Abstract
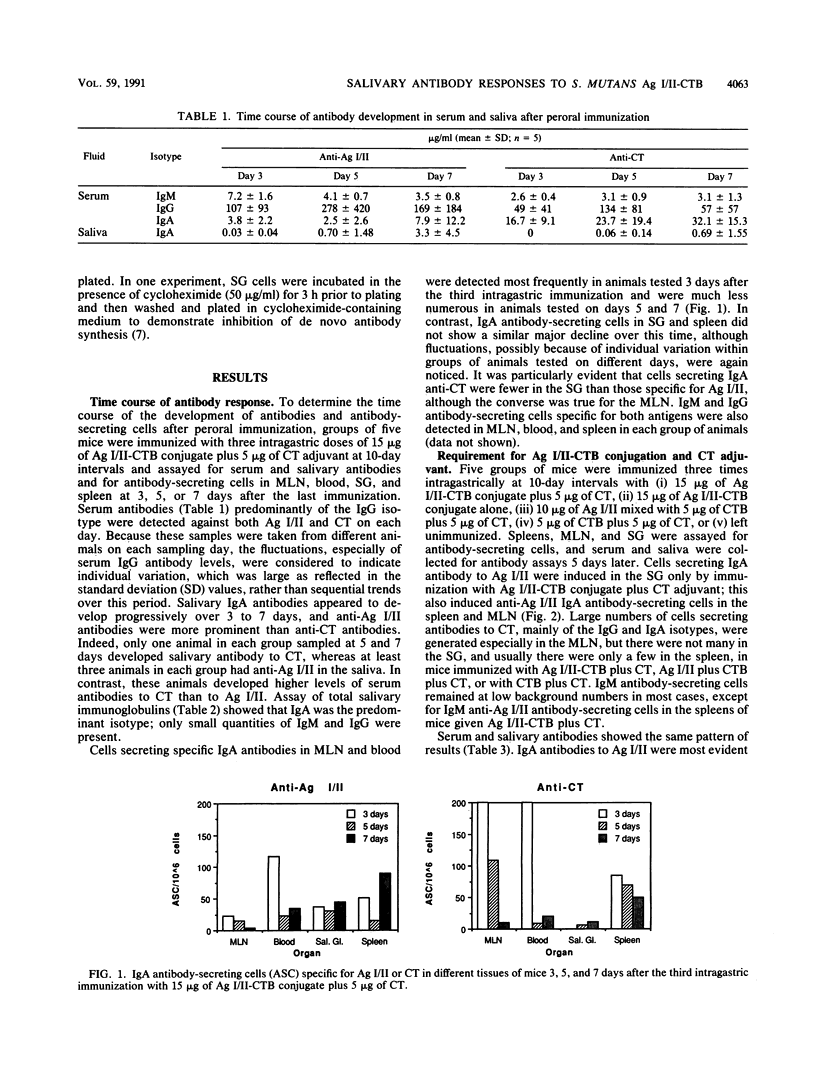
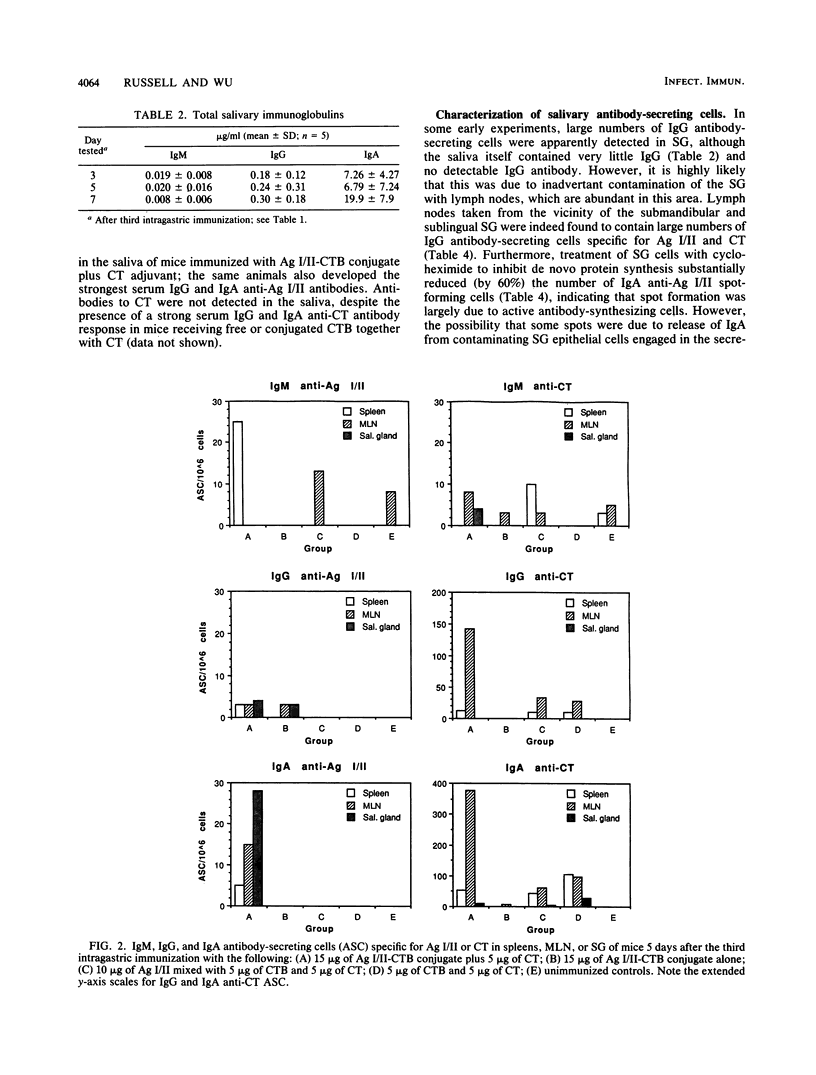
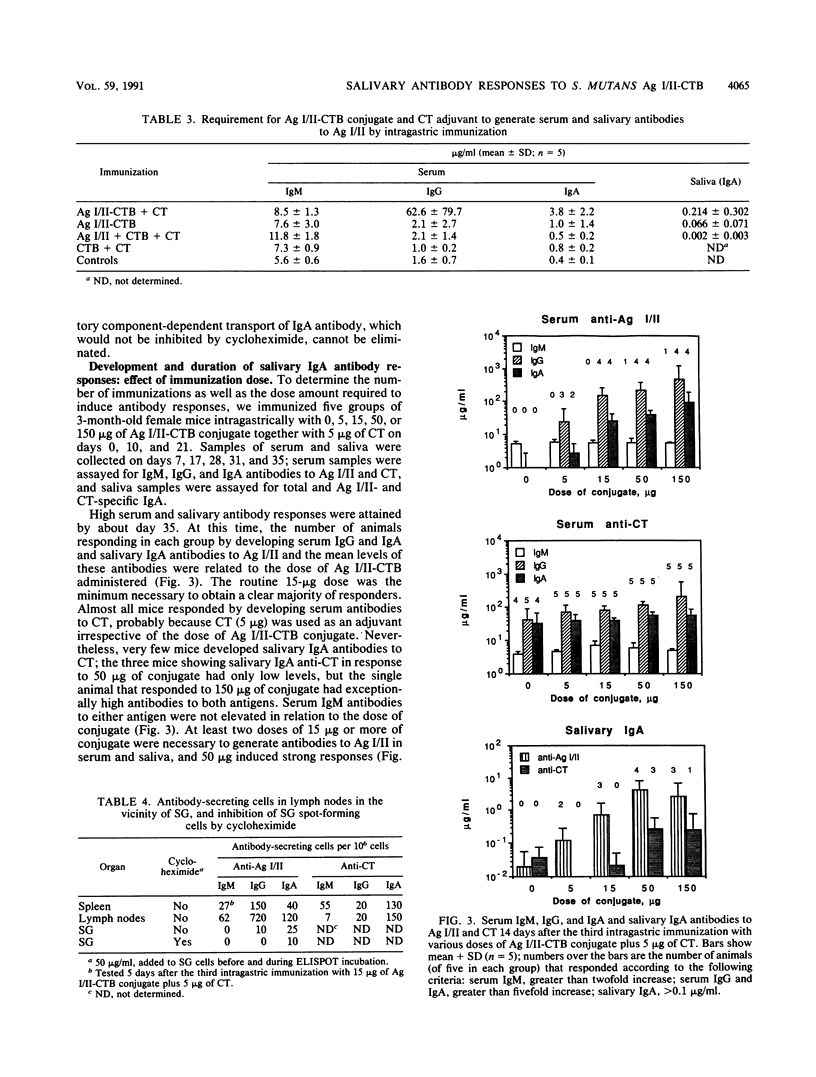
After peroral immunization of mice with surface protein antigen (Ag) I/II of Streptococcus mutans conjugated to the cholera toxin B (CTB) subunit, cells actively secreting immunoglobulin A (IgA) antibodies specific for Ag I/II, but not for CT, were induced in the salivary glands; salivary IgA anti-Ag I/II antibodies and total salivary IgA were also elevated. The development of large numbers of IgA and IgG antibody-secreting cells in the mesenteric lymph nodes and spleen and high levels of serum IgA and IgG antibodies to Ag I/II and CT demonstrated that a response to both antigens occurred. At least two to three intragastric doses of 15 micrograms or more of Ag I/II-CTB conjugate, plus free CT as an adjuvant, were needed to induce the salivary IgA anti-Ag I/II response, which peaked at about 35 days and persisted at lower levels for 5 to 6 months. A single booster intragastric immunization did not induce enhanced salivary IgA anti-Ag I/II antibodies relative to the primary response, but serum IgA and IgG antibodies to both Ag I/II and CT showed evidence of marked anamnestic responses. The results indicated that relatively long-term mucosal IgA antibody responses could be induced by peroral immunization with small quantities of a CTB-conjugated protein. However, additional factors governed the distribution of cells secreting antibodies of different specificities, or capable of mounting anamnestic responses, between different compartments of the mucosal and circulatory immune systems.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avrameas S., Ternynck T. Peroxidase labelled antibody and Fab conjugates with enhanced intracellular penetration. Immunochemistry. 1971 Dec;8(12):1175–1179. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90395-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bromander A., Holmgren J., Lycke N. Cholera toxin stimulates IL-1 production and enhances antigen presentation by macrophages in vitro. J Immunol. 1991 May 1;146(9):2908–2914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson J., Drevin H., Axén R. Protein thiolation and reversible protein-protein conjugation. N-Succinimidyl 3-(2-pyridyldithio)propionate, a new heterobifunctional reagent. Biochem J. 1978 Sep 1;173(3):723–737. doi: 10.1042/bj1730723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challacombe S. J., Russell M. W., Hawkes J. Passage of intact IgG from plasma to the oral cavity via crevicular fluid. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Dec;34(3):417–422. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen K. S., Strober W. Cholera holotoxin and its B subunit enhance Peyer's patch B cell responses induced by orally administered influenza virus: disproportionate cholera toxin enhancement of the IgA B cell response. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Feb;20(2):433–436. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke C. J., Wilson A. D., Williams N. A., Stokes C. R. Mucosal priming of T-lymphocyte responses to fed protein antigens using cholera toxin as an adjuvant. Immunology. 1991 Mar;72(3):323–328. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czerkinsky C. C., Nilsson L. A., Nygren H., Ouchterlony O., Tarkowski A. A solid-phase enzyme-linked immunospot (ELISPOT) assay for enumeration of specific antibody-secreting cells. