Abstract
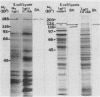
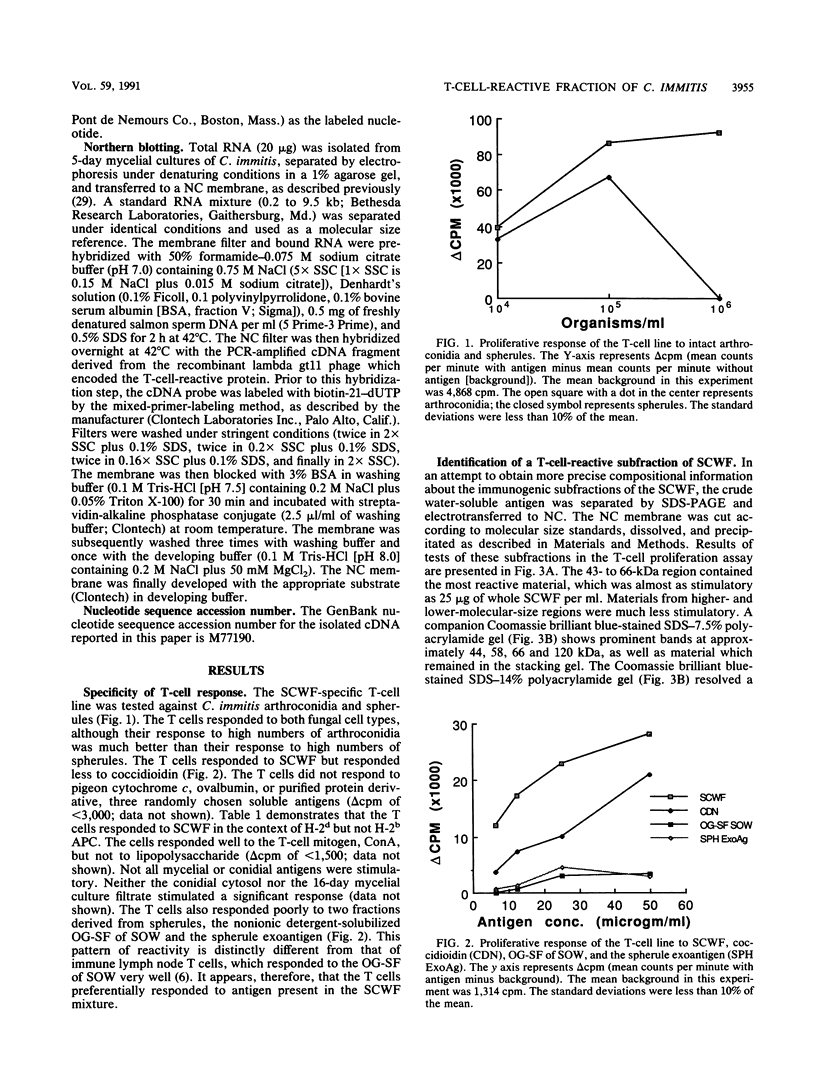
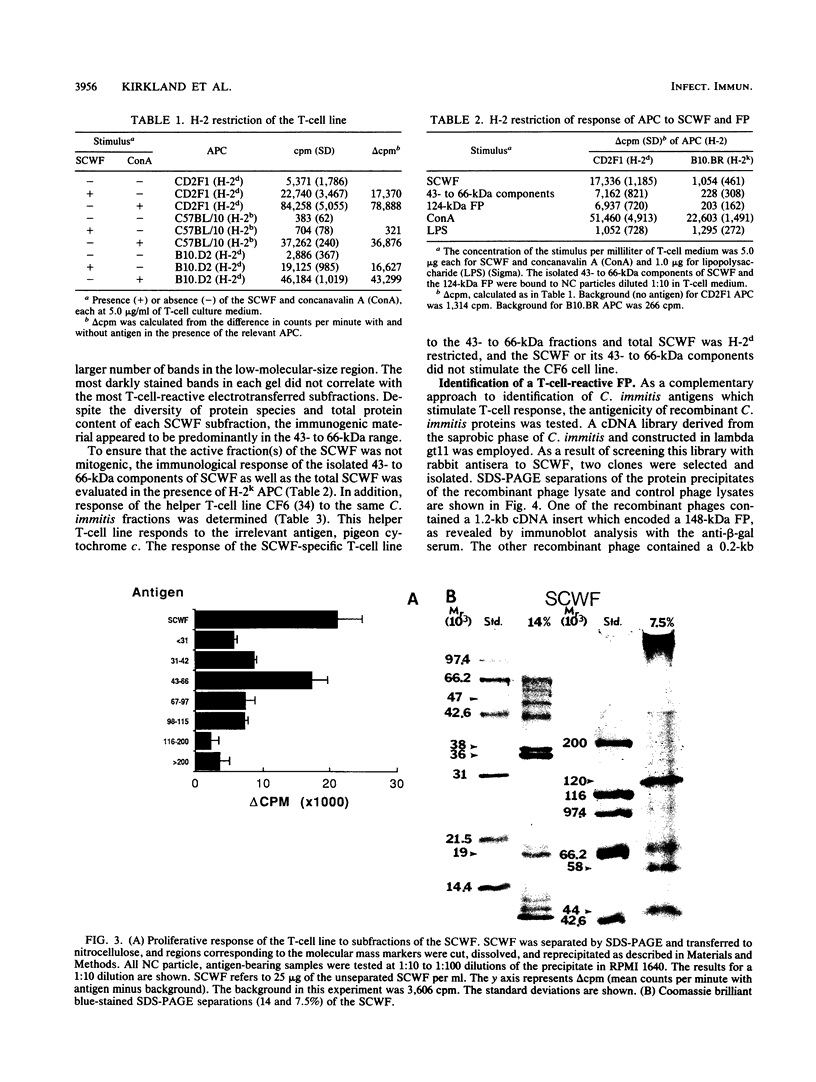
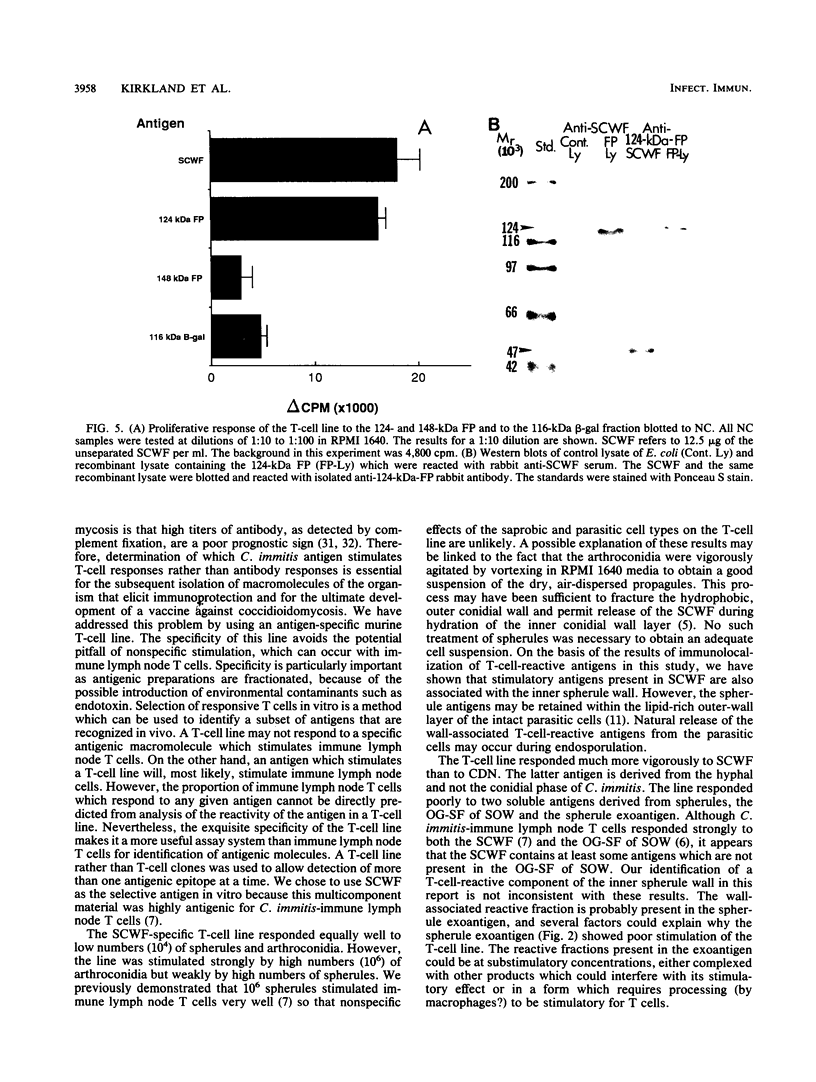
The principal mechanism of resistance to coccidioidomycosis in experimental animals has been reported to be T-cell-mediated immunity. We have generated a Coccidioides immitis antigen-specific murine T-cell line to identify specific macromolecules capable of eliciting an immune mouse T-cell proliferative response. The murine T cells were stimulated in vitro with a soluble conidial wall fraction (SCWF), which has been previously characterized by humoral and cellular immunoassays. The SCWF was separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and electrotransferred to a nitrocellulose membrane, and the stained blot was cut into seven pieces based on the molecular size of the SCWF components. The nitrocellulose membrane strips were converted into antigen-bearing particles and tested in a T-cell proliferation assay. Antigenic components of the SCWF in the molecular size range of 43 to 66 kDa were identified as the most immunoreactive. In a parallel study, we used a cDNA expression library derived from mRNA of the mycelial phase of C. immitis, which was constructed in lambda gt11 to identify clones that encoded T-cell-reactive fusion proteins (FPs). The cDNA library was screened by using anti-SCWF rabbit serum, and the FPs expressed in Escherichia coli were isolated and tested for T-cell response in the same manner as the SCWF components. The nucleotide sequence of a 0.2-kb cDNA insert encoding a protein which elicited vigorous T-cell response was determined. The isolated cDNA insert hybridized to a single 1.9-kb mRNA band in a Northern blot of the total RNA fraction of the mycelial phase of C. immitis. Antibody with affinity for the T-cell-reactive FP was isolated from anti-SCWF rabbit serum by solid-phase immunoadsorption. The FP-specific antibody reacted with a 47-kDa polypeptide in Western blots (immunoblots) of the SCWF. The same antibody preparation was used for immunoelectron microscopy to show that the FP was localized in the walls of arthroconidia and spherules of C. immitis. Attempts to clone and sequence the entire gene which encodes the T-cell-reactive protein are under way. The results of this study should lead to the determination of the complete structure of an important T-cell-stimulating antigen of C. immitis.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beaman L. V., Pappagianis D., Benjamini E. Mechanisms of resistance to infection with Coccidioides immitis in mice. