Abstract
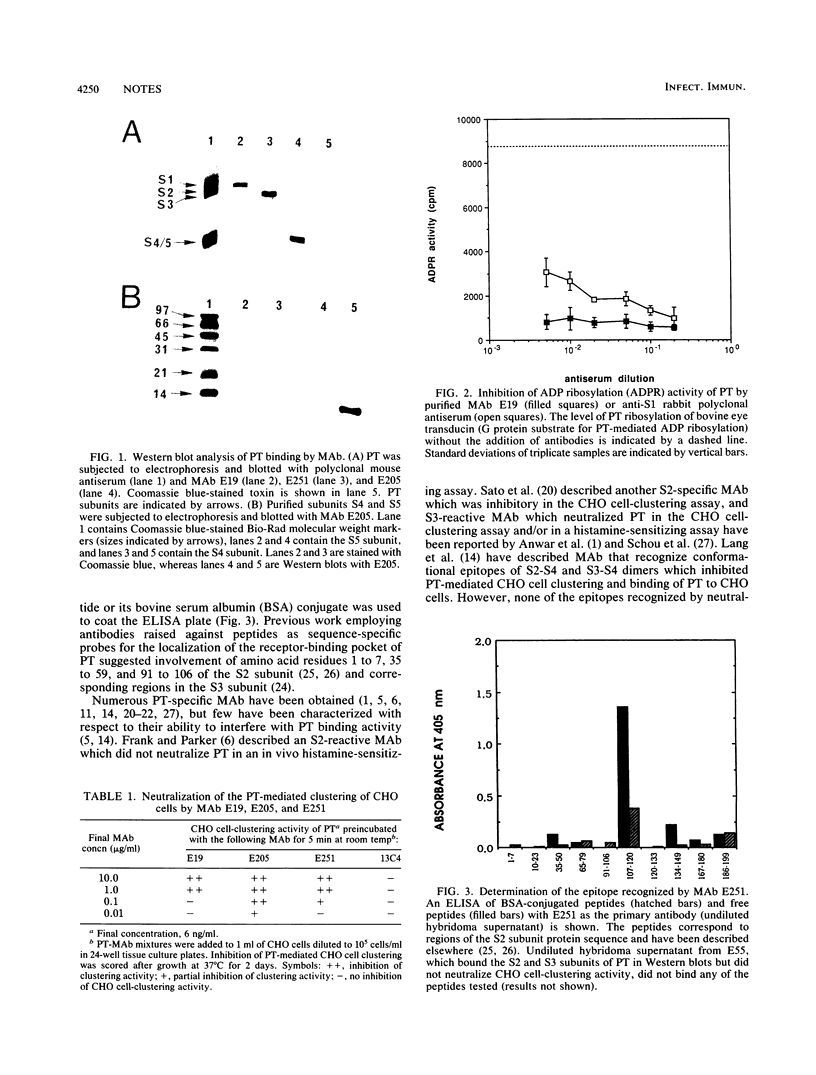
Three murine monoclonal antibodies (MAb), E19, E205, and E251, raised against pertussis toxin reacted in Western blots (immunoblots) with the S1, S4, and S2-S3 subunits, respectively, and neutralized the Chinese hamster ovary cell-clustering activity of pertussis toxin. MAb E251 recognized a linear synthetic peptide corresponding to amino acids 107 to 120 of the S2 subunit, suggesting a role for this region in receptor binding.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartley T. D., Whiteley D. W., Mar V. L., Burns D. L., Burnette W. N. Pertussis holotoxoid formed in vitro with a genetically deactivated S1 subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8353–8357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ey P. L., Prowse S. J., Jenkin C. R. Isolation of pure IgG1, IgG2a and IgG2b immunoglobulins from mouse serum using protein A-sepharose. Immunochemistry. 1978 Jul;15(7):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank D. W., Parker C. D. Interaction of monoclonal antibodies with pertussis toxin and its subunits. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):195–201. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.195-201.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillenius P., Jätmaa E., Askelöf P., Granström M., Tiru M. The standardization of an assay for pertussis toxin and antitoxin in microplate culture of Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Stand. 1985 Jan;13(1):61–66. doi: 10.1016/s0092-1157(85)80034-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewlett E. L., Sauer K. T., Myers G. A., Cowell J. L., Guerrant R. L. Induction of a novel morphological response in Chinese hamster ovary cells by pertussis toxin. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1198–1203. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1198-1203.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearney J. F., Radbruch A., Liesegang B., Rajewsky K. A new mouse myeloma cell line that has lost immunoglobulin expression but permits the construction of antibody-secreting hybrid cell lines. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1548–1550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenimer J. G., Kim K. J., Probst P. G., Manclark C. R., Burstyn D. G., Cowell J. L. Monoclonal antibodies to pertussis toxin: utilization as probes of toxin function. Hybridoma. 1989 Feb;8(1):37–51. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1989.8.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A., Mountzouros K. T., Schad P. A., Cieplak W., Cowell J. L. Pertussis toxin analog with reduced enzymatic and biological activities is a protective immunogen. Infect Immun. 1990 Oct;58(10):3337–3347. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.10.3337-3347.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang A. B., Ganss M. T., Cryz S. J., Jr Monoclonal antibodies that define neutralizing epitopes of pertussis toxin: conformational dependence and epitope mapping. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2660–2665. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2660-2665.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loosmore S. M., Zealey G. R., Boux H. A., Cockle S. A., Radika K., Fahim R. E., Zobrist G. J., Yacoob R. K., Chong P. C., Yao F. L. Engineering of genetically detoxified pertussis toxin analogs for development of a recombinant whooping cough vaccine. Infect Immun. 1990 Nov;58(11):3653–3662. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.11.3653-3662.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munoz J. J., Arai H., Cole R. L. Mouse-protecting and histamine-sensitizing activities of pertussigen and fimbrial hemagglutinin from Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):243–250. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.243-250.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nencioni L., Pizza M., Bugnoli M., De Magistris T., Di Tommaso A., Giovannoni F., Manetti R., Marsili I., Matteucci G., Nucci D. Characterization of genetically inactivated pertussis toxin mutants: candidates for a new vaccine against whooping cough. Infect Immun. 1990 May;58(5):1308–1315. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.5.1308-1315.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A., Irons L. I., Ashworth L. A. Pertussis vaccine: present status and future prospects. Vaccine. 1985 Mar;3(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(85)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Ito A., Chiba J., Sato Y. Monoclonal antibody against pertussis toxin: effect on toxin activity and pertussis infections. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):422–428. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.422-428.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Sato Y., Ito A., Ohishi I. Effect of monoclonal antibody to pertussis toxin on toxin activity. Infect Immun. 1987 Apr;55(4):909–915. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.4.909-915.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Sato Y. Protective activities in mice of monoclonal antibodies against pertussis toxin. Infect Immun. 1990 Oct;58(10):3369–3374. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.10.3369-3374.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Arai H. Leucocytosis-promoting factor of Bordetella pertussis. I. Purification and characterization. Infect Immun. 1972 Dec;6(6):899–904. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.6.899-904.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. A., Raupach B., Szulczynski M., Marzillier J. Identification of linear B-cell determinants of pertussis toxin associated with the receptor recognition site of the S3 subunit. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1402–1408. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1402-1408.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. A., Schmidt W. Inhibition of pertussis toxin binding to model receptors by antipeptide antibodies directed at an antigenic domain of the S2 subunit. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3828–3833. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3828-3833.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt W., Schmidt M. A. Mapping of linear B-cell epitopes of the S2 subunit of pertussis toxin. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):438–445. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.438-445.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schou C., Au-Jensen M., Heron I. The interaction between pertussis toxin and 10 monoclonal antibodies. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand C. 1987 Oct;95(5):177–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1987.tb00028.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strockbine N. A., Marques L. R., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies against Shiga-like toxin from Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):695–700. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.695-700.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhoeyen M., Milstein C., Winter G. Reshaping human antibodies: grafting an antilysozyme activity. Science. 1988 Mar 25;239(4847):1534–1536. doi: 10.1126/science.2451287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehland J., Weber K. Turnover of the carboxy-terminal tyrosine of alpha-tubulin and means of reaching elevated levels of detyrosination in living cells. J Cell Sci. 1987 Sep;88(Pt 2):185–203. doi: 10.1242/jcs.88.2.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]