Abstract
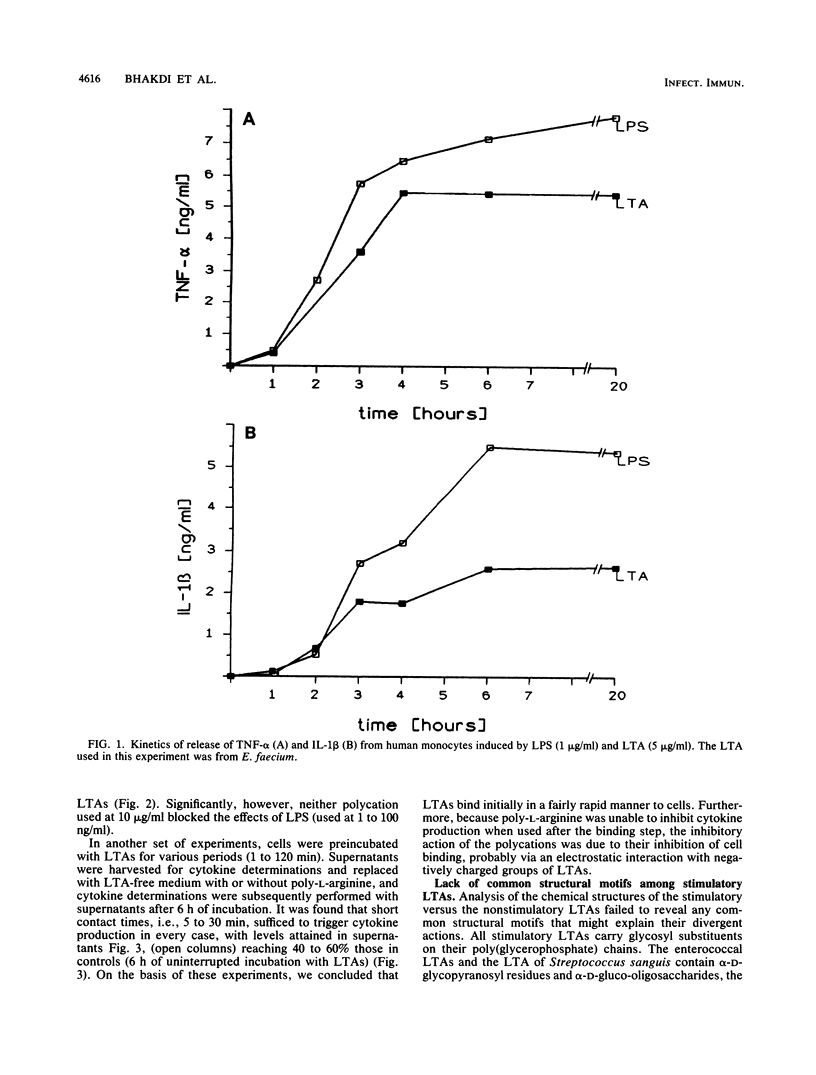
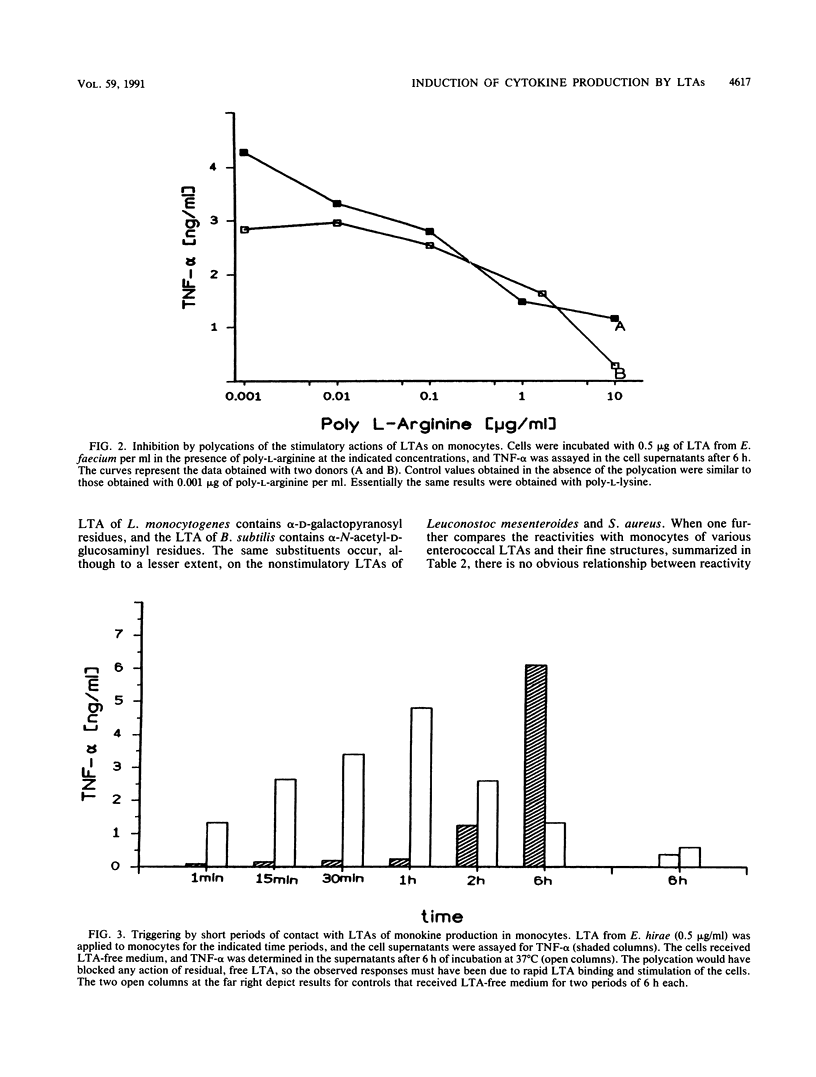
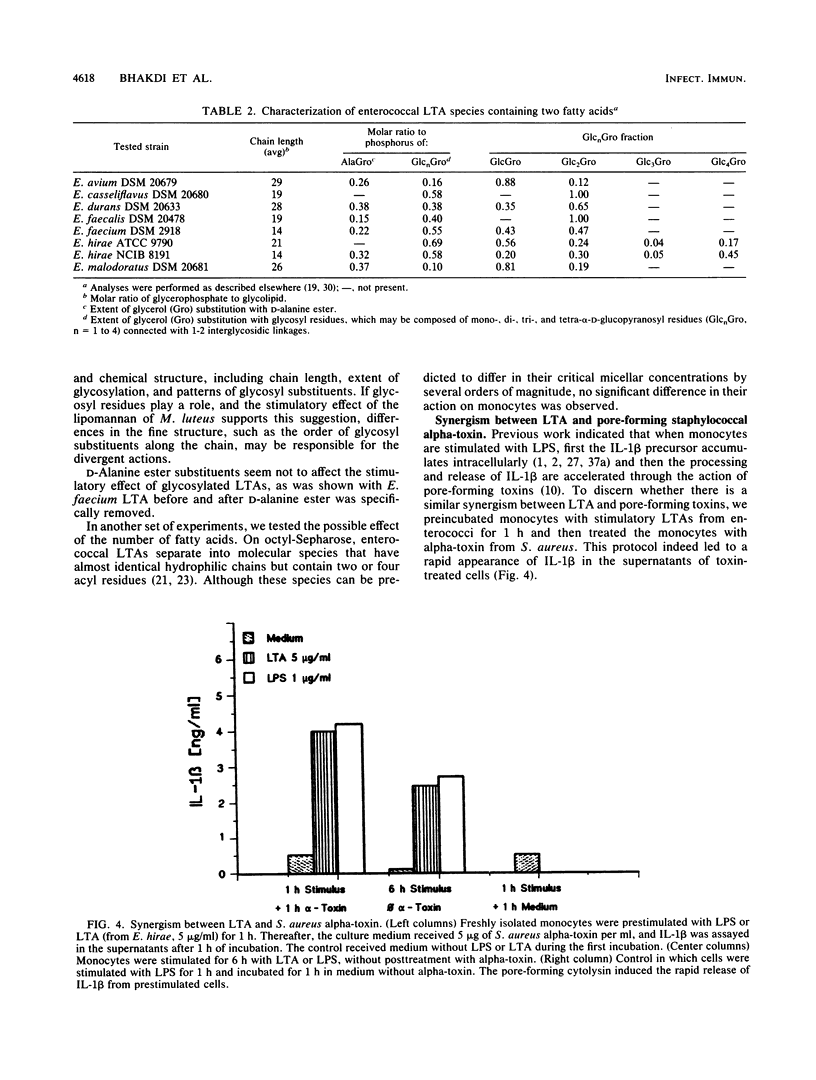
Lipoteichoic acids (LTAs) isolated from bacterial species, including Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes A, Enterococcus faecalis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Listeria monocytogenes, were tested for their ability to stimulate the production of interleukin-1 beta (IL-1 beta), IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor alpha in cultured human monocytes. LTAs from S. aureus and S. pneumoniae failed to induce monokine production when applied in the concentration range of 0.05 to 5.0 micrograms/ml. However, LTAs from several enterococcal species (0.5 to 5 micrograms/ml) induced the release of all three monokines at levels similar to those observed after lipopolysaccharide stimulation. The kinetics of IL-1 beta and tumor necrosis factor alpha release elicited by LTAs closely resembled those observed following lipopolysaccharide application. Cytokine production occurred in the presence of both fetal calf serum and autologous human serum. Hence, it was not dependent on complement activation and could not be suppressed by naturally occurring human antibodies. Deacylation caused the total loss of monocyte stimulatory capacity. Deacylated LTAs were unable to prevent monocyte activation by intact LTAs, so primary binding of these molecules probably does not involve a simple interaction of a membrane receptor with the hydrophilic portion of the molecule. The results identify some species of LTAs as inducers of monokine production in human monocytes.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakouche O., Brown D. C., Lachman L. B. Subcellular localization of human monocyte interleukin 1: evidence for an inactive precursor molecule and a possible mechanism for IL 1 release. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4249–4255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayne E. K., Rupp E. A., Limjuco G., Chin J., Schmidt J. A. Immunocytochemical detection of interleukin 1 within stimulated human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1986 May 1;163(5):1267–1280. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.5.1267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H., Chiang T. M., Ofek I., Kang A. H. Interaction of lipoteichoic acid of group A streptococci with human platelets. Infect Immun. 1977 May;16(2):649–654. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.2.649-654.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H., Dale J. B., Grebe S., Ahmed A., Simpson W. A., Ofek I. Lymphocytes binding and T cell mitogenic properties of group A streptococcal lipoteichoic acid. J Immunol. 1979 Jan;122(1):189–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H., Dale J. B., Simpson W. A., Evans J. D., Knox K. W., Ofek I., Wicken A. J. Erythrocyte binding properties of streptococcal lipoteichoic acids. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):618–625. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.618-625.