Abstract
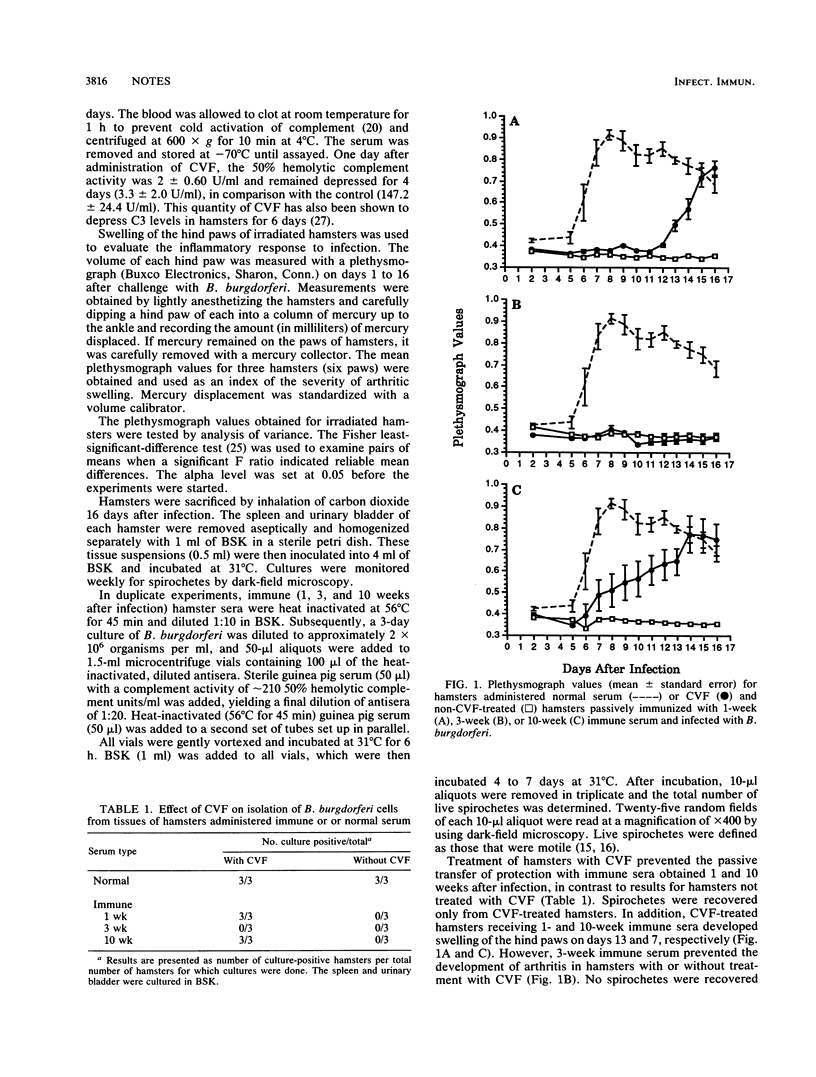
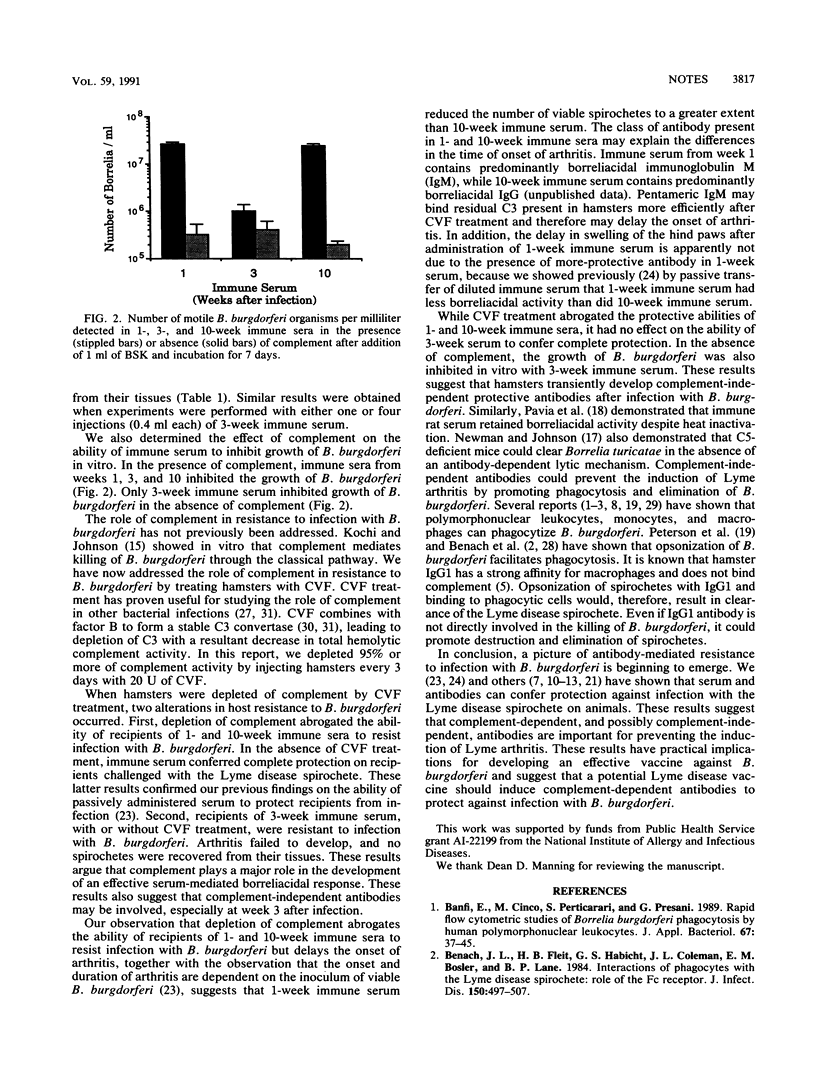
When irradiated hamsters are passively immunized with immune serum before challenge with Borrelia burgdorferi, they are completely protected from arthritis and infection. The complement dependency of this protection was addressed by treating hamsters with cobra venom factor. Depletion of complement abrogated the ability of immune serum obtained 1 and 10 weeks after infection to confer complete protection. By contrast, depletion of complement had no effect on the ability of 3-week immune serum to confer protection. These results suggest that complement-dependent, and possibly complement-independent, antibodies are important for preventing the induction of Lyme arthritis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banfi E., Cinco M., Perticarari S., Presani G. Rapid flow cytometric studies of Borrelia burgdorferi phagocytosis by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Appl Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;67(1):37–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1989.tb04952.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benach J. L., Fleit H. B., Habicht G. S., Coleman J. L., Bosler E. M., Lane B. P. Interactions of phagocytes with the Lyme disease spirochete: role of the Fc receptor. J Infect Dis. 1984 Oct;150(4):497–507. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.4.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benach J. L., Habicht G. S., Gocinski B. L., Coleman J. L. Phagocytic cell responses to in vivo and in vitro exposure to the Lyme disease spirochete. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):599–605. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callister S. M., Case K. L., Agger W. A., Schell R. F., Johnson R. C., Ellingson J. L. Effects of bovine serum albumin on the ability of Barbour-Stoenner-Kelly medium to detect Borrelia burgdorferi. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Feb;28(2):363–365. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.2.363-365.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coe J., Peel L., Smith R. F. The immune response in the hamster. V. Biologic activities of 7S-gamma-1 and 7S-gamma-2 globulins. J Immunol. 1971 Jul;107(1):76–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duray P. H. The surgical pathology of human Lyme disease. An enlarging picture. Am J Surg Pathol. 1987;11 (Suppl 1):47–60. doi: 10.1097/00000478-198700111-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fikrig E., Barthold S. W., Kantor F. S., Flavell R. A. Protection of mice against the Lyme disease agent by immunizing with recombinant OspA. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):553–556. doi: 10.1126/science.2237407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgilis K., Steere A. C., Klempner M. S. Infectivity of Borrelia burgdorferi correlates with resistance to elimination by phagocytic cells. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jan;163(1):150–155. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.1.150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hejka A., Schmitz J. L., England D. M., Callister S. M., Schell R. F. Histopathology of Lyme arthritis in LSH hamsters. Am J Pathol. 1989 May;134(5):1113–1123. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Kodner C. L., Russell M. E. Vaccination of hamsters against experimental infection with Borrelia burgdorferi. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1986 Dec;263(1-2):45–48. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(86)80101-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Kodner C., Russell M. Active immunization of hamsters against experimental infection with Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):897–898. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.897-898.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Kodner C., Russell M., Duray P. H. Experimental infection of the hamster with Borrelia burgdorferi. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:258–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31859.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Kodner C., Russell M. Passive immunization of hamsters against experimental infection with the Lyme disease spirochete. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):713–714. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.713-714.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Marek N., Kodner C. Infection of Syrian hamsters with Lyme disease spirochetes. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Dec;20(6):1099–1101. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.6.1099-1101.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochi S. K., Johnson R. C. Role of immunoglobulin G in killing of Borrelia burgdorferi by the classical complement pathway. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):314–321. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.314-321.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovrich S. D., Callister S. M., Schmitz J. L., Alder J. D., Schell R. F. Borreliacidal activity of sera from hamsters infected with the Lyme disease spirochete. Infect Immun. 1991 Aug;59(8):2522–2528. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.8.2522-2528.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman K., Jr, Johnson R. C. In vivo evidence that an intact lytic complement pathway is not essential for successful removal of circulating Borrelia turicatae from mouse blood. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):465–469. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.465-469.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavia C. S., Kissel V., Bittker S., Cabello F., Levine S. Antiborrelial activity of serum from rats injected with the Lyme disease spirochete. J Infect Dis. 1991 Mar;163(3):656–659. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.3.656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Clawson C. C., Lee D. A., Garlich D. J., Quie P. G., Johnson R. C. Human phagocyte interactions with the Lyme disease spirochete. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):608–611. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.608-611.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaible U. E., Kramer M. D., Eichmann K., Modolell M., Museteanu C., Simon M. M. Monoclonal antibodies specific for the outer surface protein A (OspA) of Borrelia burgdorferi prevent Lyme borreliosis in severe combined immunodeficiency (scid) mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3768–3772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz J. L., Schell R. F., Hejka A. G., England D. M. Passive immunization prevents induction of Lyme arthritis in LSH hamsters. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):144–148. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.144-148.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz J. L., Schell R. F., Hejka A., England D. M., Konick L. Induction of lyme arthritis in LSH hamsters. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2336–2342. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2336-2342.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz J. L., Schell R. F., Lovrich S. D., Callister S. M., Coe J. E. Characterization of the protective antibody response to Borrelia burgdorferi in experimentally infected LSH hamsters. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):1916–1921. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.1916-1921.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Grodzicki R. L., Kornblatt A. N., Craft J. E., Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W., Schmid G. P., Johnson E., Malawista S. E. The spirochetal etiology of Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 31;308(13):733–740. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303313081301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner B. M., Schell R. F., Harris O. N. The effect of C3 depletion on resistance of hamsters to infection with the yaws spirochete. Sex Transm Dis. 1986 Oct-Dec;13(4):245–250. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198610000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szczepanski A., Benach J. L. Lyme borreliosis: host responses to Borrelia burgdorferi. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Mar;55(1):21–34. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.1.21-34.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkelstein J. A. Complement and the host's defense against the pneumococcus. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1984;11(3):187–208. doi: 10.3109/10408418409105903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



