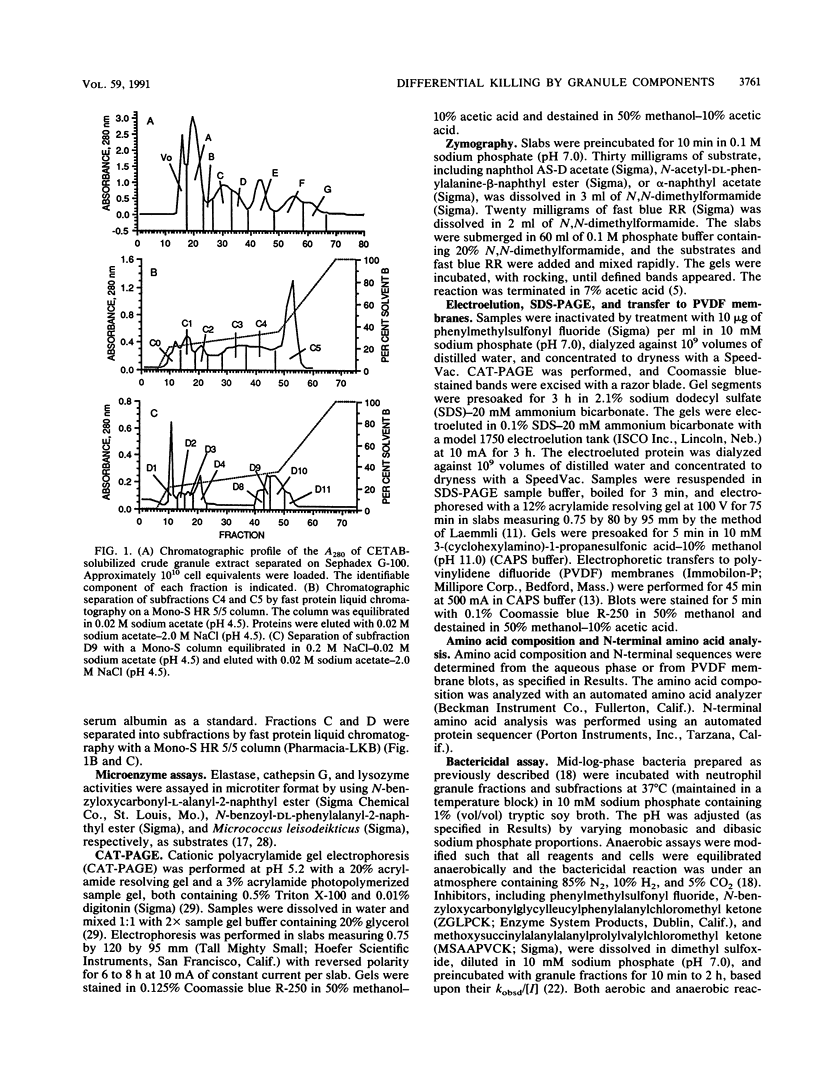
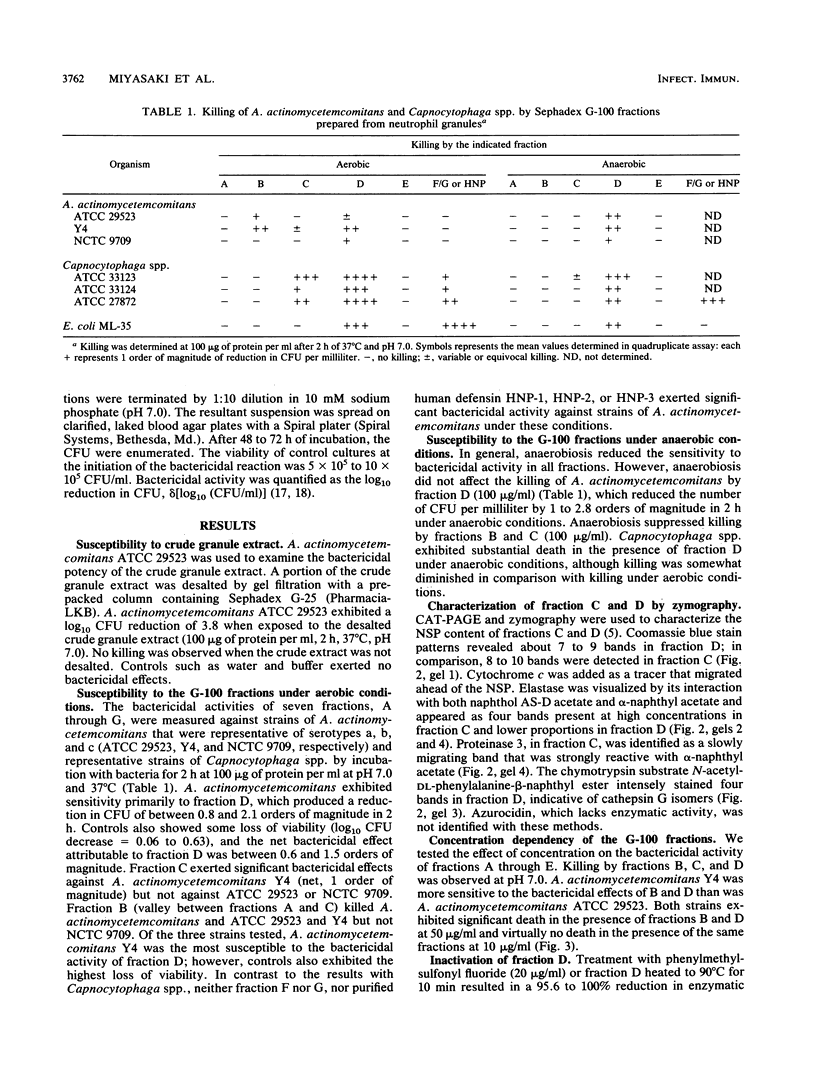
Abstract
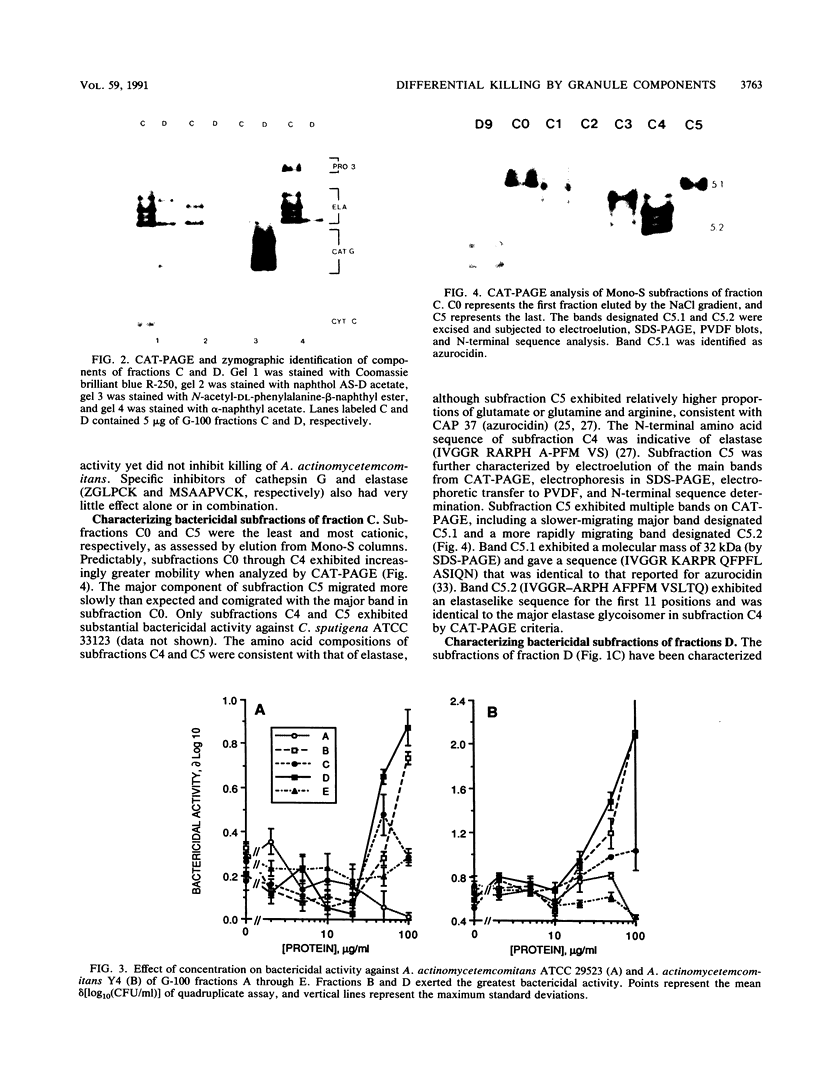
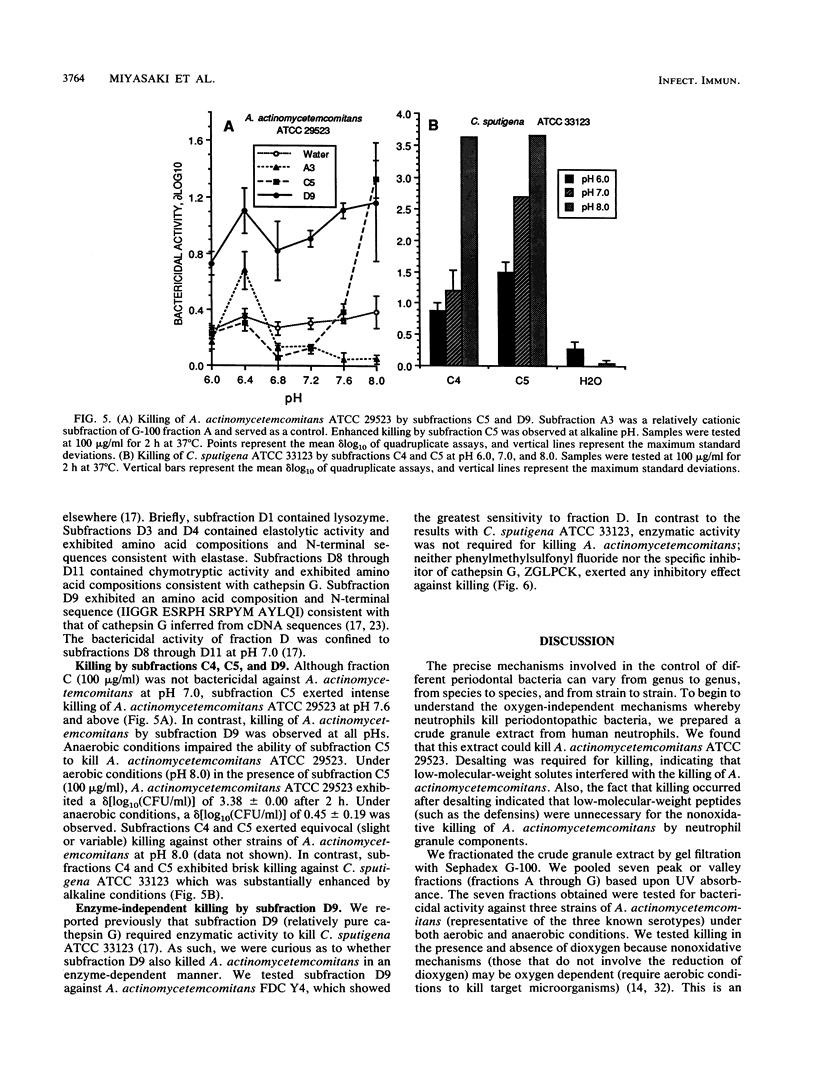
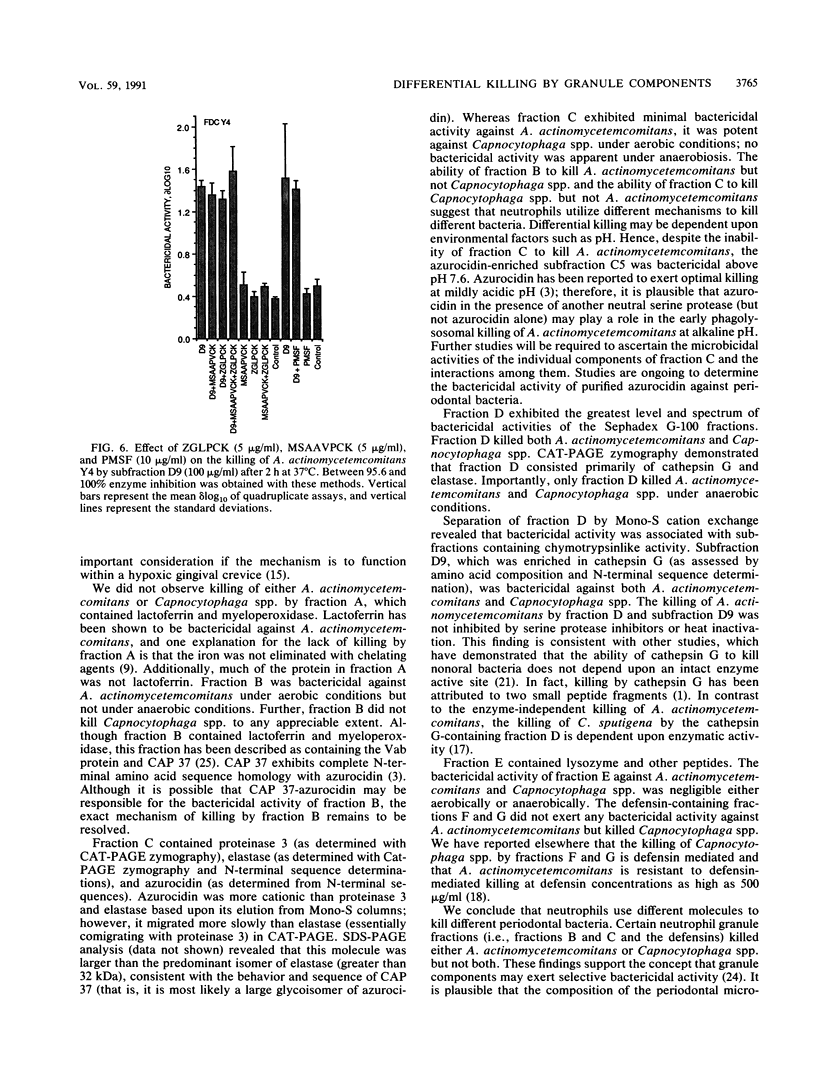
The purpose of this study was to determine whether granule fractions of human neutrophils differentially kill Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans and Capnocytophaga spp. Granule extracts were subjected to gel filtration, and seven fractions (designated A through G) were obtained. Under aerobic conditions at pH 7.0, representative strains of A. actinomycetemcomitans were killed by fraction D and variably by fraction B. In contrast, the Capnocytophaga spp. were killed by fractions C, D, F, and G. Fractions A (containing lactoferrin and myeloperoxidase) and E (containing lysozyme) exerted little bactericidal activity under these conditions. Anaerobiosis had little effect on the bactericidal activity of fractions D and F but inhibited that of fractions B and C. Electrophoresis, zymography, determination of amino acid composition, and N-terminal sequence analysis revealed that fraction C contained elastase, proteinase 3, and azurocidin. Fraction D contained lysozyme, elastase, and cathepsin G. Subfractions of C and D containing elastase (subfraction C4), a mixture of elastase and azurocidin (subfraction C5), and cathepsin G (subfraction D9) were found to be bactericidal. The bactericidal effects of fraction D and subfraction D9 against A. actinomycetemcomitans was not inhibited by heat inactivation, phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, or N-benzyloxycarbonylglycylleucylphenylalanylchloromethyl ketone. We conclude that (i) A. actinomycetemcomitans and Capnocytophaga spp. were sensitive to the bactericidal effects of different neutrophil granule components, (ii) both were sensitive to the bactericidal effects of neutral serine proteases, and (iii) the killing of A. actinomycetemcomitans by cathepsin G-containing fractions was independent of oxygen and neutral serine protease activity.