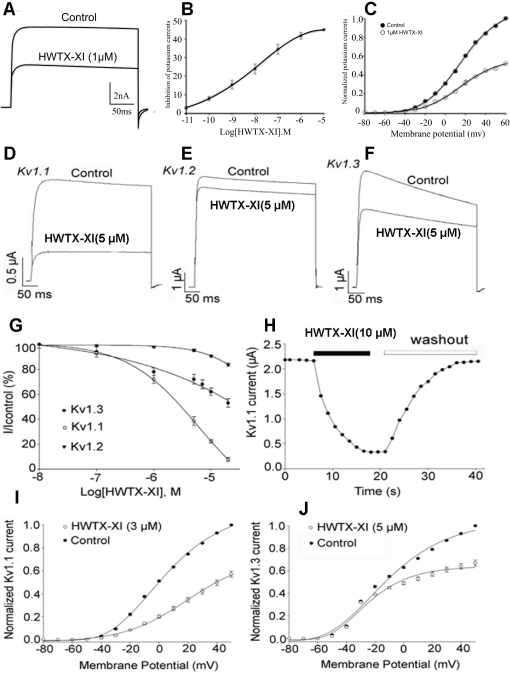
There were a number of errors in the legend for Figure 3, panels D-H. The corrected text is shown here:
Figure 3. Effects of HWTX-XI on Kv channels.
(A) 1 µM HWTX-XI evidently reduced the control potassium currents amplitude in rat DRG neurons by 41.7±1.8% (n = 5). (B) Concentration-response relationship for HWTX-XI inhibition of potassium currents expressed on rat DRG neurons. Each data point (mean±S.E.) arises from 5–7 cells. The solid line through the data is a fit of I/Imax = 1/[1+exp(C–IC50)/Κ]. (C) Effect of HWTX-XI on steady-state current-voltage relationship of potassium channels on rat DRG neurons. DRG cells were held at −80 mV and stepped to test potentials of −80 to +60 mV (mean±SD, n = 4). (D–F) 5 µM HWTX-XI evidently reduced the control potassium currents (Kv1.1, D; Kv1.2, E; Kv1.3, F) amplitude in X. laevis oocytes. (G) Concentration-response relationship for HWTX-XI inhibition of potassium currents expressed in X. laevis oocytes. Each data point (mean±S.E.) arises from 5–7 cells. The solid line through the data is a fit of I/Imax = 1/[1+exp(C−IC50)/Κ]. (H) At a concentration of 10 µM, HWTX-XI produced a rapid (τ<12±2 s for steady-state inhibition, n = 5) inhibition which is readily reversible with the time constant of 21±3 s upon removal of the toxin. (I–J) The current-voltage curves of Kv1.1 (I) and Kv1.3(J) currents activated by 3 µM and 5 µM HWTX-XI respectively.