Abstract
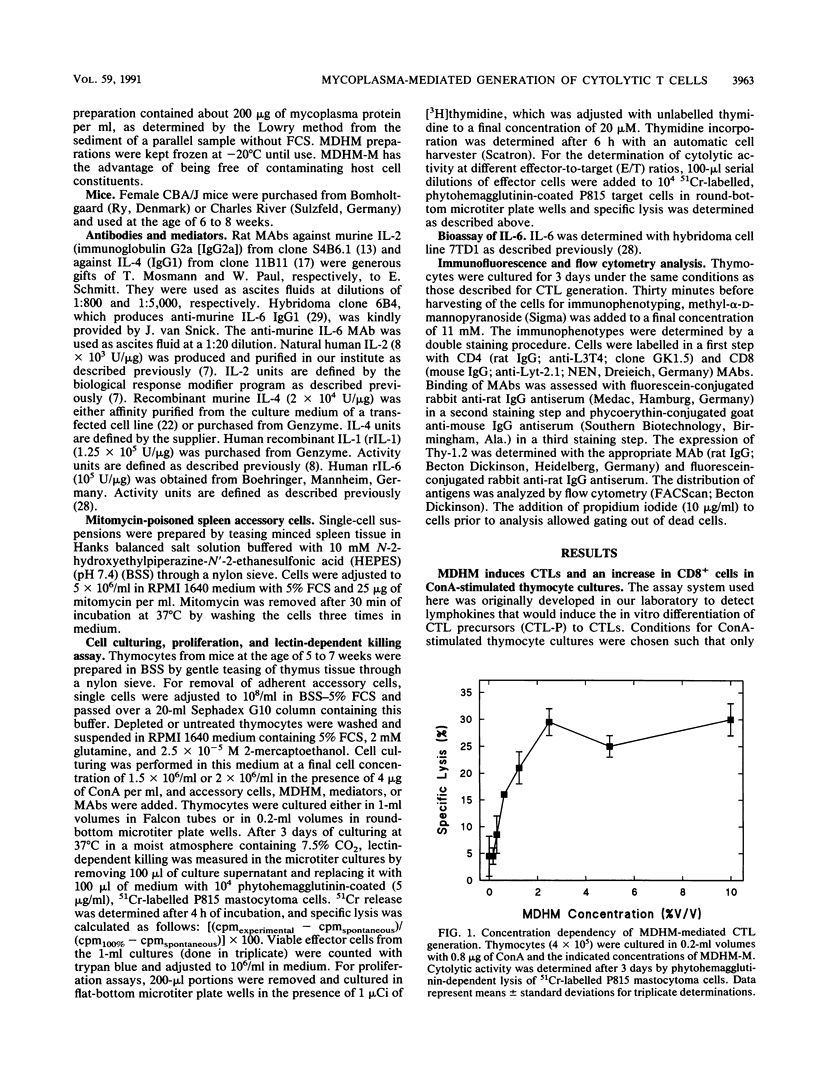
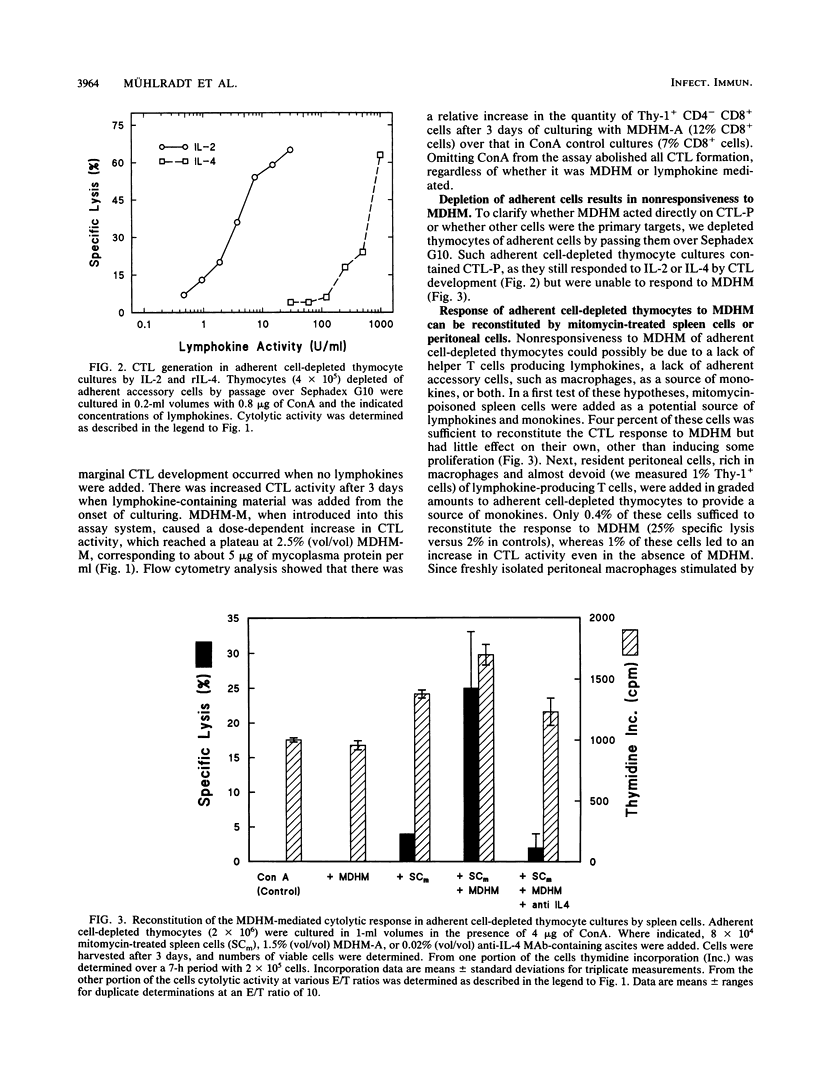
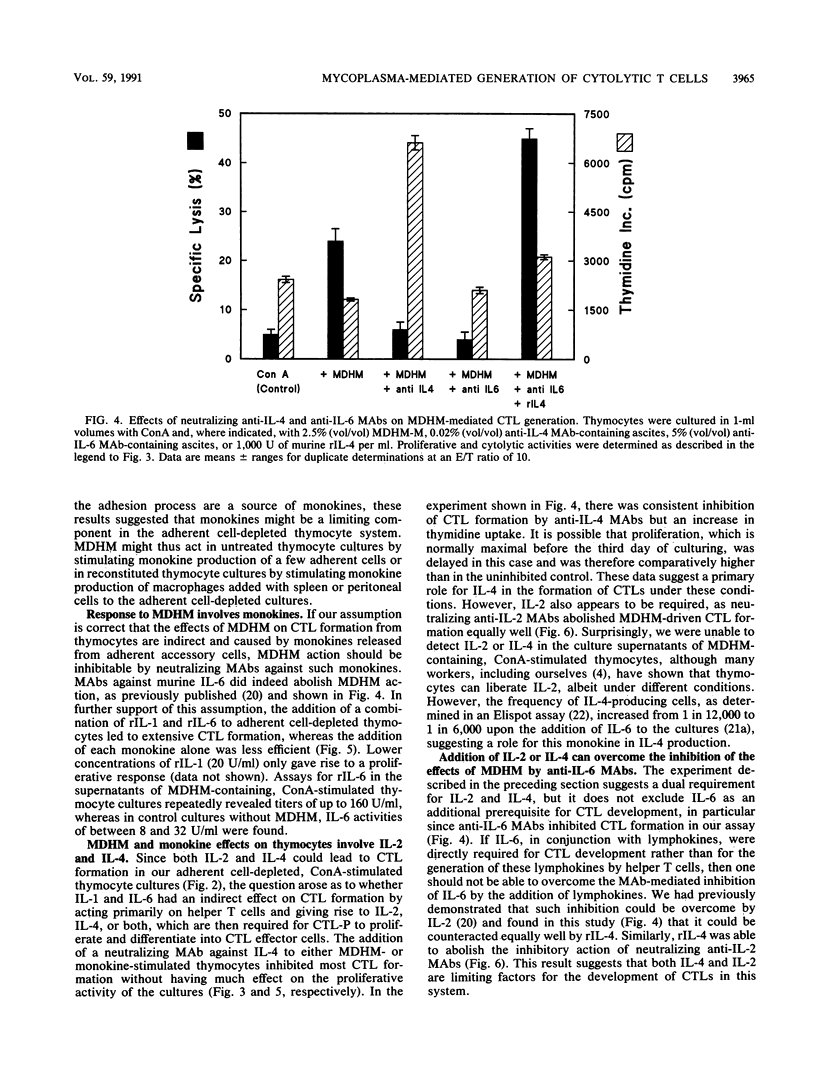
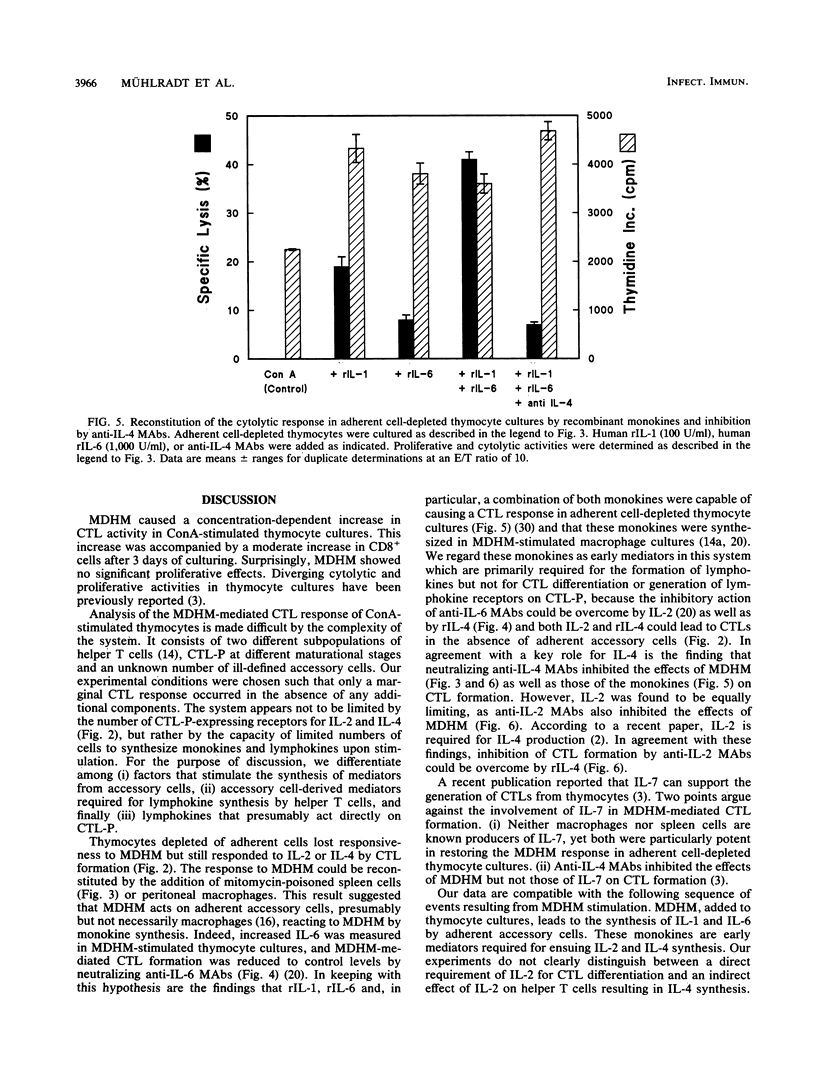
The capacity of Mycoplasma fermentans-derived high-molecular-weight material (MDHM) to generate cytolytic T cells from mitogen-stimulated murine thymocytes was studied in detail. The role of MDHM and the involvement of monokines and lymphokines resulting from the addition of MDHM to thymocyte cultures were examined in complete and adherent cell-depleted culture systems by the addition of neutralizing monoclonal antibodies against interleukin-2 (IL-2), IL-4, and IL-6 and in reconstitution experiments with recombinant mediators. The data presented here suggest that MDHM is crucial only in the first phase of a reaction sequence beginning with the stimulation of adherent accessory cells and resulting in the synthesis of IL-1 and IL-6. The lymphokines IL-2 and, primarily, IL-4 are required in a second step which, once these lymphokines are formed, can proceed in the absence of MDHM and accessory cells and leads to the formation of cytolytic T cells. The elucidation of the MDHM-induced reaction sequence may be of relevance in view of the hypothetical role of mycoplasmas in rheumatic disease in humans. M. fermentans is an organism capable of infecting humans and in an early report has been discussed as a causative agent for rheumatoid arthritis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkin C. L., Cole B. C., Sullivan G. J., Washburn L. R., Wiley B. B. Stimulation of mouse lymphocytes by a mitogen derived from Mycoplasma arthritidis. V. A small basic protein from culture supernatants is a potent T cell mitogen. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 1;137(5):1581–1589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Sasson S. Z., Le Gros G., Conrad D. H., Finkelman F. D., Paul W. E. IL-4 production by T cells from naive donors. IL-2 is required for IL-4 production. J Immunol. 1990 Aug 15;145(4):1127–1136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertagnolli M., Herrmann S. IL-7 supports the generation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes from thymocytes. Multiple lymphokines required for proliferation and cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1990 Sep 15;145(6):1706–1712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bödeker B. G., van Eijk R. V., Mühlradt P. F. Mitogenic effects of partially purified interleukin 2 on thymocyte subpopulations and spleen t cells of the mouse. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Sep;10(9):702–707. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erard F., Corthesy P., Nabholz M., Lowenthal J. W., Zaech P., Plaetinck G., MacDonald H. R. Interleukin 2 is both necessary and sufficient for the growth and differentiation of lectin-stimulated cytolytic T lymphocyte precursors. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1644–1652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar W. L., Johnson H. M., Farrar J. J. Regulation of the production of immune interferon and cytotoxic T lymphocytes by interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1981 Mar;126(3):1120–1125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grote W., Klaar J., Mühlradt P. F., Monner D. A. Large scale production and purification of human IL-2 from buffy coat lymphocytes stimulated with 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate and calcium ionophore A23187. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Oct 23;103(1):15–25. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90236-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Günther C., Röllinghoff M., Beuscher H. U. Proteolysis of the native murine IL 1 beta precursor is required to generate IL 1 beta bioactivity. Immunobiology. 1989 Feb;178(4-5):436–448. doi: 10.1016/s0171-2985(89)80064-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T., Matsuda T., Turner M., Miyasaka N., Buchan G., Tang B., Sato K., Shimizu M., Maini R., Feldmann M. Excessive production of interleukin 6/B cell stimulatory factor-2 in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Nov;18(11):1797–1801. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830181122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins S. J., Humphreys M., Jayson M. I. Cytokines in synovial fluid. I. The presence of biologically active and immunoreactive IL-1. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Jun;72(3):422–427. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houssiau F. A., Devogelaer J. P., Van Damme J., de Deuxchaisnes C. N., Van Snick J. Interleukin-6 in synovial fluid and serum of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory arthritides. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Jun;31(6):784–788. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchner H., Bauer A., Moritz T., Herbst F. Lymphocyte activation and induction of interferon gamma in human leucocyte cultures by the mitogen in Mycoplasma arthritidis supernatant (MAS). Scand J Immunol. 1986 Nov;24(5):609–613. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1986.tb02177.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Cherwinski H., Bond M. W., Giedlin M. A., Coffman R. L. Two types of murine helper T cell clone. I. Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2348–2357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Coffman R. L. TH1 and TH2 cells: different patterns of lymphokine secretion lead to different functional properties. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:145–173. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.001045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mühlradt P. F., Schade U. MDHM, a macrophage-stimulatory product of Mycoplasma fermentans, leads to in vitro interleukin-1 (IL-1), IL-6, tumor necrosis factor, and prostaglandin production and is pyrogenic in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):3969–3974. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.3969-3974.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordström D. C. DNA synthesis in CD4- and CD8-positive cells in synovial fluid of patients with reactive and rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 1989;8(6):269–272. doi: 10.1007/BF00270983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata M., Matsubara H., Takai Y., Kosaka H., Katagiri T., Sano H., Ishimura K., Fujita H., Hamaoka T., Fujiwara H. Capacities of a newly established thymic stromal cell clone to express Ia antigens and to produce interleukin-6, colony-stimulating factor, and thymic stroma-derived T-cell growth factor. J Leukoc Biol. 1989 Jan;45(1):69–78. doi: 10.1002/jlb.45.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohara J., Paul W. E. Production of a monoclonal antibody to and molecular characterization of B-cell stimulatory factor-1. Nature. 