Abstract
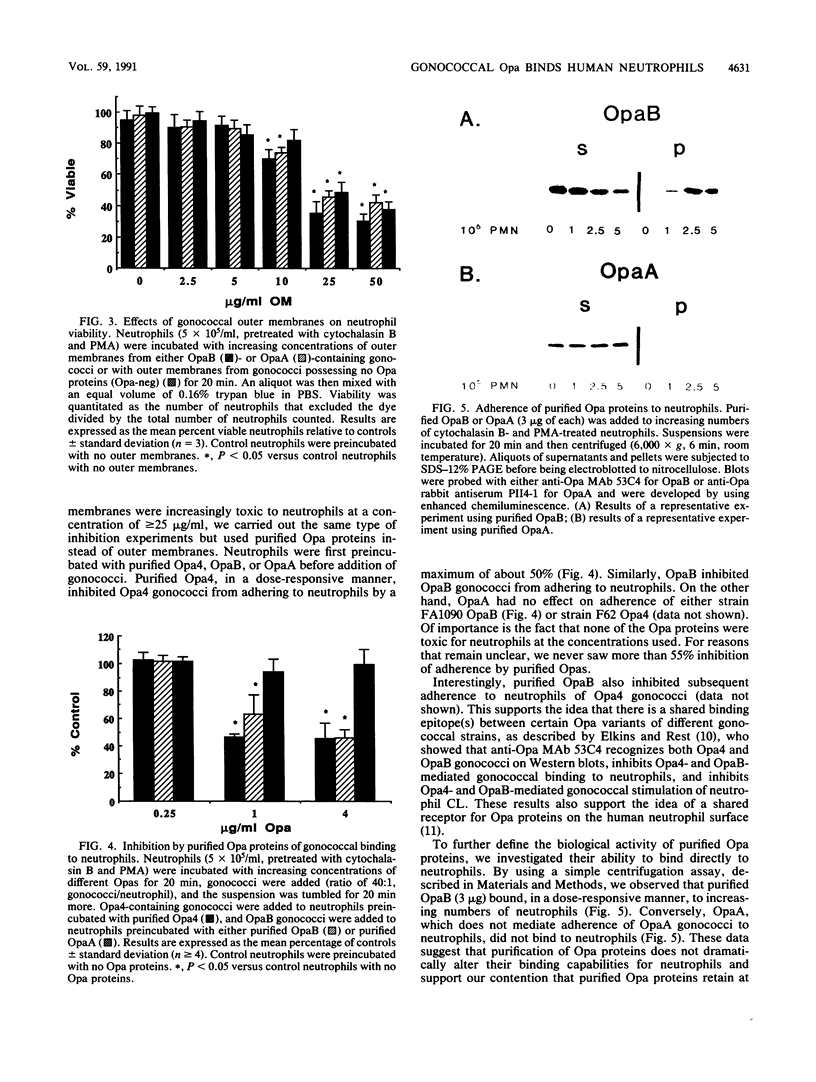
We investigated the role of gonococcal outer membrane protein PII (also called Opa protein) in nonopsonic adherence to human neutrophils. Gonococcal outer membranes, purified Opa in detergent (Opa), purified Opa in liposomes (Opa+ lips), and peptides composing the second hypervariable (HV2) region of OpaB (strain FA1090) in liposomes (pepHV2 lips) were tested for their abilities to inhibit subsequent gonococcal adherence to human neutrophils. Outer membranes from gonococci possessing adherent Opa, liposomes containing adherent Opa, purified adherent Opa, and two of three liposome preparations (pepHV2 lips) containing peptides from the HV2 region of an adherent Opa inhibited subsequent adherence to neutrophils of homologous Opa+ gonococci. On the other hand, outer membranes from Opa- gonococci, outer membranes containing a nonadherent Opa (OpaA from strain FA1090), purified OpaA, and OpaA lips had little or no inhibitory effect. Outer membranes containing adherent Opas, purified adherent Opas, and liposomes containing such Opas all bound to neutrophils, whereas preparations containing OpaA or no Opa protein did not. The results indicate that (i) Opa proteins can bind to neutrophils in a partially purified or purified form and (ii) the HV2 region of Opa appears to at least partially mediate Opa's biological role.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barritt D. S., Schwalbe R. S., Klapper D. G., Cannon J. G. Antigenic and structural differences among six proteins II expressed by a single strain of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2026–2031. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2026-2031.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black W. J., Schwalbe R. S., Nachamkin I., Cannon J. G. Characterization of Neisseria gonorrhoeae protein II phase variation by use of monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):453–457. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.453-457.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. S., Gotschlich E. C. Gonococcal membrane proteins: speculation on their role in pathogenesis. Prog Allergy. 1983;33:298–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. S., Johnston K. H., Russell-Jones G. J., Gotschlich E. C. A rapid, sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-antibody on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connell T. D., Black W. J., Kawula T. H., Barritt D. S., Dempsey J. A., Kverneland K., Jr, Stephenson A., Schepart B. S., Murphy G. L., Cannon J. G. Recombination among protein II genes of Neisseria gonorrhoeae generates new coding sequences and increases structural variability in the protein II family. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Mar;2(2):227–236. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00024.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connell T. D., Shaffer D., Cannon J. G. Characterization of the repertoire of hypervariable regions in the Protein II (opa) gene family of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Mar;4(3):439–449. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00610.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis A. T., Estensen R., Quie P. G. Cytochalasin B. 3. Inhibition of human polymorphonuclear leukocyte phagocytosis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 May;137(1):161–164. doi: 10.3181/00379727-137-35535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkins C., Rest R. F. Monoclonal antibodies to outer membrane protein PII block interactions of Neisseria gonorrhoeae with human neutrophils. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):1078–1084. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.1078-1084.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell C. F., Rest R. F. Up-regulation of human neutrophil receptors for Neisseria gonorrhoeae expressing PII outer membrane proteins. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):2777–2784. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.2777-2784.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante A., Thong Y. H. Optimal conditions for simultaneous purification of mononuclear and polymorphonuclear leucocytes from human blood by the Hypaque-Ficoll method. J Immunol Methods. 1980;36(2):109–117. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer S. H., Rest R. F. Gonococci possessing only certain P.II outer membrane proteins interact with human neutrophils. Infect Immun. 1988 Jun;56(6):1574–1579. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.6.1574-1579.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forslin L., Danielsson D. In vitro studies of the adherence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and other urogenital bacteria to vaginal and uroepithelial cells, with special regard to the menstrual cycle. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 1980;11(6):327–340. doi: 10.1159/000299854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Fries E., Kartenbeck J. Reconstitution of Semliki forest virus membrane. J Cell Biol. 1977 Dec;75(3):866–880. doi: 10.1083/jcb.75.3.866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg D. S., Jr, Cohen I. R., Norins L. C., Schroeter A. L., Reising G. Neisseria gonorrhoeae. II. Colonial variation and pathogenicity during 35 months in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):596–605. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.596-605.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King G. J., Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. XV. Identification of surface proteins of Neisseria gonorrhoeae correlated with leukocyte association. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):575–584. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.575-584.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King G., James J. F., Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. XI. Comparison of in vivo and vitro association of Neisseria gonorrhoeae with human neutrophils. J Infect Dis. 1978 Jan;137(1):38–43. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.1.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesse A. J., Campagnari A. A., Bittner W. E., Apicella M. A. Increased resolution of lipopolysaccharides and lipooligosaccharides utilizing tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Immunol Methods. 1990 Jan 24;126(1):109–117. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90018-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandrell R., Schneider H., Apicella M., Zollinger W., Rice P. A., Griffiss J. M. Antigenic and physical diversity of Neisseria gonorrhoeae lipooligosaccharides. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):63–69. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.63-69.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mimms L. T., Zampighi G., Nozaki Y., Tanford C., Reynolds J. A. Phospholipid vesicle formation and transmembrane protein incorporation using octyl glucoside. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):833–840. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G. L., Connell T. D., Barritt D. S., Koomey M., Cannon J. G. Phase variation of gonococcal protein II: regulation of gene expression by slipped-strand mispairing of a repetitive DNA sequence. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):539–547. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90577-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
