Abstract
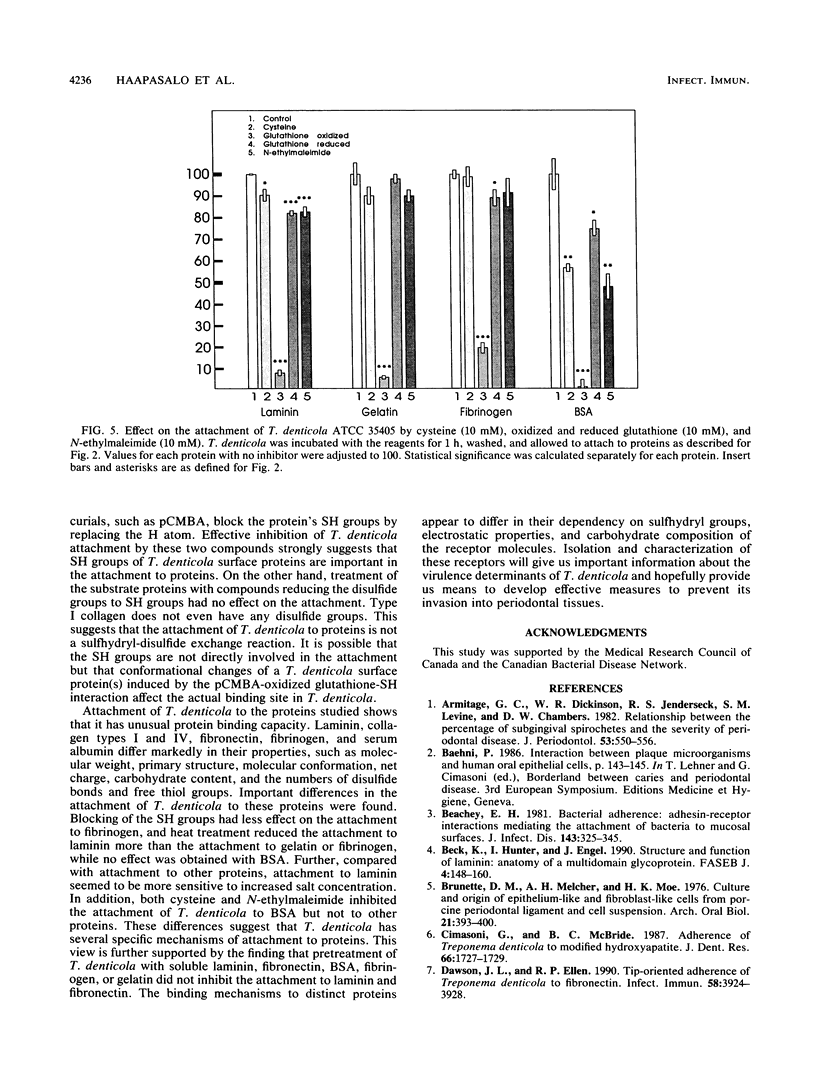
Attachment of Treponema denticola ATCC 35405 to laminin, a major basement membrane protein, and to other proteins was studied. Microdilution plates were coated with the proteins, and the attachment of T. denticola was measured by the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay technique. Compared with bovine serum albumin (BSA), T. denticola had a high affinity to laminin, fibronectin, fibrinogen, and gelatin, as well as to type I and type IV collagens. Attachment to RGD peptide (Gly-Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser, the integrin recognition sequence) was only about 30% of that to laminin and was comparable to attachment to BSA. Tests with laminin fragments obtained through elastase digestion showed that the spirochetes attached well to an A-chain 140-kDa fragment involved in eukaryote cell attachment but did not attach to a 50-kDa fragment that includes the heparin binding site. Pretreatment of T. denticola with soluble laminin, fibronectin, gelatin, BSA, or fibrinogen had no effect on the attachment of the bacteria to laminin or fibronectin. A wide variety of compounds were tested for their possible inhibitory actions on the attachment. While most treatments of T. denticola ATCC 35405 had little or no effect on the attachment to proteins, sulfhydryl reagents p-chloromercuribenzoic acid (pCMBA) and oxidized glutathione inhibited the attachment by 70 to 99%, depending on the protein. When T. denticola was first allowed to attach to proteins, addition of pCMBA or oxidized glutathione could no longer reverse the attachment. Heat treatment of the spirochetes also markedly reduced the attachment to laminin, gelatin, and fibrinogen but not to BSA. Mixed glycosidase treatment of the spirochetes inhibited the attachment by 20 to 80%. None of the above treatments of the substrate proteins had any marked effect on the spirochete attachment. The results indicate that T. denticola has the capacity to bind to many different kinds of proteins by utilizing specific attachment mechanisms. The binding appears to involve protein SH groups and/or carbohydrate residues on the surface of T. denticola.