1985 May 23;315(6017):333–336. doi: 10.1038/315333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada M., Kitahara M., Kishimoto S., Matsuda T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. IL-6/BSF-2 functions as a killer helper factor in the in vitro induction of cytotoxic T cells. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1543–1549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer J. D., McKenzie D. T., Swain S. L., Dutton R. W. B cell stimulatory factor 1 (interleukin 4) is sufficient for the proliferation and differentiation of lectin-stimulated cytolytic T lymphocyte precursors. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1464–1470. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quentmeier H., Schmitt E., Kirchhoff H., Grote W., Mühlradt P. F. Mycoplasma fermentans-derived high-molecular-weight material induces interleukin-6 release in cultures of murine macrophages and human monocytes. Infect Immun. 1990 May;58(5):1273–1280. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.5.1273-1280.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renauld J. C., Vink A., Van Snick J. Accessory signals in murine cytolytic T cell responses. Dual requirement for IL-1 and IL-6. J Immunol. 1989 Sep 15;143(6):1894–1898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt E., Van Brandwijk R., Fischer H. G., Rüde E. Establishment of different T cell sublines using either interleukin 2 or interleukin 4 as growth factors. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Aug;20(8):1709–1715. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sher T., Yamin A., Rottem S., Gallily R. In vitro induction of tumor necrosis factor alpha, tumor cytolysis, and blast transformation by Spiroplasma membranes. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990 Jul 4;82(13):1142–1145. doi: 10.1093/jnci/82.13.1142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart P. M., Cassell G. H., Woodward J. G. Differential induction of bone marrow macrophage proliferation by mycoplasmas involves granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Infect Immun. 1990 Nov;58(11):3558–3563. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.11.3558-3563.