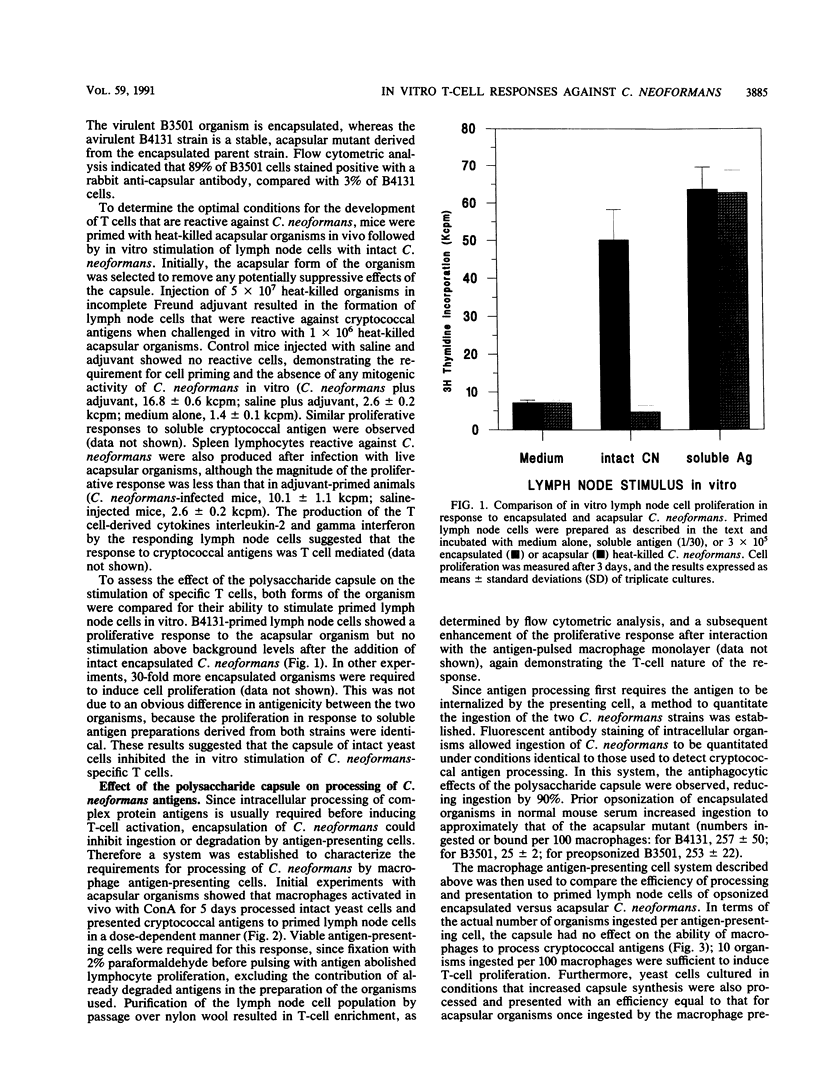
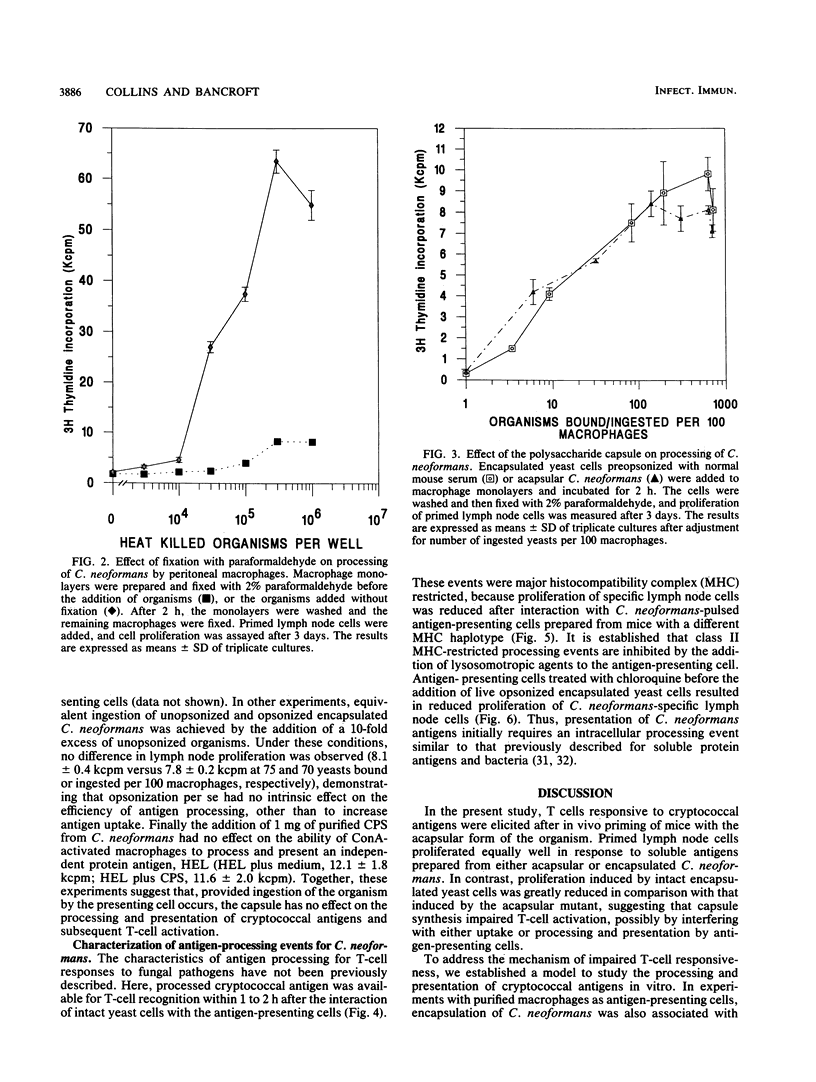
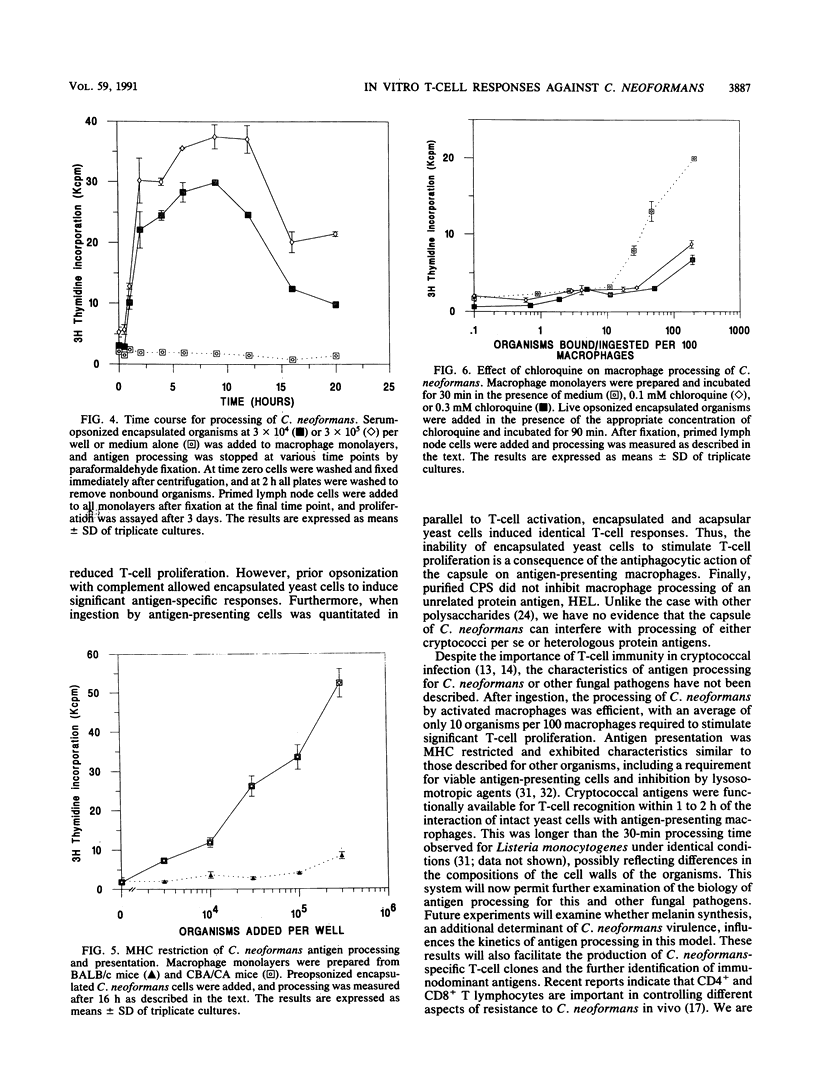
Abstract
The encapsulated yeast Cryptococcus neoformans is a significant cause of opportunistic infection in patients with impaired cell-mediated immunity. The major virulence determinant of the organism is an antiphagocytic polysaccharide capsule synthesized after entry into the host. Using both an encapsulated virulent strain and an acapsular avirulent mutant, we have demonstrated the reduced ability of the encapsulated strain to stimulate specific T-cell responses in vitro. This reduction was mediated by the antiphagocytic action of the capsule rather than by direct inhibition of antigen processing and presentation, since prior opsonization with complement enhanced the ingestion of encapsulated yeast cells by purified antigen-presenting cells and allowed significant T-cell activation. Once ingestion had occurred, cryptococci were efficiently processed by activated macrophages via a chloroquine-sensitive pathway. Cryptococcal antigens were available for T-cell recognition within 1 to 2 h of interaction with macrophages and presented in a major histocompatibility complex-restricted manner. Our results suggest that the antiphagocytic action of the polysaccharide capsule is an important determinant for the development of T-cell immunity to C. neoformans.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson J., Grönvik K. O., Larsson E. L., Coutinho A. Studies on T lymphocyte activation. I. Requirements for the mitogen-dependent production of T cell growth factors. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Aug;9(8):581–587. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolaños B., Mitchell T. G. Phagocytosis of Cryptococcus neoformans by rat alveolar macrophages. J Med Vet Mycol. 1989;27(4):203–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breen J. F., Lee I. C., Vogel F. R., Friedman H. Cryptococcal capsular polysaccharide-induced modulation of murine immune responses. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):47–51. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.47-51.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cauley L. K., Murphy J. W. Response of congenitally athymic (nude) and phenotypically normal mice to Cryptococcus neoformans infection. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):644–651. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.644-651.