Full text
PDF


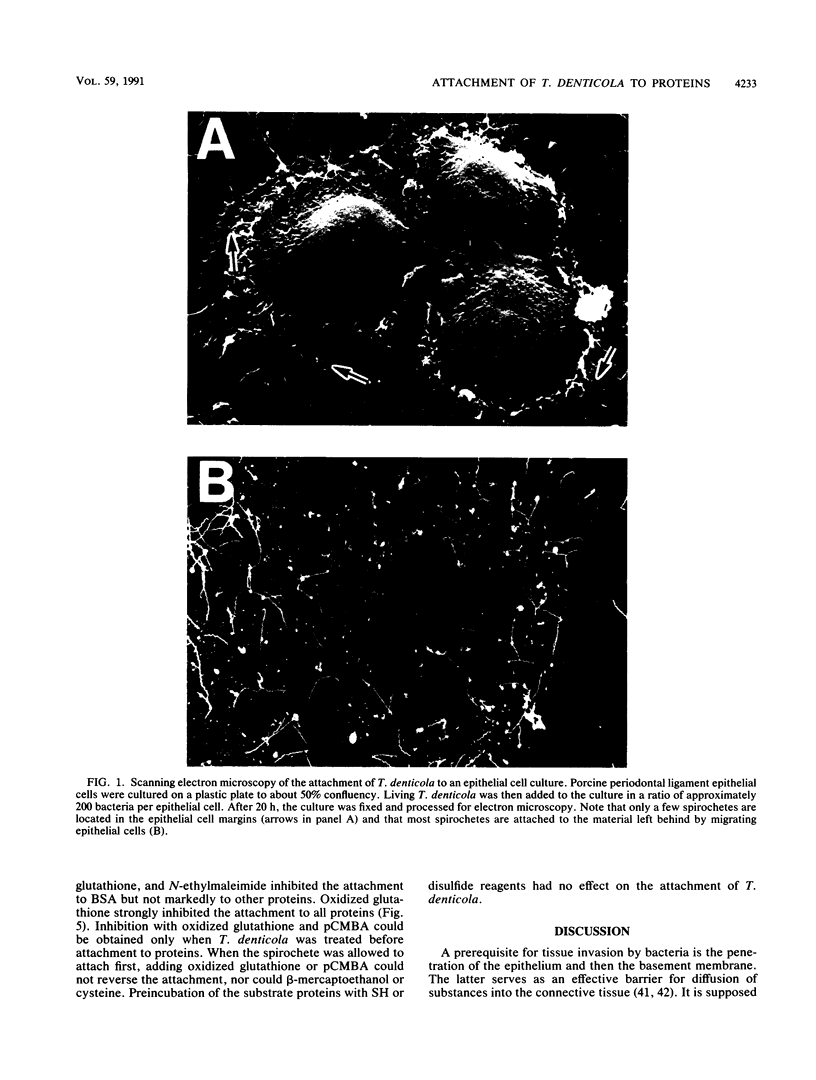
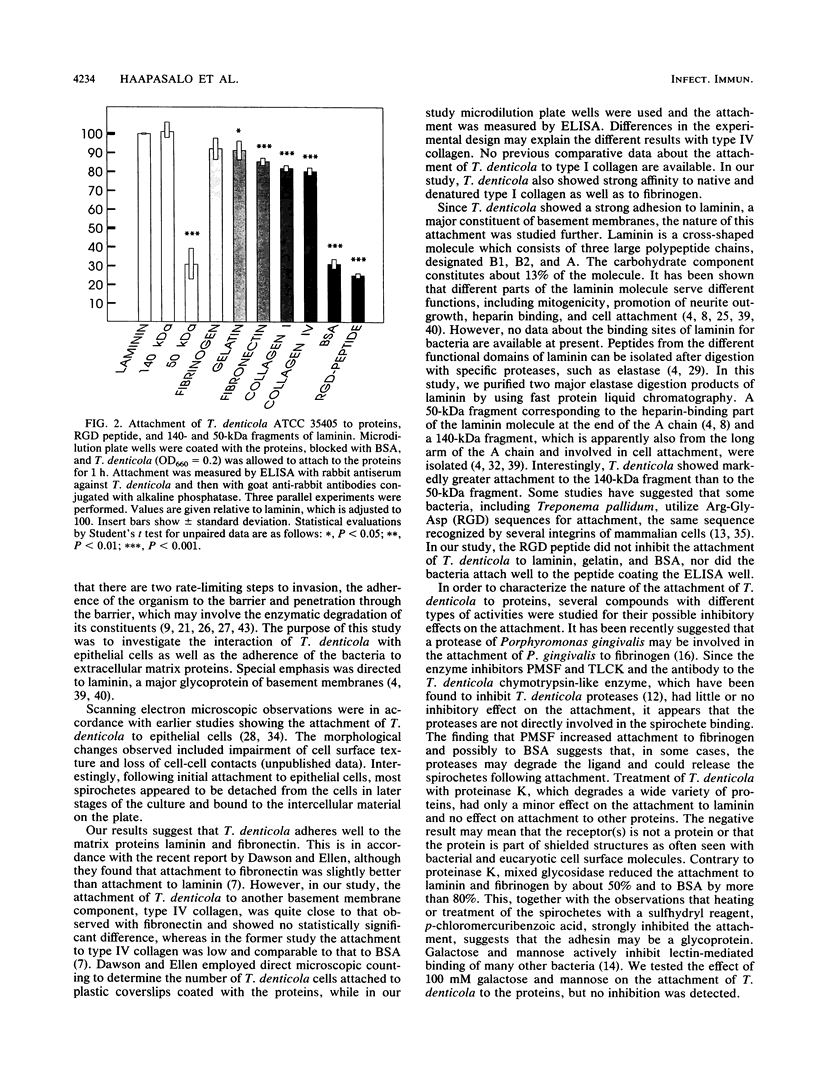
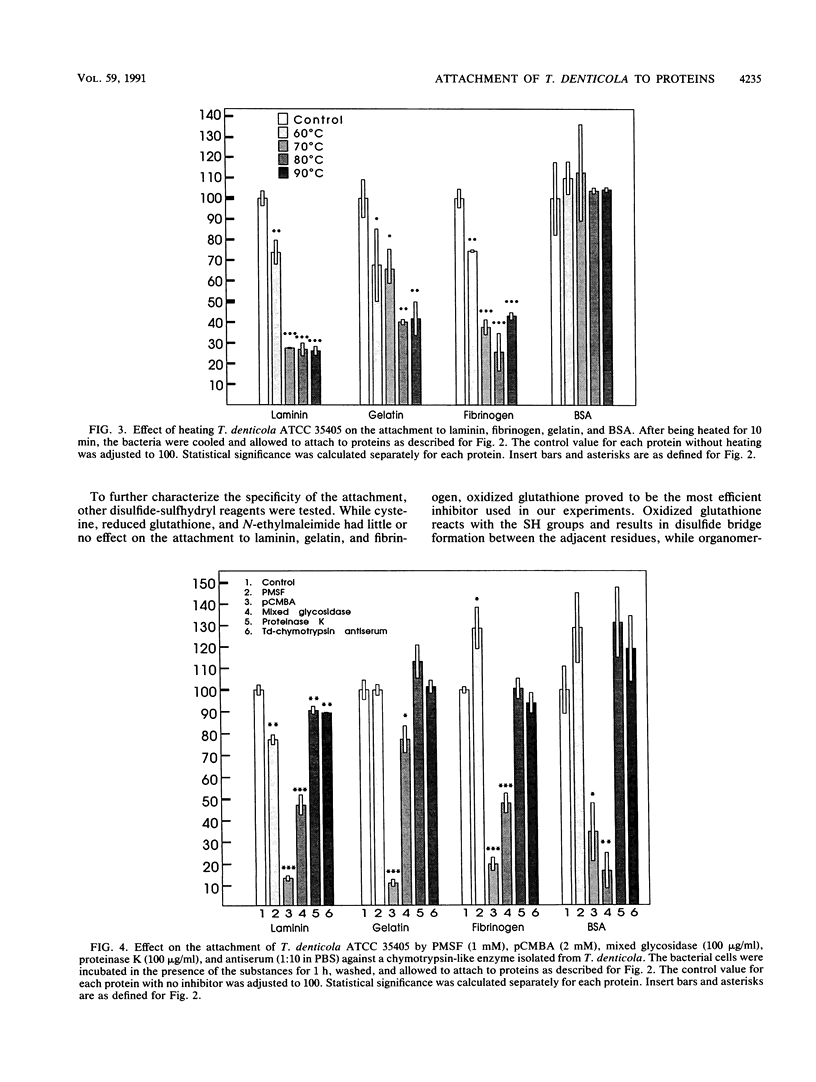

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armitage G. C., Dickinson W. R., Jenderseck R. S., Levine S. M., Chambers D. W. Relationship between the percentage of subgingival spirochetes and the severity of periodontal disease. J Periodontol. 1982 Sep;53(9):550–556. doi: 10.1902/jop.1982.53.9.550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H. Bacterial adherence: adhesin-receptor interactions mediating the attachment of bacteria to mucosal surface. J Infect Dis. 1981 Mar;143(3):325–345. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.3.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck K., Hunter I., Engel J. Structure and function of laminin: anatomy of a multidomain glycoprotein. FASEB J. 1990 Feb 1;4(2):148–160. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.2.2404817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunette D. M., Melcher A. H., Moe H. K. Culture and origin of epithelium-like and fibroblast-like cells from porcine periodontal ligament explants and cell suspensions. Arch Oral Biol. 1976;21(7):393–400. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(76)90001-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cimasoni G., McBride B. C. Adherence of Treponema denticola to modified hydroxyapatite. J Dent Res. 1987 Dec;66(12):1727–1729. doi: 10.1177/00220345870660120601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson J. R., Ellen R. P. Tip-oriented adherence of Treponema denticola to fibronectin. Infect Immun. 1990 Dec;58(12):3924–3928. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.12.3924-3928.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar D., Timpl R., Thoenen H. The heparin-binding domain of laminin is responsible for its effects on neurite outgrowth and neuronal survival. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1463–1468. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01997.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiehn N. E. Enzyme activities from eight small-sized oral spirochetes. Scand J Dent Res. 1986 Apr;94(2):132–140. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1986.tb01377.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Cleveland P., Johnson R. C., Miller J. N., Sykes J. A. Scanning electron microscopy of Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain) attached to cultured mammalian cells. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;130(3):1333–1344. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.3.1333-1344.