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):109–121. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90308-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czerkinsky C., Moldoveanu Z., Mestecky J., Nilsson L. A., Ouchterlony O. A novel two colour ELISPOT assay. I. Simultaneous detection of distinct types of antibody-secreting cells. J Immunol Methods. 1988 Nov 25;115(1):31–37. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90306-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czerkinsky C., Russell M. W., Lycke N., Lindblad M., Holmgren J. Oral administration of a streptococcal antigen coupled to cholera toxin B subunit evokes strong antibody responses in salivary glands and extramucosal tissues. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1072–1077. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1072-1077.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czerkinsky C., Svennerholm A. M., Quiding M., Jonsson R., Holmgren J. Antibody-producing cells in peripheral blood and salivary glands after oral cholera vaccination of humans. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):996–1001. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.996-1001.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldridge J. H., Gilley R. M., Staas J. K., Moldoveanu Z., Meulbroek J. A., Tice T. R. Biodegradable microspheres: vaccine delivery system for oral immunization. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1989;146:59–66. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74529-4_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson C. O. Cholera toxin and its subunits as potential oral adjuvants. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1989;146:29–33. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74529-4_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson C. O., Ealding W. Generalized systemic and mucosal immunity in mice after mucosal stimulation with cholera toxin. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):2736–2741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson C. O., Ealding W. Ir gene control of the murine secretory IgA response to cholera toxin. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Mar;17(3):425–428. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton S. R., Keren D. F., Boitnott J. K., Robertson S. M., Yardley J. H. Enhancement by cholera toxin of IgA secretion from intestinal crypt epithelium. Gut. 1980 May;21(5):365–369. doi: 10.1136/gut.21.5.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson H. A., Lange S., Lönnroth I. Internalization in vivo of cholera toxin in the small intestinal epithelium of the rat. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand A. 1984 Jan;92(1):15–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1984.tb04372.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husband A. J., Gowans J. L. The origin and antigen-dependent distribution of IgA-containing cells in the intestine. J Exp Med. 1978 Nov 1;148(5):1146–1160. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.5.1146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner T., Russell M. W., Caldwell J., Smith R. Immunization with purified protein antigens from Streptococcus mutans against dental caries in rhesus monkeys. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):407–415. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.407-415.