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):681–685. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.681-685.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman L., Pappagianis D., Benjamini E. Significance of T cells in resistance to experimental murine coccidioidomycosis. Infect Immun. 1977 Sep;17(3):580–585. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.3.580-585.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. T., Kirkland T. N., Franco M., Zhu S., Yuan L., Sun S. H., Hearn V. M. Immunoreactivity of a surface wall fraction produced by spherules of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2695–2701. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2695-2701.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. T., Kirkland T. N., Sun S. H. An immunoreactive, water-soluble conidial wall fraction of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):657–667. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.657-667.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. T., Kruse D., Seshan K. R. Antigen complex of Coccidioides immitis which elicits a precipitin antibody response in patients. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2434–2446. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2434-2446.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. T., Kruse D., Zhu S. W., Seshan K. R., Wheat R. W. Composition, serologic reactivity, and immunolocalization of a 120-kilodalton tube precipitin antigen of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):179–188. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.179-188.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. T., Seshan K. R., Franco M., Bukownik E., Sun S. H., Hearn V. M. Isolation and morphology of an immunoreactive outer wall fraction produced by spherules of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2686–2694. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2686-2694.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. T., Zhu S. W., Pan S. C., Yuan L., Kruse D., Sun S. H. Isolation of antigens with proteolytic activity from Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1524–1534. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1524-1534.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Brummer E., Lecara G. In vitro lymphocyte responses of coccidioidin skin test-positive and -negative persons to coccidioidin, spherulin, and a coccidioides cell wall antigen. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):751–755. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.751-755.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A. Immunosuppression by cell wall antigens of Coccidioides immitis. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10 (Suppl 2):S415–S418. doi: 10.1093/cid/10.supplement_2.s415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Kennell W., Boncyk L., Murphy J. W. Induction and expression of cell-mediated immune responses in inbred mice infected with Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):13–17. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.13-17.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Kennell W. Suppression of T-lymphocyte response by Coccidioides immitis antigen. Infect Immun. 1988 Jun;56(6):1424–1429. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.6.1424-1429.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Mead C. G., Pavey E. F. Comparisons of mycelia- and spherule-derived antigens in cellular immune assays of Coccidioides immitis-infected guinea pigs. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):687–692. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.687-692.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Pope R. M. Serum-mediated suppression of lymphocyte transformation responses in coccidioidomycosis. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1058–1062. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1058-1062.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drutz D. J., Catanzaro A. Coccidioidomycosis. Part I. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Mar;117(3):559–585. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.117.3.559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. P., Stevens D. A. In vitro assays of cellular immunity in progressive coccidioidomycosis: evaluation of suppression with parasitic-phase antigen. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Jun;123(6):665–669. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.123.6.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimoto M., Fathman C. G. Antigen-reactive T cell clones. I. Transcomplementing hybrid I-A-region gene products function effectively in antigen presentation. J Exp Med. 1980 Oct 1;152(4):759–770. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.4.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruse D., Cole G. T. Isolation of tube precipitin antibody-reactive fractions of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):169–178. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.169-178.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. P., Stoker N. G., Grant K. A., Handzel Z. T., Hussain R., McAdam K. P., Dockrell H. M. Cellular immune responses of leprosy contacts to fractionated Mycobacterium leprae antigens. Infect Immun. 1989 Aug;57(8):2475–2480. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.8.2475-2480.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine H. B., Cobb J. M., Scalarone G. M. Spherule coccidioidin in delayed dermal sensitivity reactions of experimental animals. Sabouraudia. 1969 Feb;7(1):20–32. doi: 10.1080/00362177085190051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappagianis D. Epidemiology of coccidioidomycosis. Curr Top Med Mycol. 1988;2:199–238. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4612-3730-3_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH C. E., SAITO M. T., BEARD R. R., KEPP R. M., CLARK R. W., EDDIE B. U. Serological tests in the diagnosis and prognosis of coccidioidomycosis. Am J Hyg. 1950 Jul;52(1):1–21. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH C. E., SAITO M. T., SIMONS S. A. Pattern of 39,500 serologic tests in coccidioidomycosis. J Am Med Assoc. 1956 Feb 18;160(7):546–552. doi: 10.1001/jama.1956.02960420026008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH C. E., WHITING E. G. The use of coccidioidin. Am Rev Tuberc. 1948 Apr;57(4):330–360. doi: 10.1164/art.1948.57.4.330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger S. B., Hedrick S. M., Fink P. J., Bookman M. A., Matis L. A. Generation of diversity in T cell receptor repertoire specific for pigeon cytochrome c. J Exp Med. 1987 Feb 1;165(2):279–301. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.2.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun S. H., Cole G. T., Drutz D. J., Harrison J. L. Electron-microscopic observations of the Coccidioides immitis parasitic cycle in vivo. J Med Vet Mycol. 1986 Jun;24(3):183–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vordemeier H. M., Harris D. P., Roman E., Lathigra R., Moreno C., Ivanyi J. Identification of T cell stimulatory peptides from the 38-kDa protein of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Immunol. 1991 Aug 1;147(3):1023–1029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y. F., Gan Z. R., Wells W. W. Cloning and sequencing the cDNA encoding pig liver thioltransferase. Gene. 1989 Nov 30;83(2):339–346. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90120-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]