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H., Ofek I. Epithelial cell binding of group A streptococci by lipoteichoic acid on fimbriae denuded of M protein. J Exp Med. 1976 Apr 1;143(4):759–771. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.4.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. The history, properties, and biological effects of cachectin. Biochemistry. 1988 Oct 4;27(20):7575–7582. doi: 10.1021/bi00420a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Milsark I. W., Cerami A. C. Passive immunization against cachectin/tumor necrosis factor protects mice from lethal effect of endotoxin. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):869–871. doi: 10.1126/science.3895437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Muhly M., Korom S., Hugo F. Release of interleukin-1 beta associated with potent cytocidal action of staphylococcal alpha-toxin on human monocytes. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3512–3519. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3512-3519.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brade L., Brade H., Fischer W. A 28 kDa protein of normal mouse serum binds lipopolysaccharides of gram-negative and lipoteichoic acids of gram-positive bacteria. Microb Pathog. 1990 Nov;9(5):355–362. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90069-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carruthers M. M., Kabat W. J. Mediation of staphylococcal adherence to mucosal cells by lipoteichoic acid. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):444–446. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.444-446.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chugh T. D., Burns G. J., Shuhaiber H. J., Bahr G. M. Adherence of Staphylococcus epidermidis to fibrin-platelet clots in vitro mediated by lipoteichoic acid. Infect Immun. 1990 Feb;58(2):315–319. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.2.315-319.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtney H., Ofek I., Simpson W. A., Beachey E. H. Characterization of lipoteichoic acid binding to polymorphonuclear leukocytes of human blood. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):625–631. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.625-631.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cybulsky M. I., Chan M. K., Movat H. Z. Acute inflammation and microthrombosis induced by endotoxin, interleukin-1, and tumor necrosis factor and their implication in gram-negative infection. Lab Invest. 1988 Apr;58(4):365–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 and its biologically related cytokines. Adv Immunol. 1989;44:153–205. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60642-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiedel B. A., Jackson R. W. Activation of the alternative complement pathway by a streptococcal lipoteichoic acid. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):286–287. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.286-287.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer W., Koch H. U., Haas R. Improved preparation of lipoteichoic acids. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;133(3):523–530. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07495.