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang X. P., Lamm M. E., Nedrud J. G. Oral administration of cholera toxin-Sendai virus conjugate potentiates gut and respiratory immunity against Sendai virus. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1495–1501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lycke N., Holmgren J. Intestinal mucosal memory and presence of memory cells in lamina propria and Peyer's patches in mice 2 years after oral immunization with cholera toxin. Scand J Immunol. 1986 May;23(5):611–616. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1986.tb01995.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lycke N., Holmgren J. Strong adjuvant properties of cholera toxin on gut mucosal immune responses to orally presented antigens. Immunology. 1986 Oct;59(2):301–308. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lycke N., Lindholm L., Holmgren J. IgA isotype restriction in the mucosal but not in the extramucosal immune response after oral immunizations with cholera toxin or cholera B subunit. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1983;72(2):119–127. doi: 10.1159/000234853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lycke N., Severinson E., Strober W. Cholera toxin acts synergistically with IL-4 to promote IgG1 switch differentiation. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 15;145(10):3316–3324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J. K., Hunjan M., Smith R., Kelly C., Lehner T. An investigation into the mechanism of protection by local passive immunization with monoclonal antibodies against Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1990 Oct;58(10):3407–3414. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.10.3407-3414.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie S. J., Halsey J. F. Cholera toxin B subunit as a carrier protein to stimulate a mucosal immune response. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):1818–1824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestecky J., Lue C., Russell M. W. Selective transport of IgA. Cellular and molecular aspects. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1991 Sep;20(3):441–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestecky J. The common mucosal immune system and current strategies for induction of immune responses in external secretions. J Clin Immunol. 1987 Jul;7(4):265–276. doi: 10.1007/BF00915547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalek S. M., Childers N. K., Katz J., Denys F. R., Berry A. K., Eldridge J. H., McGhee J. R., Curtiss R., 3rd Liposomes as oral adjuvants. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1989;146:51–58. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74529-4_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalek S. M., McGhee J. R., Mestecky J., Arnold R. R., Bozzo L. Ingestion of Streptococcus mutans induces secretory immunoglobulin A and caries immunity. Science. 1976 Jun 18;192(4245):1238–1240. doi: 10.1126/science.1273589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz E., Zubiaga A. M., Merrow M., Sauter N. P., Huber B. T. Cholera toxin discriminates between T helper 1 and 2 cells in T cell receptor-mediated activation: role of cAMP in T cell proliferation. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):95–103. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Cray W. C., Jr Determinants of the localization, magnitude, and duration of a specific mucosal IgA plasma cell response in enterically immunized rats. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1311–1315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F. The role of antigen form and function in the primary and secondary intestinal immune responses to cholera toxin and toxoid in rats. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):195–206. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell M. W., Bergmeier L. A., Zanders E. D., Lehner T. Protein antigens of Streptococcus mutans: purification and properties of a double antigen and its protease-resistant component. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):486–493. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.486-493.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell M. W., Mestecky J. Induction of the mucosal immune response. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10 (Suppl 2):S440–S446. doi: 10.1093/cid/10.supplement_2.s440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svennerholm A. M., Sack D. A., Holmgren J., Bardhan P. K. Intestinal antibody responses after immunisation with cholera B subunit. Lancet. 1982 Feb 6;1(8267):305–308. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91568-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi I., Okahashi N., Kanamoto T., Asakawa H., Koga T. Intranasal immunization of mice with recombinant protein antigen of serotype c Streptococcus mutans and cholera toxin B subunit. Arch Oral Biol. 1990;35(6):475–477. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(90)90211-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura S. I., Samegai Y., Kurata H., Kikuta K., Nagamine T., Aizawa C., Kurata T. Enhancement of protective antibody responses by cholera toxin B subunit inoculated intranasally with influenza vaccine. Vaccine. 1989 Jun;7(3):257–262. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(89)90240-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Heijden P. J., Bianchi A. T., Dol M., Pals J. W., Stok W., Bokhout B. A. Manipulation of intestinal immune responses against ovalbumin by cholera toxin and its B subunit in mice. Immunology. 1991 Jan;72(1):89–93. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachsmann D., Klein J. P., Scholler M., Ogier J., Ackermans F., Frank R. M. Serum and salivary antibody responses in rats orally immunized with Streptococcus mutans carbohydrate protein conjugate associated with liposomes. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):408–413. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.408-413.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson A. D., Clarke C. J., Stokes C. R. Whole cholera toxin and B subunit act synergistically as an adjuvant for the mucosal immune response of mice to keyhole limpet haemocyanin. Scand J Immunol. 1990 Apr;31(4):443–451. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1990.tb02791.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson A. D., Stokes C. R., Bourne F. J. Adjuvant effect of cholera toxin on the mucosal immune response to soluble proteins. Differences between mouse strains and protein antigens. Scand J Immunol. 1989 Jun;29(6):739–745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. Y., Russell M. W. Immunological cross-reactivity between Streptococcus mutans and human heart tissue examined by cross-immunization experiments. Infect Immun. 1990 Nov;58(11):3545–3552. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.11.3545-3552.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



