Abstract
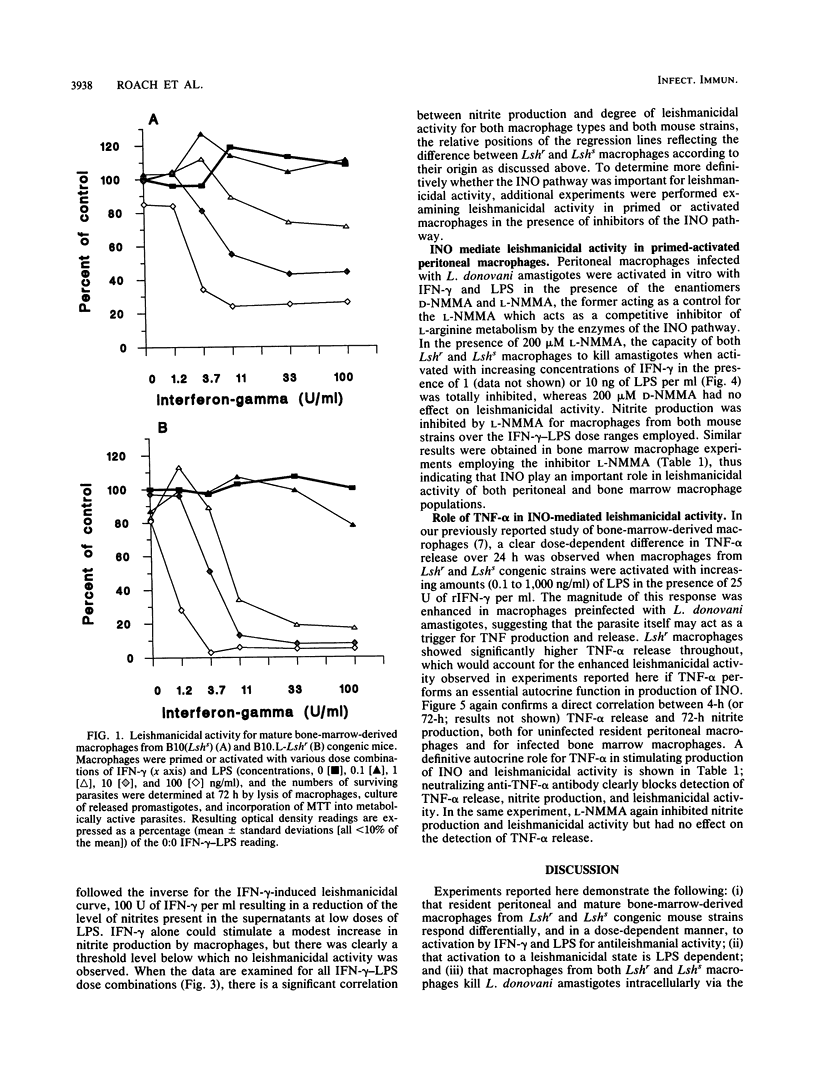
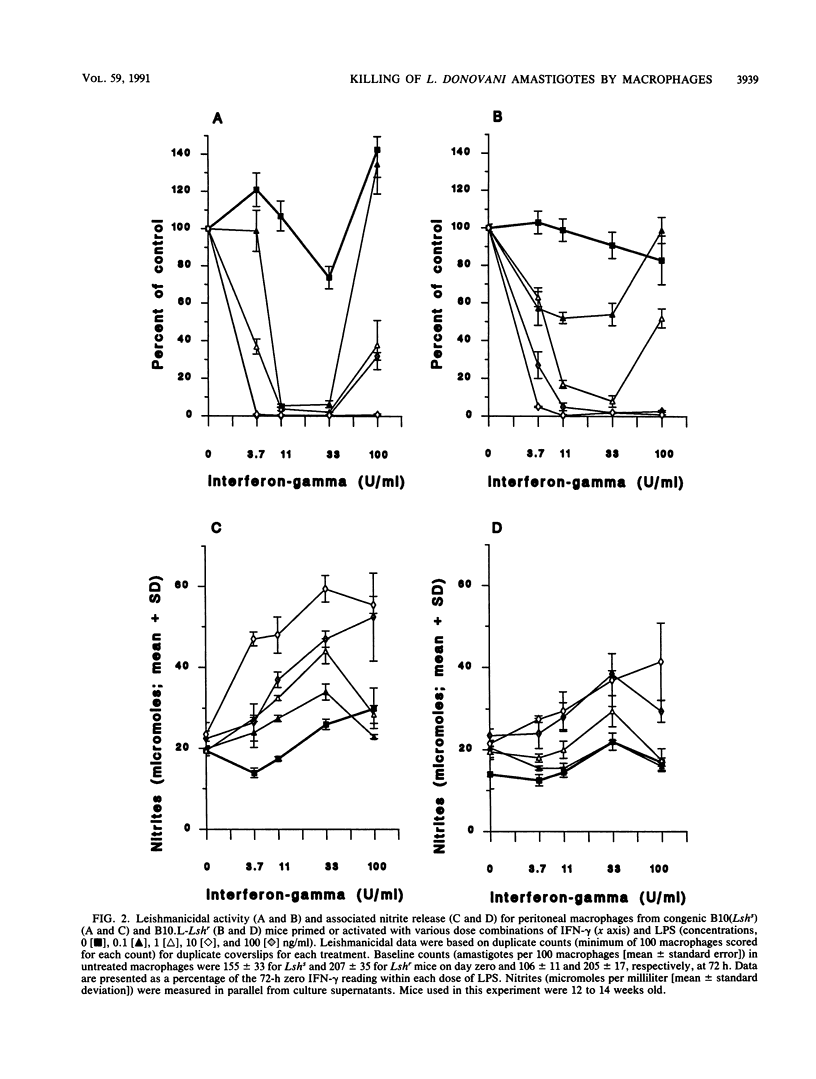
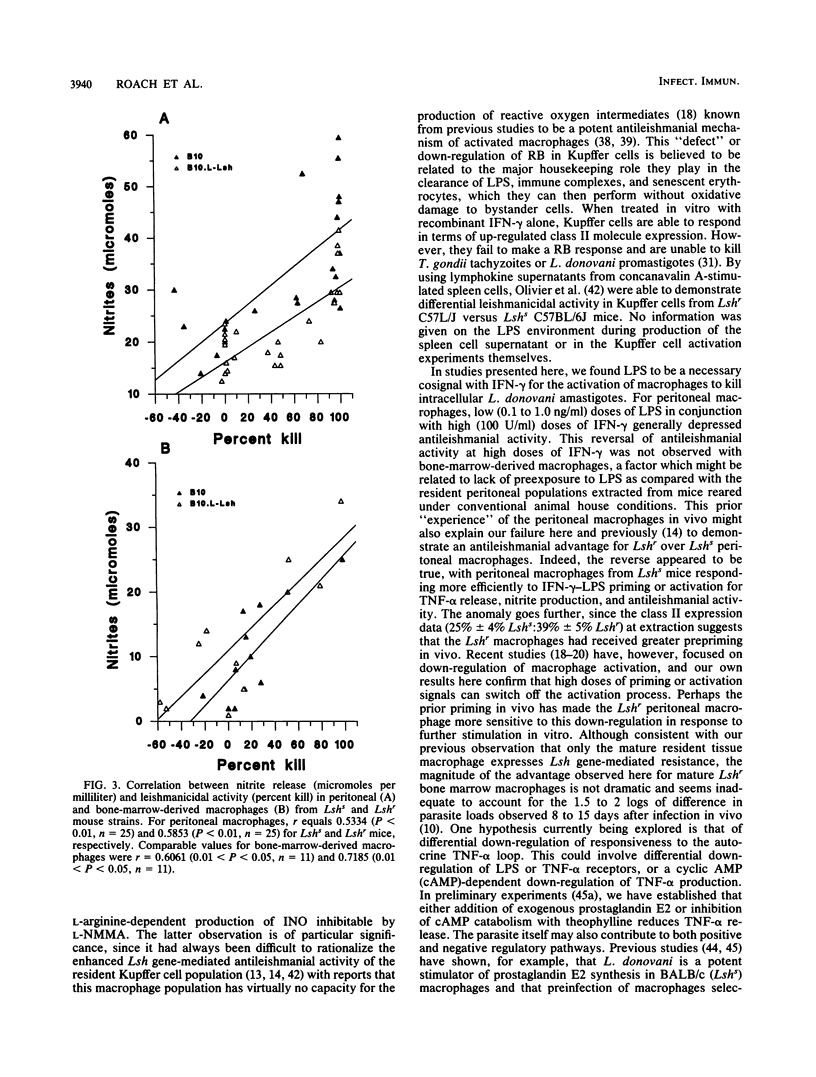
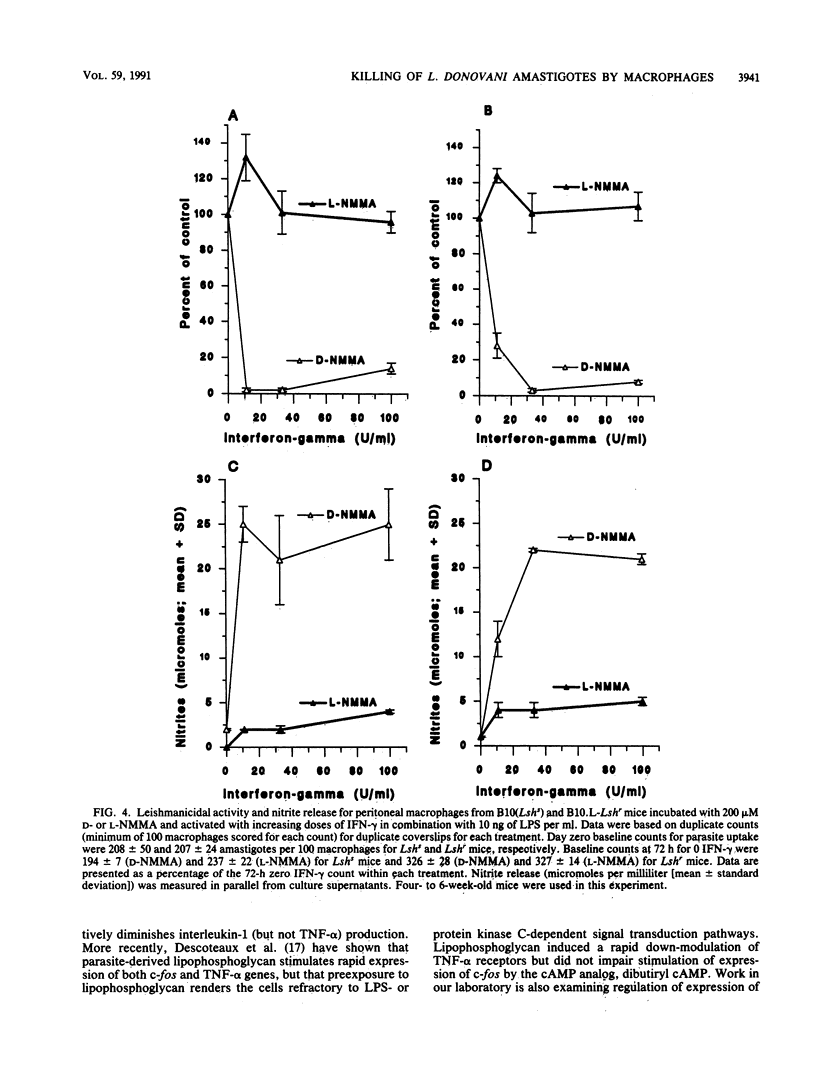
The capacity of mature bone-marrow-derived macrophages and resident peritoneal macrophages from Lshr versus Lshs congenic mice to kill intracellular Leishmania donovani amastigotes when activated by recombinant gamma interferon-lipopolysaccharide (rIFN-gamma-LPS) was examined. IFN-gamma alone in doses up to 100 U/ml was unable to activate macrophages to kill L. donovani amastigotes in vitro; LPS was a necessary secondary stimulus. Similarly, LPS alone in doses up to 100 ng/ml produced no leishmanicidal activity. In bone marrow macrophages, a dose-dependent increase in leishmanicidal activity was observed as increasing rIFN-gamma-LPS dose combinations were introduced, with Lshr macrophages maintaining a significant but not dramatic advantage within any particular dose combination. For peritoneal macrophages, the reverse was true, with macrophages from Lshs mice being more efficient at killing for doses of LPS up to 10 ng/ml with doses of rIFN-gamma in the range of 11 to 33 U/ml. The degree of killing in both bone marrow and peritoneal macrophages correlated well with the levels of nitrites measured in the supernatants at 72 h, and a highly significant correlation was observed between 4-, 24-, or 72-h tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) release and nitrite production measured at 72 h. Inclusion of 200 microM NG-monomethyl-L-arginine, a competitive inhibitor of the L-arginine-dependent pathway for the synthesis of inorganic nitrogen oxides, inhibited the killing, as did the addition of neutralizing anti-TNF-alpha antibody. These results are consistent with previous data showing an important autocrine role for TNF-alpha in enhancing production of inorganic nitrogen oxides by primed or activated macrophages. In addition, our results suggest that production of TNF-alpha and nitrites after priming or activation signals may be under a different regulatory control in mature bone marrow macrophages than in the resident peritoneal macrophage population.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams L. B., Hibbs J. B., Jr, Taintor R. R., Krahenbuhl J. L. Microbiostatic effect of murine-activated macrophages for Toxoplasma gondii. Role for synthesis of inorganic nitrogen oxides from L-arginine. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 1;144(7):2725–2729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austyn J. M., Gordon S. F4/80, a monoclonal antibody directed specifically against the mouse macrophage. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Oct;11(10):805–815. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830111013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B. A., Milsark I. W., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor: production, distribution, and metabolic fate in vivo. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):3972–3977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya A., Dorf M. E., Springer T. A. A shared alloantigenic determinant on Ia antigens encoded by the I-A and I-E subregions: evidence for I region gene duplication. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2488–2495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell J. M., Roach T. I., Kiderlen A., Kaye P. M. Role of Lsh in regulating macrophage priming/activation. Res Immunol. 1989 Oct;140(8):798–805. doi: 10.1016/0923-2494(89)90036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell J. M. The macrophage resistance gene Lsh/Ity/Bcg. Res Immunol. 1989 Oct;140(8):767–769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell J. M., Toole S., King M., Dawda P., Roach T. I., Cooper A. Analysis of Lsh gene expression in congenic B10.L-Lshr mice. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1988;137:301–309. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-50059-6_45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenstock E., Jann K. Natural resistance of mice to Salmonella typhimurium: bactericidal activity and chemiluminescence response of murine peritoneal macrophages. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Jul;125(1):173–183. doi: 10.1099/00221287-125-1-173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. J. Regulation of Leishmania populations within the host. II. genetic control of acute susceptibility of mice to Leishmania donovani infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Oct;30(1):130–140. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buschman E., Taniyama T., Nakamura R., Skamene E. Functional expression of the Bcg gene in macrophages. Res Immunol. 1989 Oct;140(8):793–797. doi: 10.1016/0923-2494(89)90035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Channon J. Y., Roberts M. B., Blackwell J. M. A study of the differential respiratory burst activity elicited by promastigotes and amastigotes of Leishmania donovani in murine resident peritoneal macrophages. Immunology. 1984 Oct;53(2):345–355. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crocker P. R., Blackwell J. M., Bradley D. J. Expression of the natural resistance gene Lsh in resident liver macrophages. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):1033–1040. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.1033-1040.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crocker P. R., Davies E. V., Blackwell J. M. Variable expression of the murine natural resistance gene Lsh in different macrophage populations infected in vitro with Leishmania donovani. Parasite Immunol. 1987 Nov;9(6):705–719. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1987.tb00540.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M., Forget A., Pelletier M., Gervais F., Skamene E. Killing of Mycobacterium smegmatis by macrophages from genetically susceptible and resistant mice. J Leukoc Biol. 1990 Jan;47(1):25–30. doi: 10.1002/jlb.47.1.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M., Forget A., Pelletier M., Skamene E. Pleiotropic effects of the Bcg gene: III. Respiratory burst in Bcg-congenic macrophages. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Sep;73(3):370–375. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descoteaux A., Turco S. J., Sacks D. L., Matlashewski G. Leishmania donovani lipophosphoglycan selectively inhibits signal transduction in macrophages. J Immunol. 1991 Apr 15;146(8):2747–2753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding A. H., Nathan C. F. Trace levels of bacterial lipopolysaccharide prevent interferon-gamma or tumor necrosis factor-alpha from enhancing mouse peritoneal macrophage respiratory burst capacity. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 15;139(6):1971–1977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding A. H., Sanchez E., Srimal S., Nathan C. F. Macrophages rapidly internalize their tumor necrosis factor receptors in response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 5;264(7):3924–3929. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding A., Nathan C. Analysis of the nonfunctional respiratory burst in murine Kupffer cells. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):1154–1170. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapier J. C., Hibbs J. B., Jr Differentiation of murine macrophages to express nonspecific cytotoxicity for tumor cells results in L-arginine-dependent inhibition of mitochondrial iron-sulfur enzymes in the macrophage effector cells. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 15;140(8):2829–2838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapier J. C., Hibbs J. B., Jr Murine cytotoxic activated macrophages inhibit aconitase in tumor cells. Inhibition involves the iron-sulfur prosthetic group and is reversible. J Clin Invest. 