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer W., Koch H. U., Rösel P., Fiedler F. Alanine ester-containing native lipoteichoic acids do not act as lipoteichoic acid carrier. Isolation, structural and functional characterization. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4557–4562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer W., Mannsfeld T., Hagen G. On the basic structure of poly(glycerophosphate) lipoteichoic acids. Biochem Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;68(1):33–43. doi: 10.1139/o90-005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer W. One-step purification of bacterial lipid macroamphiphiles by hydrophobic interaction chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1991 May 1;194(2):353–358. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90240-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores E. A., Bistrian B. R., Pomposelli J. J., Dinarello C. A., Blackburn G. L., Istfan N. W. Infusion of tumor necrosis factor/cachectin promotes muscle catabolism in the rat. A synergistic effect with interleukin 1. J Clin Invest. 1989 May;83(5):1614–1622. doi: 10.1172/JCI114059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara M. The Forssman antigen of pneumococcus. Jpn J Exp Med. 1967 Dec;37(6):581–592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg I., Fligiel S. E., Ward P. A., Varani J. Lipoteichoic acid-antilipoteichoic acid complexes induce superoxide generation by human neutrophils. Inflammation. 1988 Dec;12(6):525–548. doi: 10.1007/BF00914316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giri J. G., Lomedico P. T., Mizel S. B. Studies on the synthesis and secretion of interleukin 1. I. A 33,000 molecular weight precursor for interleukin 1. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):343–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hummell D. S., Swift A. J., Tomasz A., Winkelstein J. A. Activation of the alternative complement pathway by pneumococcal lipoteichoic acid. Infect Immun. 1985 Feb;47(2):384–387. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.2.384-387.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leopold K., Fischer W. Separation of the poly(glycerophosphate) lipoteichoic acids of Enterococcus faecalis Kiel 27738, Enterococcus hirae ATCC 9790 and Leuconostoc mesenteroides DSM 20343 into molecular species by affinity chromatography on concanavalin A. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Mar 14;196(2):475–482. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15839.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy R., Kotb M., Nagauker O., Majumdar G., Alkan M., Ofek I., Beachey E. H. Stimulation of oxidative burst in human monocytes by lipoteichoic acids. Infect Immun. 1990 Feb;58(2):566–568. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.2.566-568.