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuck S. L., Sande M. A. Infections with Cryptococcus neoformans in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1989 Sep 21;321(12):794–799. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198909213211205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond R. D., May J. E., Kane M. A., Frank M. M., Bennett J. E. The role of the classical and alternate complement pathways in host defenses against Cryptococcus neoformans infection. J Immunol. 1974 Jun;112(6):2260–2270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dismukes W. E. Cryptococcal meningitis in patients with AIDS. J Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;157(4):624–628. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.4.624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dykstra M. A., Friedman L., Murphy J. W. Capsule size of Cryptococcus neoformans: control and relationship to virulence. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):129–135. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.129-135.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farhi F., Bulmer G. S., Tacker J. R. Cryptococcus neoformans IV. The Not-So-Encapsulated Yeast. Infect Immun. 1970 Jun;1(6):526–531. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.6.526-531.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidel P. L., Jr, Murphy J. W. Characterization of a cell population which amplifies the anticryptococcal delayed-type hypersensitivity response. Infect Immun. 1990 Feb;58(2):393–398. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.2.393-398.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromtling R. A., Shadomy H. J., Jacobson E. S. Decreased virulence in stable, acapsular mutants of cryptococcus neoformans. Mycopathologia. 1982 Jul 23;79(1):23–29. doi: 10.1007/BF00636177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman J. S., Kaufman L., Koenig M. G. Diagnosis of cryptococcal meningitis. Value of immunologic detection of cryptococcal antigen. N Engl J Med. 1971 Aug 19;285(8):434–436. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197108192850804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybill J. R., Alford R. H. Cell-mediated immunity in Cryptococcosis. Cell Immunol. 1974 Oct;14(1):12–21. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(74)90164-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybill J. R., Drutz D. J. Host defense in cryptococcosis. II. Cryptococcosis in the nude mouse. Cell Immunol. 