Abstract
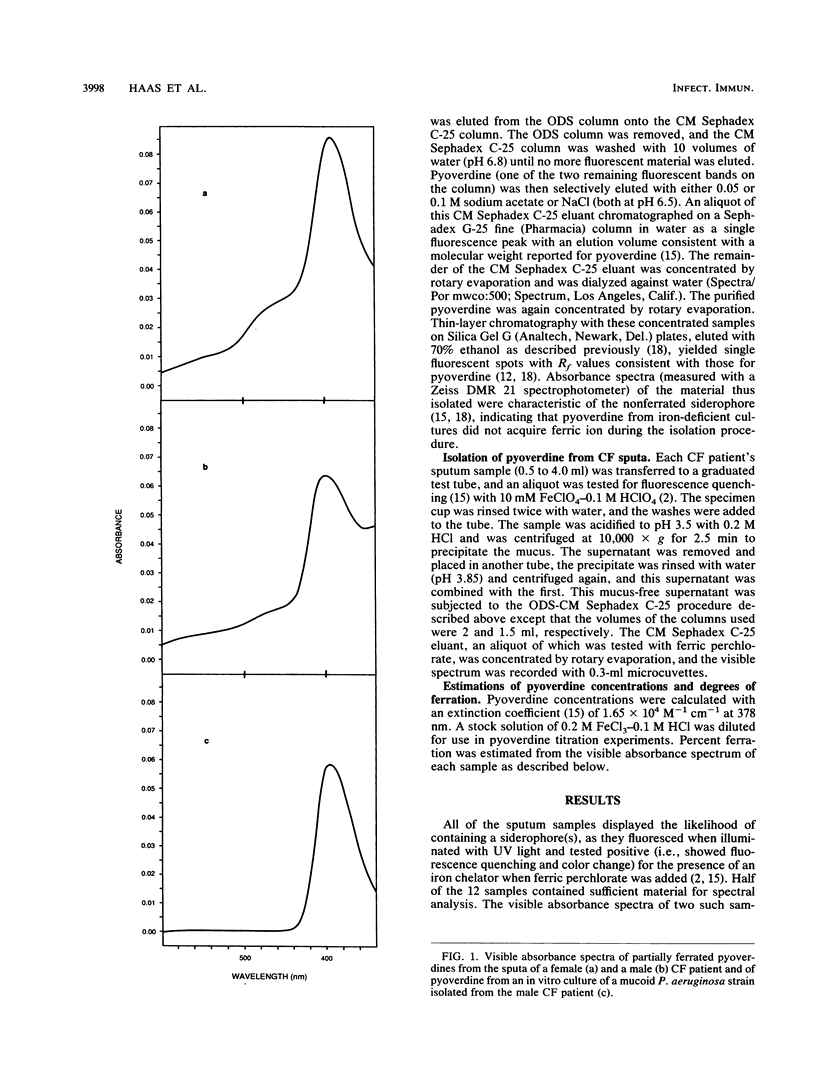
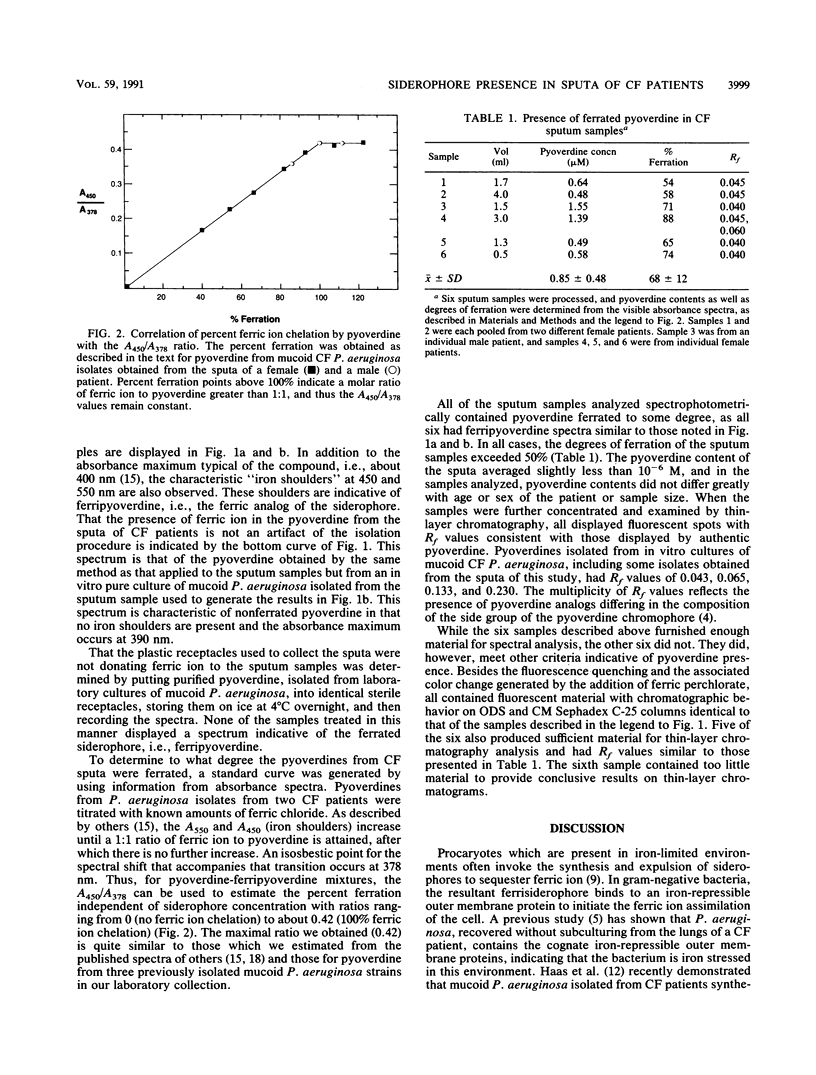
Sputum samples from the lungs of cystic fibrosis patients harboring Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections were collected and examined for the presence of the siderophore pyoverdine. Fluorescence quenching, due to the addition of ferric ion, as well as column and thin-layer chromatography results indicated that all samples contained the siderophore. Six samples furnished sufficient material after purification to allow us to obtain visible absorbance spectra. These spectra were characteristic of the ferrated analog of the P. aeruginosa pyoverdine, that is, ferripyoverdine, and in all cases they indicated a degree of ferration in excess of 50%. P. aeruginosa in the cystic fibrosis lung is thus iron stressed and responds by synthesizing pyoverdine, which subsequently binds ferric ion.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ankenbauer R., Sriyosachati S., Cox C. D. Effects of siderophores on the growth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in human serum and transferrin. Infect Immun. 1985 Jul;49(1):132–140. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.1.132-140.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkin C. L., Neilands J. B. Rhodotorulic acid, a diketopiperazine dihydroxamic acid with growth-factor activity. I. Isolation and characterization. Biochemistry. 1968 Oct;7(10):3734–3739. doi: 10.1021/bi00850a054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briskot G., Taraz K., Budzikiewicz H. Siderophore vom Pyoverdin-Typ aus Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Z Naturforsch C. 1986 May-Jun;41(5-6):497–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery T. Iron metabolism in humans and plants. Am Sci. 1982 Nov-Dec;70(6):626–632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enard C., Diolez A., Expert D. Systemic virulence of Erwinia chrysanthemi 3937 requires a functional iron assimilation system. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2419–2426. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2419-2426.