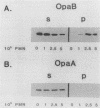
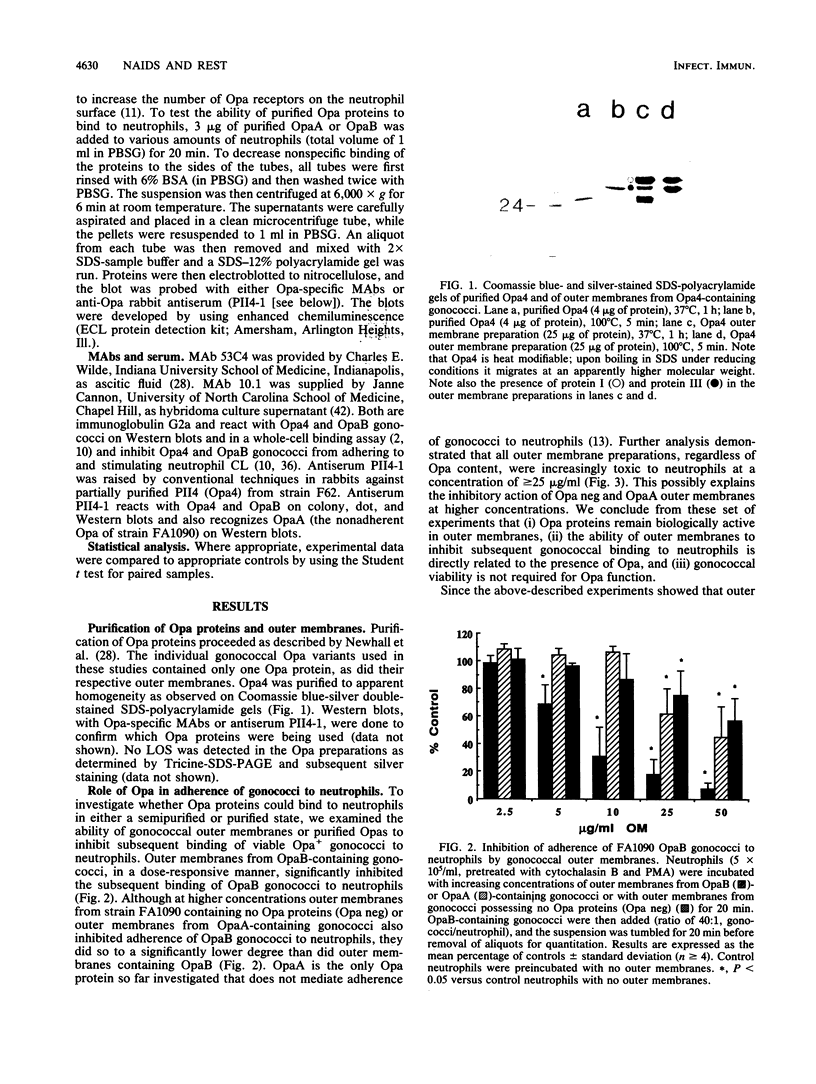
- Newhall WJ5th, Mail L. B., Wilde C. E., 3rd, Jones R. B. Purification and antigenic relatedness of proteins II of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):576–580. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.576-580.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyberg G., Strömberg N., Jonsson A., Karlsson K. A., Normark S. Erythrocyte gangliosides act as receptors for Neisseria subflava: identification of the Sia-1 adhesin. Infect Immun. 1990 Aug;58(8):2555–2563. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.8.2555-2563.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Beachey E. H., Bisno A. L. Resistance of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to phagocytosis: relationship to colonial morphology and surface pili. J Infect Dis. 1974 Mar;129(3):310–316. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.3.310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paruchuri D. K., Seifert H. S., Ajioka R. S., Karlsson K. A., So M. Identification and characterization of a Neisseria gonorrhoeae gene encoding a glycolipid-binding adhesin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):333–337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porat R., Johns M. A., McCabe W. R. Selective pressures and lipopolysaccharide subunits as determinants of resistance of clinical isolates of gram-negative bacilli to human serum. Infect Immun. 1987 Feb;55(2):320–328. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.2.320-328.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Punsalang A. P., Jr, Sawyer W. D. Role of pili in the virulence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):255–263. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.255-263.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rest R. F., Fischer S. H., Ingham Z. Z., Jones J. F. Interactions of Neisseria gonorrhoeae with human neutrophils: effects of serum and gonococcal opacity on phagocyte killing and chemiluminescence. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):737–744. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.737-744.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rest R. F. Killing of Neisseria gonorrhoeae by human polymorphonuclear neutrophil granule extracts. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):574–579. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.574-579.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rest R. F., Lee N., Bowden C. Stimulation of human leukocytes by protein II+ gonococci is mediated by lectin-like gonococcal components. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):116–122. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.116-122.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rest R. F., Pretzer E. Degradation of gonococcal outer membrane proteins by human neutrophil lysosomal proteases. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):62–68. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.62-68.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafer W. M., Rest R. F. Interactions of gonococci with phagocytic cells. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1989;43:121–145. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.43.100189.001005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern A., Brown M., Nickel P., Meyer T. F. Opacity genes in Neisseria gonorrhoeae: control of phase and antigenic variation. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):61–71. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90366-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stromberg N., Deal C., Nyberg G., Normark S., So M., Karlsson K. A. Identification of carbohydrate structures that are possible receptors for Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4902–4906. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugasawara R. J., Cannon J. G., Black W. J., Nachamkin I., Sweet R. L., Brooks G. F. Inhibition of Neisseria gonorrhoeae attachment to HeLa cells with monoclonal antibody directed against a protein II. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):980–985. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.980-985.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Sparks E., Young D., King G. Studies on Gonococcus infection. X. Pili and leukocyte association factor as mediators of interactions between gonococci and eukaryotic cells in vitro. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1352–1361. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1352-1361.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Sparks E., Zeligs B., Siam M. A., Parrott C. Studies on gonococcus infection. V. Observations on in vitro interactions of gonococci and human neutrophils. Infect Immun. 1974 Sep;10(3):633–644. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.3.633-644.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. XII. Colony color and opacity varienats of gonococci. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):320–331. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.320-331.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szewczyk B., Kozloff L. M. A method for the efficient blotting of strongly basic proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose. Anal Biochem. 1985 Nov 1;150(2):403–407. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90528-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. W., Hill J. C., Tyeryar F. J., Jr Interaction of gonococci with phagocytic leukocytes from men and mice. Infect Immun. 1973 Jul;8(1):98–104. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.1.98-104.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virji M., Heckels J. E. The effect of protein II and pili on the interaction of Neisseria gonorrhoeae with human polymorphonuclear leucocytes. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Feb;132(2):503–512. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-2-503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward M. E., Watt P. J. Adherence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to urethral mucosal cells: an electron-microscopic study of human gonorrhea. J Infect Dis. 1972 Dec;126(6):601–605. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.6.601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright D. G., Gallin J. I. Secretory responses of human neutrophils: exocytosis of specific (secondary) granules by human neutrophils during adherence in vitro and during exudation in vivo. J Immunol. 1979 Jul;123(1):285–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zak K., Diaz J. L., Jackson D., Heckels J. E. Antigenic variation during infection with Neisseria gonorrhoeae: detection of antibodies to surface proteins in sera of patients with gonorrhea. J Infect Dis. 1984 Feb;149(2):166–174. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.2.166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Ley P. Three copies of a single protein II-encoding sequence in the genome of Neisseria gonorrhoeae JS3: evidence for gene conversion and gene duplication. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Nov;2(6):797–806. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00091.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]