1978 Oct;40(2):263–274. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90334-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin F. M., Jr Roles of macrophage Fc and C3b receptors in phagocytosis of immunologically coated Cryptococcus neoformans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3853–3857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay R. J., Reiss E. Delayed-type hypersensitivity responses in infected mice elicited by cytoplasmic fractions of Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):72–79. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.72-79.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. O., Harmsen A. G. Intrapulmonary growth and dissemination of an avirulent strain of Cryptococcus neoformans in mice depleted of CD4+ or CD8+ T cells. J Exp Med. 1991 Mar 1;173(3):755–758. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.3.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Cazin J. Nonencapsulated Variant of Cryptococcus neoformans I. Virulence Studies and Characterization of Soluble Polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1971 Feb;3(2):287–294. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.2.287-294.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Follette J. L. Opsonization of encapsulated Cryptococcus neoformans by specific anticapsular antibody. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):978–984. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.978-984.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Gulley W. F., Cazin J., Jr Immune response to Cryptococcus neoformans soluble polysaccharide: immunological unresponsiveness. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):701–707. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.701-707.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Mastroianni R. P. Inhibition of phagocytosis by cryptococcal polysaccharide: dissociation of the attachment and ingestion phases of phagocytosis. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):62–67. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.62-67.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Pfrommer G. S. Activation of the complement system by Cryptococcus neoformans leads to binding of iC3b to the yeast. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):1–5. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.1-5.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitz S. M., DiBenedetto D. J. Paradoxical role of capsule in murine bronchoalveolar macrophage-mediated killing of Cryptococcus neoformans. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 15;142(2):659–665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leyva-Cobian F., Unanue E. R. Intracellular interference with antigen presentation. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1445–1450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim T. S., Murphy J. W. Transfer of immunity to cryptococcosis by T-enriched splenic lymphocytes from Cryptococcus neoformans-sensitized mice. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):5–11. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.5-11.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell T. G., Friedman L. In vitro phagocytosis and intracellular fate of variously encapsulated strains of Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1972 Apr;5(4):491–498. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.4.491-498.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mody C. H., Lipscomb M. F., Street N. E., Toews G. B. Depletion of CD4+ (L3T4+) lymphocytes in vivo impairs murine host defense to Cryptococcus neoformans. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 15;144(4):1472–1477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. W., Cozad G. C. Immunological unresponsiveness induced by cryptococcal capsular polysaccharide assayed by the hemolytic plaque technique. Infect Immun. 1972 Jun;5(6):896–901. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.6.896-901.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. W. Influence of cryptococcal antigens on cell-mediated immunity. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10 (Suppl 2):S432–S435. doi: 10.1093/cid/10.supplement_2.s432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Cerottini J. C. Antigen presentation. FASEB J. 1989 Nov;3(13):2496–2502. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.13.2572499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler H. K., Unanue E. R. Decrease in macrophage antigen catabolism caused by ammonia and chloroquine is associated with inhibition of antigen presentation to T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):175–178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler K., Unanue E. R. Identification of a macrophage antigen-processing event required for I-region-restricted antigen presentation to T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):1869–1875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