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths E., Humphreys J. Isolation of enterochelin from the peritoneal washings of guinea pigs lethally infected with Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):286–289. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.286-289.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING E. O., WARD M. K., RANEY D. E. Two simple media for the demonstration of pyocyanin and fluorescin. J Lab Clin Med. 1954 Aug;44(2):301–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodge J. S., Emery T. Anaerobic iron uptake by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):801–804. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.801-804.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilands J. B. Microbial iron compounds. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:715–731. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philson S. B., Llinás M. Siderochromes from Pseudomonas fluorescens. I. Isolation and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8081–8085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwyn B., Neilands J. B. Universal chemical assay for the detection and determination of siderophores. Anal Biochem. 1987 Jan;160(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90612-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokol P. A. Surface expression of ferripyochelin-binding protein is required for virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2021–2025. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2021-2025.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolmasky M. E., Actis L. A., Toranzo A. E., Barja J. L., Crosa J. H. Plasmids mediating iron uptake in Vibrio anguillarum strains isolated from turbot in Spain. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Aug;131(8):1989–1997. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-8-1989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolmasky M. E., Crosa J. H. Molecular cloning and expression of genetic determinants for the iron uptake system mediated by the Vibrio anguillarum plasmid pJM1. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):860–866. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.860-866.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


