Abstract
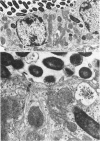
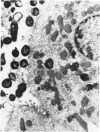
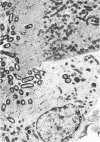
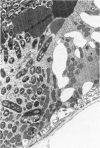
Despite significant advances in our understanding or renal tubular cell function, the in vivo handling of E. coli by renal tubules has not been previously investigated. The present studies were, therefore, designed to study this aspect of nephron function. Live and dead E. coli and vehicle alone were microinjected into the proximal tubular lumen of a single nephron of rats, and the microinjected tubules were morphologically studied at one-half, two, four, and six hours after. The bacteria initially contacted the luminal cell membrane. The luminal cell membrane adjacent to the bacteria subsequently invaginated, and both live and dead E. coli eventually became internalized into the tubular epithelial cytoplasm. Since dead E. coli are unlikely to invade the cells, their intracytoplasmic localization is a result of tubular epithelial phagocytosis. Similar microinjections of dead E. coli together with rat erythrocytes revealed a preferential phagocytosis of dead E. coli. Examination of the microinjected nephron with dead E. coli 48 hours after also demonstrated a development of microscopic interstitial nephritis surrounding the microinjected tubule. In conclusion, the renal tubular epithelia of the proximal and distal segments of rat nephron have phagocytic potential for E. coli which are further capable of inducing an inflammatory reaction around the microinjected tubule.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fukushi Y., Orikasa S., Kagayama M. An electron microscopic study of the interaction between vesical epitherlium and E. Coli. Invest Urol. 1979 Jul;17(1):61–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lande M. A., Birk D. E., Nagpal M. L., Rader R. L. Phagocytic properties of human keratocyte cultures. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1981 Apr;20(4):481–489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLLENHAUER H. H. PLASTIC EMBEDDING MIXTURES FOR USE IN ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. Stain Technol. 1964 Mar;39:111–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen K. M., Applegate C. W., Tisher C. C. Phagocytosis of erythrocytes by the proximal tubule of the rat kidney. Cell Tissue Res. 1982;226(2):363–374. doi: 10.1007/BF00218366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maesaka J. K., McCaffery M. Evidence for renal tubular leakage in maleic acid-induced Fanconi syndrome. Am J Physiol. 1980 Nov;239(5):F507–F513. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1980.239.5.F507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDowell E. M., Trump B. F. Histologic fixatives suitable for diagnostic light and electron microscopy. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1976 Aug;100(8):405–414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myagkaya G., Schellens J. P., Vreeling-Sindelárová H. Lysosomal breakdown of erythrocytes in the sheep placenta. An ultrastructural study. Cell Tissue Res. 1979 Mar 9;197(1):79–94. doi: 10.1007/BF00233555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLATT H. The engulfment of particulate and colloidal materials by epidermal cells. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1963 Jul;86:113–122. doi: 10.1002/path.1700860114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rácz P., Kaiserling E., Tenner K., Wuthe H. H. Experimental Listeria cystitis. II. Further evidence of the epithelial phase in experimental Listeria infection. An electron microscopic study. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol. 1973 May 15;13(1):24–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherberich J. E., Schäfer K., Mondorf W., Gauhl C., Sietzen W. Escherichia coli receptors on human kidney brush-border membranes. Lancet. 1977 Dec 3;2(8049):1181–1181. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91574-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimamura T., Kissane J. M., Györkey F. Experimental hydroneophrosis. Nephron dissection and electron microscopy of the kidney following obstruction of the ureter and in recovery from obstruction. Lab Invest. 1966 Mar;15(3):629–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimamura T., Maesaka J. K. A method to identify microinjected nephrons of rat. Stain Technol. 1984 Jul;59(4):221–224. doi: 10.3109/10520298409113860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakefield J. S., Hicks R. M. Erythrophagocytosis by the epithelial cells of the bladder. J Cell Sci. 1974 Aug;15(3):555–573. doi: 10.1242/jcs.15.3.555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]