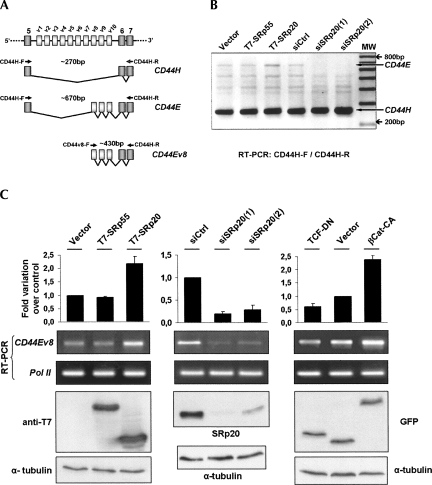
FIGURE 8.
Effect of β-catenin/TCF4 transcriptional activity and SRp20 protein levels on alternative splicing of endogenous CD44. (A) The drawing shows the variable exon region of the CD44 gene. (Diagonal lines) The two analyzed splicing patterns; the amplified minigene-derived transcripts CD44H and CD44E as well as the primers used for their amplification are depicted below. (B) RT-PCR analysis of endogenous CD44 transcripts with primers CD44H-F and CD44-R annealing to the constitutive exons that flank the variable exon region. CD44 transcripts were amplified from DLD-1 cells transfected with either T7-tagged SR proteins or siRNAs to deplete endogenous SRp20. Note the specific changes in CD44E, as indicated. (C) Quantitation of endogenous CD44E generation using an exon v8-specific forward primer. CD44E was amplified from DLD-1 cells transfected with (left panel) SRp55 or SRp20, (middle panel) with specific siRNAs to deplete endogenous SRp20, (right panel) or with βCat-CA and TCF-DN to modulate β-catenin/TCF4 transcriptional activity. Below the RT-PCR images, the corresponding Western blot images are shown to document the expression levels of overexpressed SR proteins, of depleted SRp20, or of βCat-CA and TCF-DN, respectively.