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bangalore N., Travis J., Onunka V. C., Pohl J., Shafer W. M. Identification of the primary antimicrobial domains in human neutrophil cathepsin G. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13584–13588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campanelli D., Detmers P. A., Nathan C. F., Gabay J. E. Azurocidin and a homologous serine protease from neutrophils. Differential antimicrobial and proteolytic properties. J Clin Invest. 1990 Mar;85(3):904–915. doi: 10.1172/JCI114518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charon J. A., Mergenhagen S. E., Gallin J. I. Gingivitis and oral ulceration in patients with neutrophil dysfunction. J Oral Pathol. 1985 Feb;14(2):150–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.1985.tb00478.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewald B., Rindler-Ludwig R., Bretz U., Baggiolini M. Subcellular localization and heterogeneity of neutral proteases in neutrophilic polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1975 Apr 1;141(4):709–723. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.4.709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabig T. G., Bearman S. I., Babior B. M. Effects of oxygen tension and pH on the respiratory burst of human neutrophils. Blood. 1979 Jun;53(6):1133–1139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganz T., Metcalf J. A., Gallin J. I., Boxer L. A., Lehrer R. I. Microbicidal/cytotoxic proteins of neutrophils are deficient in two disorders: Chediak-Higashi syndrome and "specific" granule deficiency. J Clin Invest. 1988 Aug;82(2):552–556. doi: 10.1172/JCI113631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganz T., Selsted M. E., Szklarek D., Harwig S. S., Daher K., Bainton D. F., Lehrer R. I. Defensins. Natural peptide antibiotics of human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1427–1435. doi: 10.1172/JCI112120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalmar J. R., Arnold R. R. Killing of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans by human lactoferrin. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2552–2557. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2552-2557.