1986 Sep;78(3):790–797. doi: 10.1172/JCI112642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger D. L., Hibbs J. B., Jr, Perfect J. R., Durack D. T. Specific amino acid (L-arginine) requirement for the microbiostatic activity of murine macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1988 Apr;81(4):1129–1136. doi: 10.1172/JCI113427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S. J., Crawford R. M., Hockmeyer J. T., Meltzer M. S., Nacy C. A. Leishmania major amastigotes initiate the L-arginine-dependent killing mechanism in IFN-gamma-stimulated macrophages by induction of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 15;145(12):4290–4297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S. J., Meltzer M. S., Hibbs J. B., Jr, Nacy C. A. Activated macrophages destroy intracellular Leishmania major amastigotes by an L-arginine-dependent killing mechanism. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 1;144(1):278–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs J. B., Jr, Taintor R. R., Vavrin Z. Macrophage cytotoxicity: role for L-arginine deiminase and imino nitrogen oxidation to nitrite. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):473–476. doi: 10.1126/science.2432665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover D. L., Nacy C. A., Meltzer M. S. Human monocyte activation for cytotoxicity against intracellular Leishmania donovani amastigotes: induction of microbicidal activity by interferon-gamma. Cell Immunol. 1985 Sep;94(2):500–511. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90274-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye P. M., Patel N. K., Blackwell J. M. Acquisition of cell-mediated immunity to Leishmania. II. LSH gene regulation of accessory cell function. Immunology. 1988 Sep;65(1):17–22. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiderlen A. F., Kaye P. M. A modified colorimetric assay of macrophage activation for intracellular cytotoxicity against Leishmania parasites. J Immunol Methods. 1990 Feb 20;127(1):11–18. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90334-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepay D. A., Nathan C. F., Steinman R. M., Murray H. W., Cohn Z. A. Murine Kupffer cells. Mononuclear phagocytes deficient in the generation of reactive oxygen intermediates. J Exp Med. 1985 May 1;161(5):1079–1096. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.5.1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liew F. Y., Cox F. E. Nonspecific defence mechanism: the role of nitric oxide. Immunol Today. 1991 Mar;12(3):A17–A21. doi: 10.1016/S0167-5699(05)80006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liew F. Y., Li Y., Millott S. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha synergizes with IFN-gamma in mediating killing of Leishmania major through the induction of nitric oxide. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 15;145(12):4306–4310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liew F. Y., Li Y., Millott S. Tumour necrosis factor (TNF-alpha) in leishmaniasis. II. TNF-alpha-induced macrophage leishmanicidal activity is mediated by nitric oxide from L-arginine. Immunology. 1990 Dec;71(4):556–559. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liew F. Y., Millott S., Parkinson C., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Macrophage killing of Leishmania parasite in vivo is mediated by nitric oxide from L-arginine. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 15;144(12):4794–4797. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lissner C. R., Swanson R. N., O'Brien A. D. Genetic control of the innate resistance of mice to Salmonella typhimurium: expression of the Ity gene in peritoneal and splenic macrophages isolated in vitro. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):3006–3013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marletta M. A., Yoon P. S., Iyengar R., Leaf C. D., Wishnok J. S. Macrophage oxidation of L-arginine to nitrite and nitrate: nitric oxide is an intermediate. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 29;27(24):8706–8711. doi: 10.1021/bi00424a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Cartelli D. M. Killing of intracellular Leishmania donovani by human mononuclear phagocytes. Evidence for oxygen-dependent and -independent leishmanicidal activity. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):32–44. doi: 10.1172/JCI110972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W. Macrophage activation: enhanced oxidative and antiprotozoal activity. Contemp Top Immunobiol. 1984;13:97–115. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-1445-6_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Rubin B. Y., Rothermel C. D. Killing of intracellular Leishmania donovani by lymphokine-stimulated human mononuclear phagocytes. Evidence that interferon-gamma is the activating lymphokine. J Clin Invest. 1983 Oct;72(4):1506–1510. doi: 10.1172/JCI111107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Spitalny G. L., Nathan C. F. Activation of mouse peritoneal macrophages in vitro and in vivo by interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1619–1622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivier M., Bertrand S., Tanner C. E. Killing of Leishmania donovani by activated liver macrophages from resistant and susceptible strains of mice. Int J Parasitol. 1989 Jul;19(4):377–383. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(89)90093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oster C. N., Nacy C. A. Macrophage activation to kill Leishmania tropica: kinetics of macrophage response to lymphokines that induce antimicrobial activities against amastigotes. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1494–1500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner N. E., Malemud C. J. Arachidonic acid metabolism by murine peritoneal macrophages infected with Leishmania donovani: in vitro evidence for parasite-induced alterations in cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase pathways. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):556–563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner N. E., Ng W., Wilson C. B., McMaster W. R., Burchett S. K. Modulation of in vitro monocyte cytokine responses to Leishmania donovani. Interferon-gamma prevents parasite-induced inhibition of interleukin 1 production and primes monocytes to respond to Leishmania by producing both tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin 1. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):1914–1924. doi: 10.1172/JCI114654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheehan K. C., Ruddle N. H., Schreiber R. D. Generation and characterization of hamster monoclonal antibodies that neutralize murine tumor necrosis factors. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 1;142(11):3884–3893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stach J. L., Gros P., Forget A., Skamene E. Phenotypic expression of genetically-controlled natural resistance to Mycobacterium bovis (BCG). J Immunol. 1984 Feb;132(2):888–892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Marletta M. A. Induction of nitrite/nitrate synthesis in murine macrophages by BCG infection, lymphokines, or interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 15;139(2):518–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Marletta M. A. Mammalian nitrate biosynthesis: mouse macrophages produce nitrite and nitrate in response to Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7738–7742. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Nathan C. F. Nitric oxide. A macrophage product responsible for cytostasis and respiratory inhibition in tumor target cells. J Exp Med. 1989 May 1;169(5):1543–1555. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.5.1543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniyama T., Tokunaga T. Monoclonal antibodies directed against mouse macrophages in different stages of activation for tumor cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):1032–1037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



