Abstract
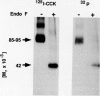
Affinity labeling has been a powerful tool for the biochemical characterization of sparse molecules which bind to a ligand probe in a specific, high-affinity manner. The rat pancreatic acinar cell receptor for cholecystokinin (CCK), the major physiologic hormonal stimulant of pancreatic exocrine secretion, has been the target of such investigation. Of interest, affinity-labeling studies have identified two distinct plasma membrane glycoproteins as candidates to represent this receptor. The initial candidate, which was identified using 125I-Bolton Hunter-labeled CCK-33 as probe, migrates on a SDS-polyacrylamide gel as a broad band in the M(r) = 80,000 range. Subsequently, using shorter probes in which the site of covalent attachment was closer to the receptor-binding domain of the probe, a band of M(r) = 85,000-95,000 was specifically labeled. Deglycosylation and protease-peptide mapping demonstrated that these bands represent distinct molecules. Using "intrinsic" probes of the receptor, in which a photolabile residue was sited within the pharmacophoric domain of the ligand, attention was focused on the latter candidate as representing the binding protein. Insight into the relationship between these proteins as they reside in the plasma membrane was contributed by labeling with a "topographical mapping" probe, which incorporates a flexible spacer of variable length between a CCK-like ligand and a photolabile residue. This procedure confirmed that these two minor membrane proteins are spatially associated with each other.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amer M. S. Studies with cholecystokinin. II. Cholecystokinetic potency of porcine gastrins I and II and related peptides in three systems. Endocrinology. 1969 May;84(5):1277–1281. doi: 10.1210/endo-84-5-1277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beglinger C., Solomon T. E., Gyr K., Moroder L., Wünsch E. Exocrine pancreatic secretion in response to a new CCK-analog, CCK33 and caerulein in dogs. Regul Pept. 1984 Jul;8(4):291–296. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(84)90038-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freidinger R. M. Cholecystokinin and gastrin antagonists. Med Res Rev. 1989 Jul-Sep;9(3):271–290. doi: 10.1002/med.2610090303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klueppelberg U. G., Gaisano H. Y., Powers S. P., Miller L. J. Use of a nitrotryptophan-containing peptide for photoaffinity labeling the pancreatic cholecystokinin receptor. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 18;28(8):3463–3468. doi: 10.1021/bi00434a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klueppelberg U. G., Gates L. K., Gorelick F. S., Miller L. J. Agonist-regulated phosphorylation of the pancreatic cholecystokinin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2403–2408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klueppelberg U. G., Powers S. P., Miller L. J. Protease peptide mapping of affinity-labeled rat pancreatic cholecystokinin-binding proteins. Biochemistry. 1989 Aug 22;28(17):7124–7129. doi: 10.1021/bi00443a051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klueppelberg U. G., Powers S. P., Miller L. J. The efficiency of covalent labeling of the pancreatic cholecystokinin receptor using a battery of crosslinkable and photolabile probes. 1990-1991 WinterReceptor. 1(1-2):1–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopin A. S., Lee Y. M., McBride E. W., Miller L. J., Lu M., Lin H. Y., Kolakowski L. F., Jr, Beinborn M. Expression cloning and characterization of the canine parietal cell gastrin receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3605–3609. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. J., Rosenzweig S. A., Jamieson J. D. Preparation and characterization of a probe for the cholecystokinin octapeptide receptor, N alpha (125I-desaminotyrosyl)CCK-8, and its interactions with pancreatic acini. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12417–12423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ondetti M. A., Rubin B., Engel S. L., Pluscec J., Sheehan J. T. Cholecystokinin-pancreozymin: recent developments. Am J Dig Dis. 1970 Feb;15(2):149–156. doi: 10.1007/BF02235646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. K., Hadac E. M., Miller L. J. Preparation and characterization of a new cholecystokinin receptor probe that can be oxidatively radioiodinated. Gastroenterology. 1986 Jun;90(6):1985–1991. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90271-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. K., Miller L. J. Affinity labeling of a novel cholecystokinin-binding protein in rat pancreatic plasmalemma using new short probes for the receptor. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):869–876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. K., Miller L. J., Hadac E. M., Powers S. P. Analysis of the carbohydrate composition of the pancreatic plasmalemmal glycoprotein affinity labeled by short probes for the cholecystokinin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13850–13856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. K., Miller L. J., Powers S. P., Hadac E. M. Biochemical characterization of the pancreatic cholecystokinin receptor using monofunctional photoactivatable probes. Pancreas. 1987;2(1):79–84. doi: 10.1097/00006676-198701000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. K., Powers S. P., Hadac E. M., Gaisano H., Miller L. J. Establishment of a new short, protease-resistant, affinity labeling reagent for the cholecystokinin receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Aug 31;147(1):346–353. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80128-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilch P. F., Czech M. P. Interaction of cross-linking agents with the insulin effector system of isolated fat cells. Covalent linkage of 125I-insulin to a plasma membrane receptor protein of 140,000 daltons. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3375–3381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers S. P., Foo I., Pinon D., Klueppelberg U. G., Hedstrom J. F., Miller L. J. Use of photoaffinity probes containing poly(ethylene glycol) spacers for topographical mapping of the cholecystokinin receptor complex. Biochemistry. 1991 Jan 22;30(3):676–682. doi: 10.1021/bi00217a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers S. P., Fourmy D., Gaisano H., Miller L. J. Intrinsic photoaffinity labeling probes for cholecystokinin (CCK)-gastrin family receptors. D-Tyr-Gly-[Nle28,31,pNO2-Phe33)CCK-26-33). J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5295–5300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehfeld J. F. Immunochemical studies on cholecystokinin. I. Development of sequence-specific radioimmunoassays for porcine triacontatriapeptide cholecystokinin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 10;253(11):4016–4021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenzweig S. A., Madison L. D., Jamieson J. D. Analysis of cholecystokinin-binding proteins using endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase F. J Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;99(3):1110–1116. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.3.1110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenzweig S. A., Miller L. J., Jamieson J. D. Identification and localization of cholecystokinin-binding sites on rat pancreatic plasma membranes and acinar cells: a biochemical and autoradiographic study. J Cell Biol. 1983 May;96(5):1288–1297. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.5.1288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto C., Goldfine I. D., Williams J. A. Pancreatic CCK receptors: characterization of covalently labeled subunits. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jan 30;118(2):623–628. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91348-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wank S. A., Harkins R., Jensen R. T., Shapira H., de Weerth A., Slattery T. Purification, molecular cloning, and functional expression of the cholecystokinin receptor from rat pancreas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):3125–3129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.3125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]