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao R. C., Wehner N. G., Skubitz K. M., Gray B. H., Hoidal J. R. Proteinase 3. A distinct human polymorphonuclear leukocyte proteinase that produces emphysema in hamsters. J Clin Invest. 1988 Dec;82(6):1963–1973. doi: 10.1172/JCI113816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavine W. S., Maderazo E. G., Stolman J., Ward P. A., Cogen R. B., Greenblatt I., Robertson P. B. Impaired neutrophil chemotaxis in patients with juvenile and rapidly progressing periodontitis. J Periodontal Res. 1979 Jan;14(1):10–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1979.tb00213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Ganz T., Szklarek D., Selsted M. E. Modulation of the in vitro candidacidal activity of human neutrophil defensins by target cell metabolism and divalent cations. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jun;81(6):1829–1835. doi: 10.1172/JCI113527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesche W. J., Gusberti F., Mettraux G., Higgins T., Syed S. Relationship between oxygen tension and subgingival bacterial flora in untreated human periodontal pockets. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):659–667. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.659-667.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesche W. J., Robinson J. P., Flynn M., Hudson J. L., Duque R. E. Reduced oxidative function in gingival crevicular neutrophils in periodontal disease. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):156–160. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.156-160.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyasaki K. T., Bodeau A. L., Ganz T., Selsted M. E., Lehrer R. I. In vitro sensitivity of oral, gram-negative, facultative bacteria to the bactericidal activity of human neutrophil defensins. Infect Immun. 1990 Dec;58(12):3934–3940. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.12.3934-3940.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyasaki K. T., Bodeau A. L. In vitro killing of oral Capnocytophaga by granule fractions of human neutrophils is associated with cathepsin G activity. J Clin Invest. 