Abstract
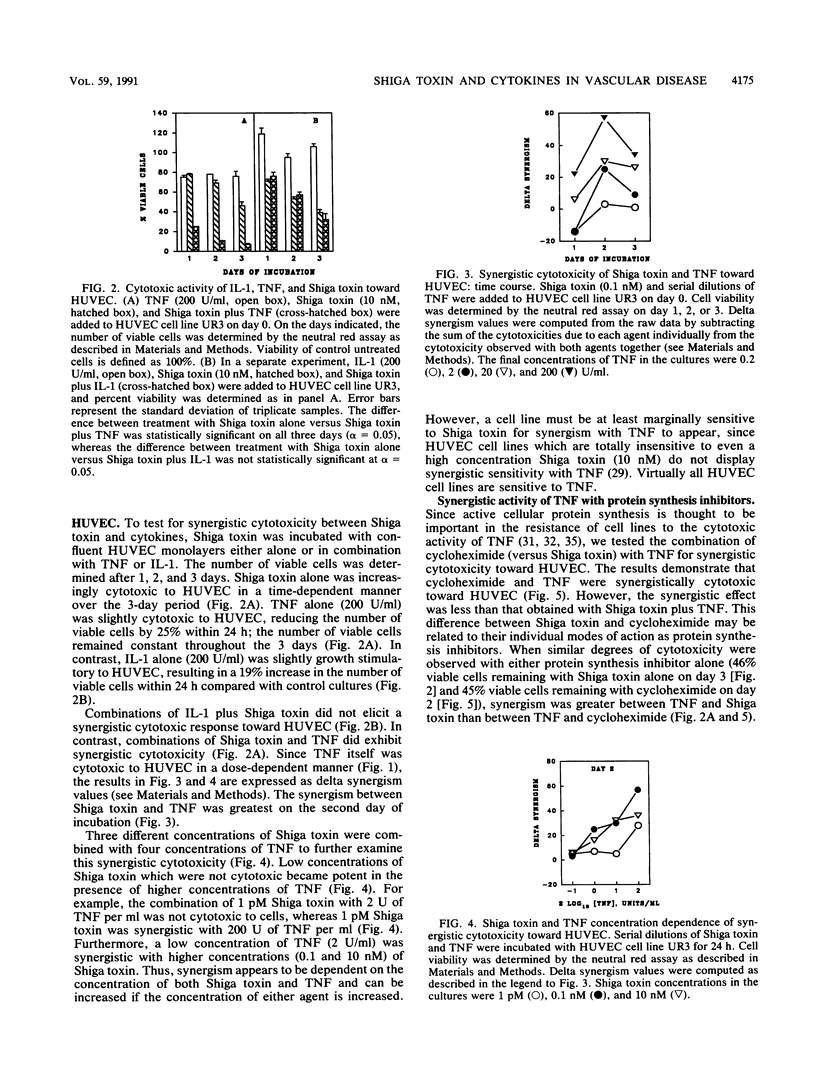
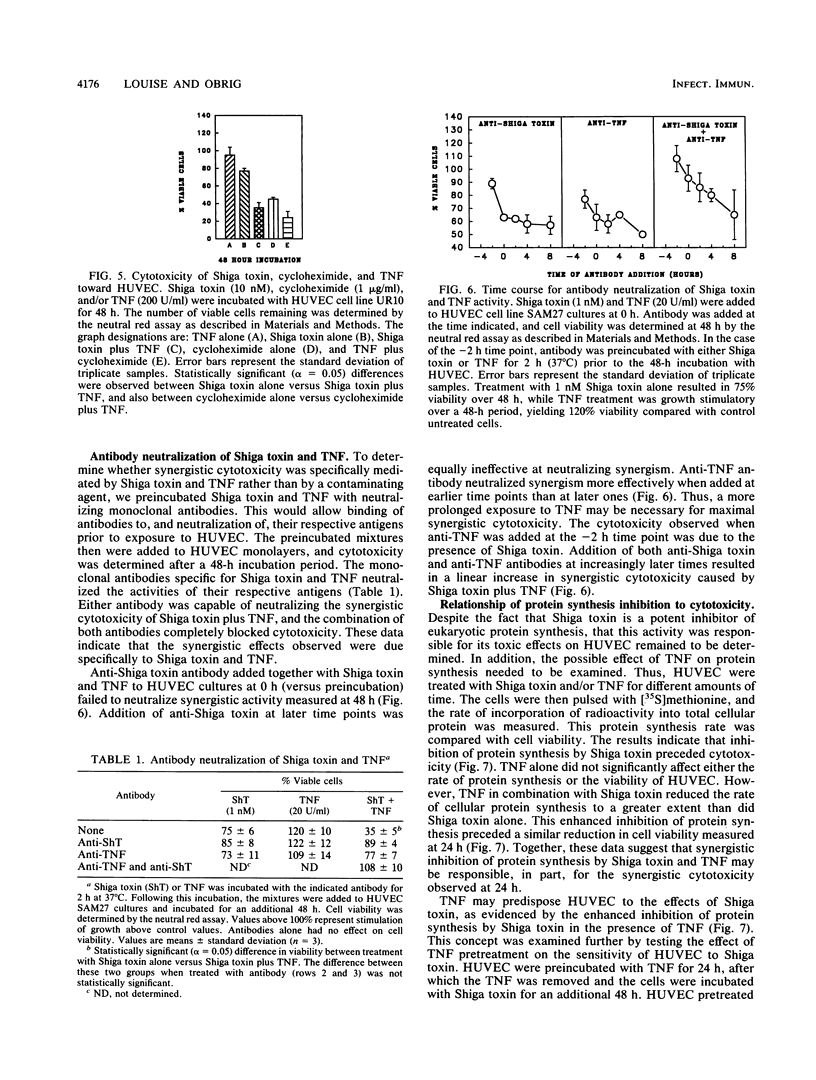
This study explores the relationship between Shiga toxin-producing Shigella or Escherichia coli strains and the development of vascular complications in humans following bacillary dysentery. We propose that endotoxin-elicited interleukin-1 or tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF) may combine with Shiga toxin to facilitate vascular damage characteristic of hemolytic-uremic syndrome. This study examines the cytotoxic effects of Shiga toxin, interleukin-1, and TNF on cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC). Both Shiga toxin and TNF were cytotoxic to HUVEC, although HUVEC obtained from individual umbilical cords differed in their sensitivities to these agents. With Shiga toxin-sensitive HUVEC, combinations of TNF with Shiga toxin resulted in a synergistic cytotoxic effect. In contrast, interleukin-1 was not cytotoxic to HUVEC, nor did it enhance cell death in combination with Shiga toxin. The synergistic cytotoxic response of HUVEC to Shiga toxin and TNF was dose and time dependent for both agents and could be neutralized by monoclonal antibodies directed against either Shiga toxin or TNF. This synergistic response was delayed, being maximal on day 2. Preincubation (24 h) of HUVEC with TNF sensitized the cells to Shiga toxin. TNF alone had no effect on HUVEC protein synthesis but enhanced the inhibitory activity of Shiga toxin. These results are consistent with a role for Shiga toxin in the development of hemolytic-uremic syndrome at the level of the vascular endothelium in humans.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akira S., Hirano T., Taga T., Kishimoto T. Biology of multifunctional cytokines: IL 6 and related molecules (IL 1 and TNF). FASEB J. 1990 Aug;4(11):2860–2867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett T. J., Potter M. E., Strockbine N. A. Evidence for participation of the macrophage in Shiga-like toxin II-induced lethality in mice. Microb Pathog. 1990 Aug;9(2):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90083-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett T. J., Potter M. E., Wachsmuth I. K. Bacterial endotoxin both enhances and inhibits the toxicity of Shiga-like toxin II in rabbits and mice. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3434–3437. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3434-3437.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd B., Lingwood C. Verotoxin receptor glycolipid in human renal tissue. Nephron. 1989;51(2):207–210. doi: 10.1159/000185286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. E., Ussery M. A., Leppla S. H., Rothman S. W. Inhibition of protein synthesis by Shiga toxin: activation of the toxin and inhibition of peptide elongation. FEBS Lett. 1980 Aug 11;117(1):84–88. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80918-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler T., Islam M. R., Azad M. A., Jones P. K. Risk factors for development of hemolytic uremic syndrome during shigellosis. J Pediatr. 1987 Jun;110(6):894–897. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(87)80405-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantey J. R. Shiga toxin--an expanding role in the pathogenesis of infectious diseases. J Infect Dis. 1985 May;151(5):766–771. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.5.766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway E. M., Bach R., Rosenberg R. D., Konigsberg W. H. Tumor necrosis factor enhances expression of tissue factor mRNA in endothelial cells. Thromb Res. 1989 Feb 1;53(3):231–241. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(89)90098-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotran R. S., Pober J. S. Effects of cytokines on vascular endothelium: their role in vascular and immune injury. Kidney Int. 1989 Apr;35(4):969–975. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiklid K., Olsnes S. Interaction of Shigella shigae cytotoxin with receptors on sensitive and insensitive cells. J Recept Res. 1980;1(2):199–213. doi: 10.3109/10799898009044098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong J. S., de Chadarevian J. P., Kaplan B. S. Hemolytic-uremic syndrome. Current concepts and management. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1982 Aug;29(4):835–856. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)34216-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontaine A., Arondel J., Sansonetti P. J. Role of Shiga toxin in the pathogenesis of bacillary dysentery, studied by using a Tox- mutant of Shigella dysenteriae 1. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3099–3109. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3099-3109.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIANANTONIO C., VITACCO M., MENDILAHARZU F., RUTTY A., MENDILAHARZU J. THE HEMOLYTIC-UREMIC SYNDROME. J Pediatr. 1964 Apr;64:478–491. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(64)80337-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser B. M., D'Amore P. A., Michels R. G., Patz A., Fenselau A. Demonstration of vasoproliferative activity from mammalian retina. J Cell Biol. 1980 Feb;84(2):298–304. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.2.298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Nachman R. L., Becker C. G., Minick C. R. Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2745–2756. doi: 10.1172/JCI107470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. M., Lior H., Bezanson G. S. Cytotoxic Escherichia coli O157:H7 associated with haemorrhagic colitis in Canada. Lancet. 1983 Jan 1;1(8314-5):76–76. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91616-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan B. S., Cleary T. G., Obrig T. G. Recent advances in understanding the pathogenesis of the hemolytic uremic syndromes. Pediatr Nephrol. 1990 May;4(3):276–283. doi: 10.1007/BF00857676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A. Infection by verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jan;2(1):15–38. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., Petric M., Lim C., Fleming P. C., Arbus G. S., Lior H. The association between idiopathic hemolytic uremic syndrome and infection by verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1985 May;151(5):775–782. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.5.775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., Steele B. T., Petric M., Lim C. Sporadic cases of haemolytic-uraemic syndrome associated with faecal cytotoxin and cytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli in stools. Lancet. 1983 Mar 19;1(8325):619–620. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91795-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirstein M., Baglioni C. Tumor necrosis factor induces synthesis of two proteins in human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9565–9567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koster F. T., Boonpucknavig V., Sujaho S., Gilman R. H., Rahaman M. M. Renal histopathology in the hemolytic-uremic syndrome following shigellosis. Clin Nephrol. 1984 Feb;21(2):126–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koster F., Levin J., Walker L., Tung K. S., Gilman R. H., Rahaman M. M., Majid M. A., Islam S., Williams R. C., Jr Hemolytic-uremic syndrome after shigellosis. Relation to endotoxemia and circulating immune complexes. N Engl J Med. 1978 Apr 27;298(17):927–933. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197804272981702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larrick J. W., Wright S. C. Cytotoxic mechanism of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. FASEB J. 1990 Nov;4(14):3215–3223. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.14.2172061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., DuPont H. L., Formal S. B., Hornick R. B., Takeuchi A., Gangarosa E. J., Snyder M. J., Libonati J. P. Pathogenesis of Shigella dysenteriae 1 (Shiga) dysentery. J Infect Dis. 1973 Mar;127(3):261–270. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.3.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg A. A., Brown J. E., Strömberg N., Westling-Ryd M., Schultz J. E., Karlsson K. A. Identification of the carbohydrate receptor for Shiga toxin produced by Shigella dysenteriae type 1. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1779–1785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Holmes R. K. Shiga and Shiga-like toxins. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):206–220. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.206-220.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obrig T. G., Del Vecchio P. J., Brown J. E., Moran T. P., Rowland B. M., Judge T. K., Rothman S. W. Direct cytotoxic action of Shiga toxin on human vascular endothelial cells. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2373–2378. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2373-2378.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obrig T. G., Del Vecchio P. J., Karmali M. A., Petric M., Moran T. P., Judge T. K. Pathogenesis of haemolytic uraemic syndrome. Lancet. 1987 Sep 19;2(8560):687–687. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92473-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obrig T. G., Moran T. P., Brown J. E. The mode of action of Shiga toxin on peptide elongation of eukaryotic protein synthesis. Biochem J. 1987 Jun 1;244(2):287–294. doi: 10.1042/bj2440287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohlman T. H., Harlan J. M. Human endothelial cell response to lipopolysaccharide, interleukin-1, and tumor necrosis factor is regulated by protein synthesis. Cell Immunol. 1989 Mar;119(1):41–52. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(89)90222-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghu G., Striker L. J., Striker G. E. Lipopolysaccharide-mediated injury to cultured human glomerular endothelial cells. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1986 Mar;38(3):275–281. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(86)90237-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghupathy P., Date A., Shastry J. C., Sudarsanam A., Jadhav M. Haemolytic-uraemic syndrome complicating shigella dystentery in south Indian children. Br Med J. 1978 Jun 10;1(6126):1518–1521. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6126.1518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisbig R., Olsnes S., Eiklid K. The cytotoxic activity of Shigella toxin. Evidence for catalytic inactivation of the 60 S ribosomal subunit. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8739–8744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson S. E., Karmali M. A., Becker L. E., Smith C. R. The histopathology of the hemolytic uremic syndrome associated with verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli infections. Hum Pathol. 1988 Sep;19(9):1102–1108. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(88)80093-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddell R. J., Clothier R. H., Balls M. An evaluation of three in vitro cytotoxicity assays. Food Chem Toxicol. 1986 Jun-Jul;24(6-7):469–471. doi: 10.1016/0278-6915(86)90095-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley L. W., Remis R. S., Helgerson S. D., McGee H. B., Wells J. G., Davis B. R., Hebert R. J., Olcott E. S., Johnson L. M., Hargrett N. T. Hemorrhagic colitis associated with a rare Escherichia coli serotype. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 24;308(12):681–685. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303243081203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Olsnes S., Brown J. E., Petersen O. W., van Deurs B. Endocytosis from coated pits of Shiga toxin: a glycolipid-binding protein from Shigella dysenteriae 1. J Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;108(4):1331–1343. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.4.1331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarpati E. M., Sadler J. E. Regulation of endothelial cell coagulant properties. Modulation of tissue factor, plasminogen activator inhibitors, and thrombomodulin by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate and tumor necrosis factor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20705–20713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