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindemann R. A., Economou J. S., Rothermel H. Production of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor by human peripheral monocytes activated by periodontal bacteria and extracted lipopolysaccharides. J Dent Res. 1988 Aug;67(8):1131–1135. doi: 10.1177/00220345880670081401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisi P. J., Chu C. W., Koch G. A., Endres S., Lonnemann G., Dinarello C. A. Development and use of a radioimmunoassay for human interleukin-1 beta. Lymphokine Res. 1987 Summer;6(3):229–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loos M., Clas F., Fischer W. Interaction of purified lipoteichoic acid with the classical complement pathway. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):595–599. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.595-599.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopatin D. E., Kessler R. E. Pretreatment with lipoteichoic acid sensitizes target cells to antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity in the presence of anti-lipoteichoic acid antibodies. Infect Immun. 1985 Jun;48(3):638–643. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.3.638-643.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Beachey E. H., Jefferson W., Campbell G. L. Cell membrane-binding properties of group A streptococcal lipoteichoic acid. J Exp Med. 1975 May 1;141(5):990–1003. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.5.990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riesenfeld-Orn I., Wolpe S., Garcia-Bustos J. F., Hoffmann M. K., Tuomanen E. Production of interleukin-1 but not tumor necrosis factor by human monocytes stimulated with pneumococcal cell surface components. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):1890–1893. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.1890-1893.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer I. I., Scott S., Hall G. L., Limjuco G., Chin J., Schmidt J. A. Interleukin 1 beta is localized in the cytoplasmic ground substance but is largely absent from the Golgi apparatus and plasma membranes of stimulated human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1988 Feb 1;167(2):389–407. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.2.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teti G., Chiofalo M. S., Tomasello F., Fava C., Mastroeni P. Mediation of Staphylococcus saprophyticus adherence to uroepithelial cells by lipoteichoic acid. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):839–842. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.839-842.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinreb B. D., Shockman G. D., Beachey E. H., Swift A. J., Winkelstein J. A. The ability to sensitize host cells for destruction by autologous complement is a general property of lipoteichoic acid. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):494–499. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.494-499.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicken A. J., Knox K. W. Bacterial cell surface amphiphiles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 27;604(1):1–26. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90583-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicken A. J., Knox K. W. Lipoteichoic acids: a new class of bacterial antigen. Science. 1975 Mar 28;187(4182):1161–1167. doi: 10.1126/science.46620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



