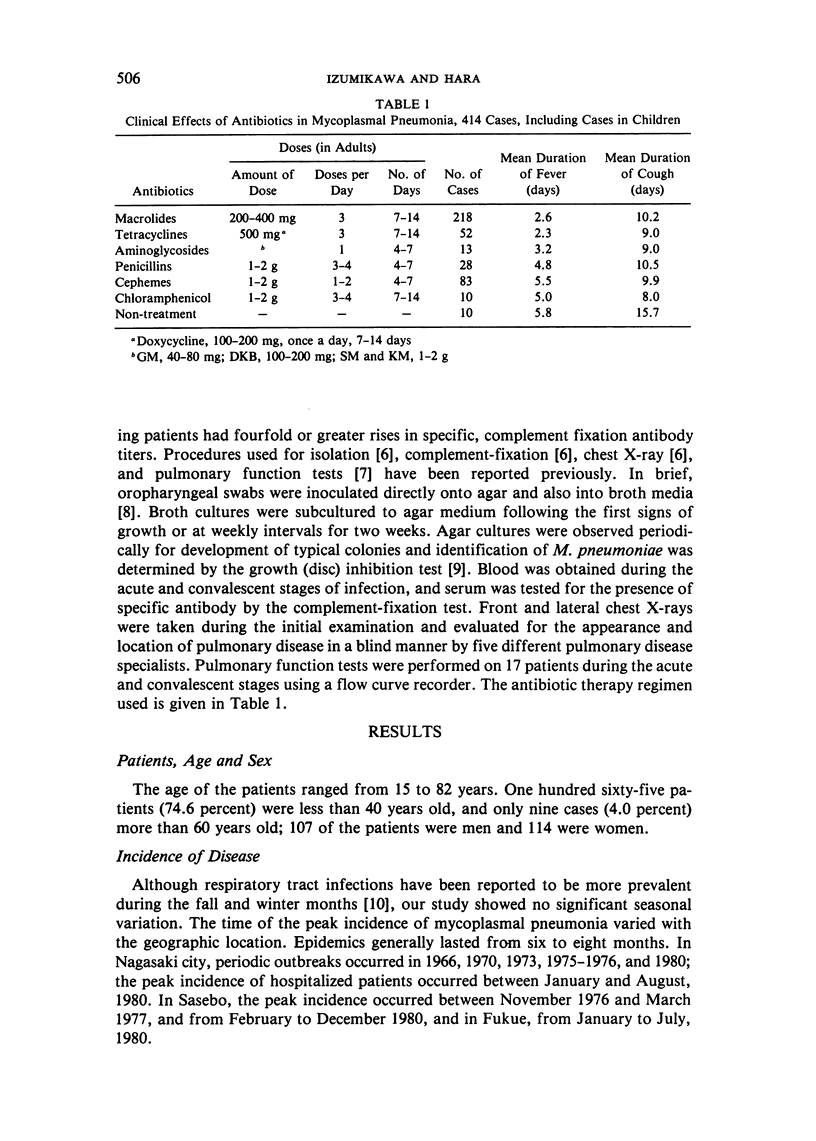
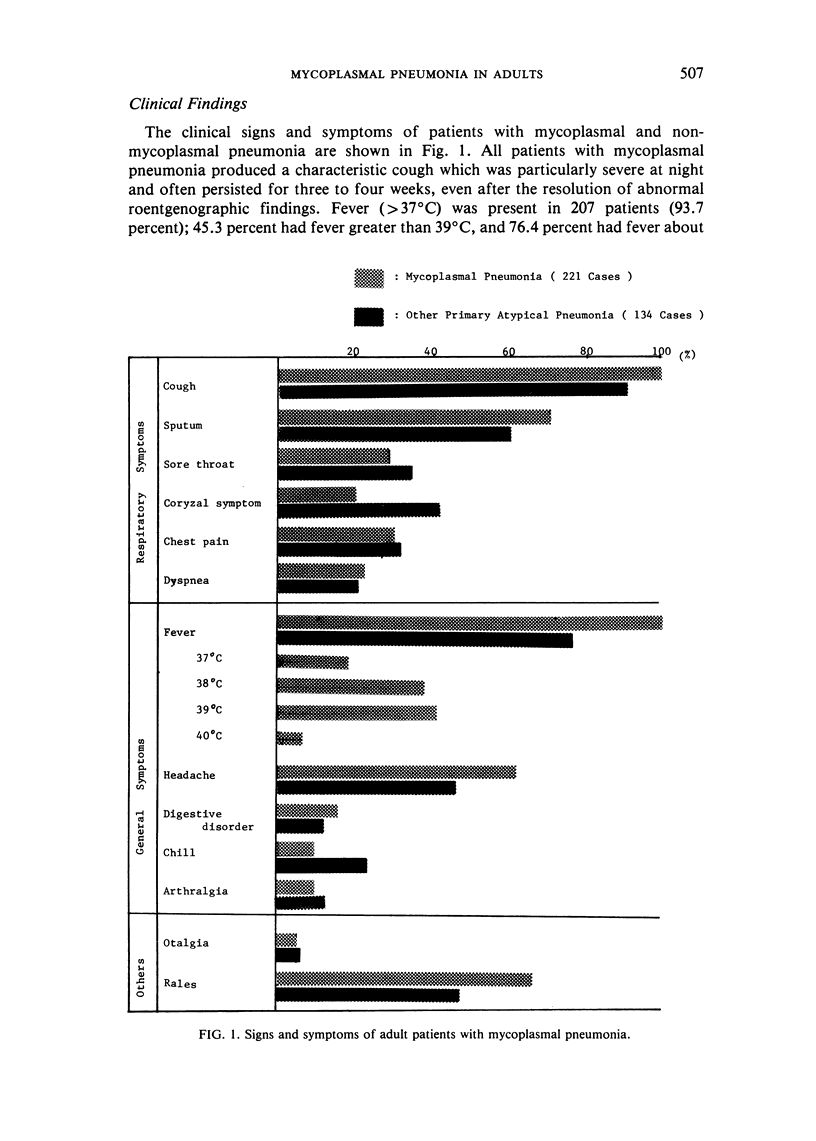
Abstract
We have examined 221 cases of mycoplasmal pneumonia in adults during the past 17 years. During this time epidemic waves occurred every three to four years. The incidence of disease was highest in patients 20 to 30 years of age. The most common clinical features were cough, fever, sputum, and rales. The most characteristic feature was a persistent cough which lasted about three to four weeks. Roentgenographic examinations showed a variety of patterns, but the most consistent feature was a feathery shadow, appearing in the lower field of either or both of the lungs. Lung function tests showed peripheral airway impairment. Although roentgenographic examination provided useful information, it could not be used as a pathognomic feature of mycoplasmal pneumonia. Tetracyclines were most effective for eliminating clinical symptoms, whereas the macrolides provided the best response based on roentgenographic evaluations.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brolin I., Wernstedt L. Radiographic appearance of mycoplasmal pneumonai. Scand J Respir Dis. 1978 Aug;59(4):179–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANOCK R. M., HAYFLICK L., BARILE M. F. Growth on artificial medium of an agent associated with atypical pneumonia and its identification as a PPLO. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jan 15;48:41–49. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLYDE W. A., Jr MYCOPLASMA SPECIES IDENTIFICATION BASED UPON GROWTH INHIBITION BY SPECIFIC ANTISERA. J Immunol. 1964 Jun;92:958–965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassell G. H., Cole B. C. Mycoplasmas as agents of human disease. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jan 8;304(2):80–89. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198101083040204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denny F. W., Clyde W. A., Jr, Glezen W. P. Mycoplasma pneumoniae disease: clinical spectrum, pathophysiology, epidemiology, and control. J Infect Dis. 1971 Jan;123(1):74–92. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.1.74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foy H. M., Kenny G. E., McMahan R., Mansy A. M., Grayston J. T. Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in an urban area. Five years of surveillance. JAMA. 1970 Nov 30;214(9):1666–1672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara K., Izumikawa K., Kinoshita I., Ota M., Ikebe A. Experimental infection with Mycoplasma pneumoniae in the young hamster: location of ferritin-labeled antibody binding to infective tissue. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1974 Dec;114(4):315–337. doi: 10.1620/tjem.114.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izumikawa K., Suzuyama Y., Sai M., Suyama N., Tomita H., Komori M., Iwasaki H., Fukui M., Hara K. Lung function in adults with mycoplasmal pneumonia. Jpn J Med. 1982 Jan;21(1):17–21. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine1962.21.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koletsky R. J., Weinstein A. J. Fulminant Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Report of a fatal case, and a review of the literature. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Sep;122(3):491–496. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.122.3.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lind K., Bentzon M. W. The incidence of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections in Denmark over the past seventeen years: a review. Infection. 1976;4(1 Suppl):29–32. doi: 10.1007/BF01638419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Masur H., Senterfit L. B., Roberts R. B. The protean manifestations of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in adults. Am J Med. 1975 Feb;58(2):229–242. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90574-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pönkä A. The occurrence and clinical picture of serologically verified Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections with emphasis on central nervous system, cardiac and joint manifestations. Ann Clin Res. 1979;11 (Suppl 24):1–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosmus H. H., Pare J. A., Masson A. M., Fraser R. G. Roentgenographic patterns of acute mycoplasma and viral pneumonitis. J Can Assoc Radiol. 1968 Jun;19(2):74–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOBESLAVSKY O., ABRAHAMOVIC M. THE ETIOLOGICAL ROLE OF MYCOPLASMA PNEUMONIAE IN OTITIS MEDIA IN CHILDREN. Pediatrics. 1965 Apr;35:652–657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