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank R. M. Bacterial penetration in the apical pocket wall of advanced human periodontitis. J Periodontal Res. 1980 Nov;15(6):563–573. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1980.tb00315.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenier D., Uitto V. J., McBride B. C. Cellular location of a Treponema denticola chymotrypsinlike protease and importance of the protease in migration through the basement membrane. Infect Immun. 1990 Feb;58(2):347–351. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.2.347-351.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolenbrander P. E. Surface recognition among oral bacteria: multigeneric coaggregations and their mediators. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1989;17(2):137–159. doi: 10.3109/10408418909105746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LISTGARTEN M. A. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC OBSERVATIONS ON THE BACTERIAL FLORA OF ACUTE NECROTIZING ULCERATIVE GINGIVITIS. J Periodontol. 1965 Jul-Aug;36:328–339. doi: 10.1902/jop.1965.36.4.328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lantz M. S., Allen R. D., Vail T. A., Switalski L. M., Hook M. Specific cell components of Bacteroides gingivalis mediate binding and degradation of human fibrinogen. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(2):495–504. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.495-504.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Listgarten M. A., Levin S. Positive correlation between the proportions of subgingival spirochetes and motile bacteria and susceptibility of human subjects to periodontal deterioration. J Clin Periodontol. 1981 Apr;8(2):122–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.1981.tb02352.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesche W. J., Syed S. A., Schmidt E., Morrison E. C. Bacterial profiles of subgingival plaques in periodontitis. J Periodontol. 1985 Aug;56(8):447–456. doi: 10.1902/jop.1985.56.8.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maltha J. C., Mikx F. H., Kuijpers F. J. Necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis in beagle dogs. III. Distribution of spirochetes in interdental gingival tissue. J Periodontal Res. 1985 Sep;20(5):522–531. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1985.tb00836.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrilees M. J., Sodek J., Aubin J. E. Effects of cells of epithelial rests of Malassez and endothelial cells on synthesis of glycosaminoglycans by periodontal ligament fibroblasts in vitro. Dev Biol. 1983 May;97(1):146–153. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Holdeman L. V., Smibert R. M., Hash D. E., Burmeister J. A., Ranney R. R. Bacteriology of severe periodontitis in young adult humans. Infect Immun. 1982 Dec;38(3):1137–1148. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.3.1137-1148.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitzan D., Sperry J. F., Wilkins T. D. Fibrinolytic activity of oral anaerobic bacteria. Arch Oral Biol. 1978;23(6):465–470. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(78)90078-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta K., Makinen K. K., Loesche W. J. Purification and characterization of an enzyme produced by Treponema denticola capable of hydrolyzing synthetic trypsin substrates. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):213–220. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.213-220.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen I. Attachment of Treponema denticola to cultured human epithelial cells. Scand J Dent Res. 1984 Feb;92(1):55–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1984.tb00860.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott U., Odermatt E., Engel J., Furthmayr H., Timpl R. Protease resistance and conformation of laminin. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Mar;123(1):63–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06499.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens R. B. Glandular epithelial cells from mice: a method for selective cultivation. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Apr;52(4):1375–1378. doi: 10.1093/jnci/52.4.1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsson M., Saladin K., Landwehr R. Binding of Ca2+ influences susceptibility of laminin to proteolytic digestion and interactions between domain-specific laminin fragments. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Nov 15;177(3):477–481. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14397.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E. Cell attachment activity of fibronectin can be duplicated by small synthetic fragments of the molecule. Nature. 1984 May 3;309(5963):30–33. doi: 10.1038/309030a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao C. N., Margulies I. M., Tralka T. S., Terranova V. P., Madri J. A., Liotta L. A. Isolation of a subunit of laminin and its role in molecular structure and tumor cell attachment. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9740–9744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reijntjens F. M., Mikx F. H., Wolters-Lutgerhorst J. M., Maltha J. C. Adherence of oral treponemes and their effect on morphological damage and detachment of epithelial cells in vitro. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):642–647. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.642-647.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Pierschbacher M. D. New perspectives in cell adhesion: RGD and integrins. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):491–497. doi: 10.1126/science.2821619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saglie F. R., Carranza F. A., Jr, Newman M. G., Cheng L., Lewin K. J. Identification of tissue-invading bacteria in human periodontal disease. J Periodontal Res. 1982 Sep;17(5):452–455. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1982.tb02024.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saglie R., Newman M. G., Carranza F. A., Jr, Pattison G. L. Bacterial invasion of gingiva in advanced periodontitis in humans. J Periodontol. 1982 Apr;53(4):217–222. doi: 10.1902/jop.1982.53.4.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salonen J., Uitto V. J., Pan Y. M., Oda D. Proliferating oral epithelial cells in culture are capable of both extracellular and intracellular degradation of interstitial collagen. Matrix. 1991 Feb;11(1):43–55. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8832(11)80226-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki M., Kleinman H. K., Huber H., Deutzmann R., Yamada Y. Laminin, a multidomain protein. The A chain has a unique globular domain and homology with the basement membrane proteoglycan and the laminin B chains. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16536–16544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki M., Yamada Y. The laminin B2 chain has a multidomain structure homologous to the B1 chain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 15;262(35):17111–17117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J., Stinson F. L., Parker R. B. The passage of tritiated bacterial endotoxin across intact gingival crevicular epithelium. J Periodontol. 1972 May;43(5):270–276. doi: 10.1902/jop.1972.43.5.270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uitto V. J. Degradation of basement membrane collagen by proteinases from human gingiva, leukocytes and bacterial plaque. J Periodontol. 1983 Dec;54(12):740–745. doi: 10.1902/jop.1983.54.12.740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uitto V. J., Grenier D., Chan E. C., McBride B. C. Isolation of a chymotrypsinlike enzyme from Treponema denticola. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2717–2722. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2717-2722.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]