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugama K., Kuwano K., Furukawa M., Himeno Y., Satoh T., Arai S. Mycoplasmas induce transcription and production of tumor necrosis factor in a monocytic cell line, THP-1, by a protein kinase C-independent pathway. Infect Immun. 1990 Nov;58(11):3564–3567. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.11.3564-3567.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai Y., Wong G. G., Clark S. C., Burakoff S. J., Herrmann S. H. B cell stimulatory factor-2 is involved in the differentiation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1988 Jan 15;140(2):508–512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takatsu K., Kikuchi Y., Takahashi T., Honjo T., Matsumoto M., Harada N., Yamaguchi N., Tominaga A. Interleukin 5, a T-cell-derived B-cell differentiation factor also induces cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4234–4238. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Snick J., Cayphas S., Vink A., Uyttenhove C., Coulie P. G., Rubira M. R., Simpson R. J. Purification and NH2-terminal amino acid sequence of a T-cell-derived lymphokine with growth factor activity for B-cell hybridomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9679–9683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vink A., Coulie P. G., Wauters P., Nordan R. P., Van Snick J. B cell growth and differentiation activity of interleukin-HP1 and related murine plasmacytoma growth factors. Synergy with interleukin 1. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Apr;18(4):607–612. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vink A., Uyttenhove C., Wauters P., Van Snick J. Accessory factors involved in murine T cell activation. Distinct roles of interleukin 6, interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Jan;20(1):1–6. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widmer M. B., Grabstein K. H. Regulation of cytolytic T-lymphocyte generation by B-cell stimulatory factor. Nature. 1987 Apr 23;326(6115):795–798. doi: 10.1038/326795a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. H., Brostoff J., Roitt I. M. Possible role of Mycoplasma fermentans in pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1970 Aug 8;2(7667):277–280. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)91328-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