1991 May;87(5):1585–1593. doi: 10.1172/JCI115172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyasaki K. T., Wilson M. E., Brunetti A. J., Genco R. J. Oxidative and nonoxidative killing of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans by human neutrophils. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):154–160. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.154-160.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niles J. L., McCluskey R. T., Ahmad M. F., Arnaout M. A. Wegener's granulomatosis autoantigen is a novel neutrophil serine proteinase. Blood. 1989 Nov 1;74(6):1888–1893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvesen G., Farley D., Shuman J., Przybyla A., Reilly C., Travis J. Molecular cloning of human cathepsin G: structural similarity to mast cell and cytotoxic T lymphocyte proteinases. Biochemistry. 1987 Apr 21;26(8):2289–2293. doi: 10.1021/bi00382a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafer W. M., Engle S. A., Martin L. E., Spitznagel J. K. Killing of Proteus mirabilis by polymorphonuclear leukocyte granule proteins: evidence for species specificity by antimicrobial proteins. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):51–53. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.51-53.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafer W. M., Martin L. E., Spitznagel J. K. Cationic antimicrobial proteins isolated from human neutrophil granulocytes in the presence of diisopropyl fluorophosphate. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):29–35. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.29-35.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shurin S. B., Socransky S. S., Sweeney E., Stossel T. P. A neutrophil disorder induced by capnocytophaga, a dental micro-organism. N Engl J Med. 1979 Oct 18;301(16):849–854. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197910183011601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha S., Watorek W., Karr S., Giles J., Bode W., Travis J. Primary structure of human neutrophil elastase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2228–2232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starkey P. M., Barrett A. J. Neutral proteinases of human spleen. Purification and criteria for homogeneity of elastase and cathepsin G. Biochem J. 1976 May 1;155(2):255–263. doi: 10.1042/bj1550255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweetman F., Ornstein L. Electrophoresis of elastase-like esterases from human neutrophils. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 May;22(5):327–339. doi: 10.1177/22.5.327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson H. L., Wilton J. M. Effects of anaerobiosis and aerobiosis on interactions of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes with the dental plaque bacteria Streptococcus mutans, Capnocytophaga ochracea, and Bacteroides gingivalis. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):932–940. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.932-940.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke T. E., Wilson-Burrows C., Offenbacher S., Henson P. Association of an abnormality of neutrophil chemotaxis in human periodontal disease with a cell surface protein. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2262–2267. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2262-2267.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton E. The preparation, properties and action on Staphylococcus aureus of purified fractions from the cationic proteins of rabbit polymorphonuclear leucocytes. Br J Exp Pathol. 1978 Aug;59(4):416–431. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilde C. G., Snable J. L., Griffith J. E., Scott R. W. Characterization of two azurphil granule proteases with active-site homology to neutrophil elastase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):2038–2041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambon J. J. Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans in human periodontal disease. J Clin Periodontol. 1985 Jan;12(1):1–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.1985.tb01348.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]