Abstract
The expression of T-cell-associated serine proteinase 1 (MTSP-1) in vivo during Leishmania major infection was analyzed in genetically resistant C57BL/6 mice and in genetically susceptible BALB/c mice. Using a monoclonal antibody as well as an RNA probe specific for MTSP-1 to stain tissue sections, we found T cells expressing MTSP-1 in skin lesions and spleens of mice of both strains. In skin lesions, MTSP-1-positive T cells could be detected as early as 3 days after infection. Most importantly, the frequency of T cells expressing MTSP-1 was significantly higher in susceptible BALB/c mice than in resistant C57BL/6 mice. These findings suggest that MTSP-1 is associated with disease-promoting T cells and that it may be an effector molecule involved in the pathogenesis of cutaneous leishmaniasis.
Full text
PDF
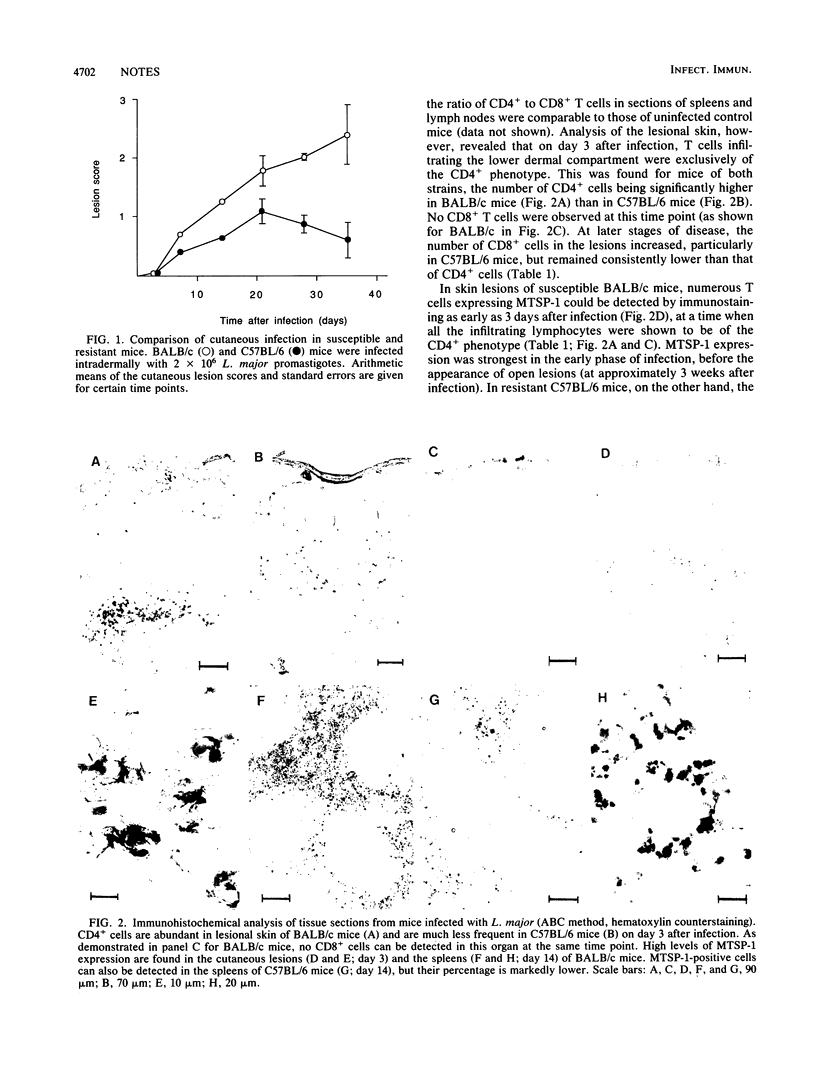
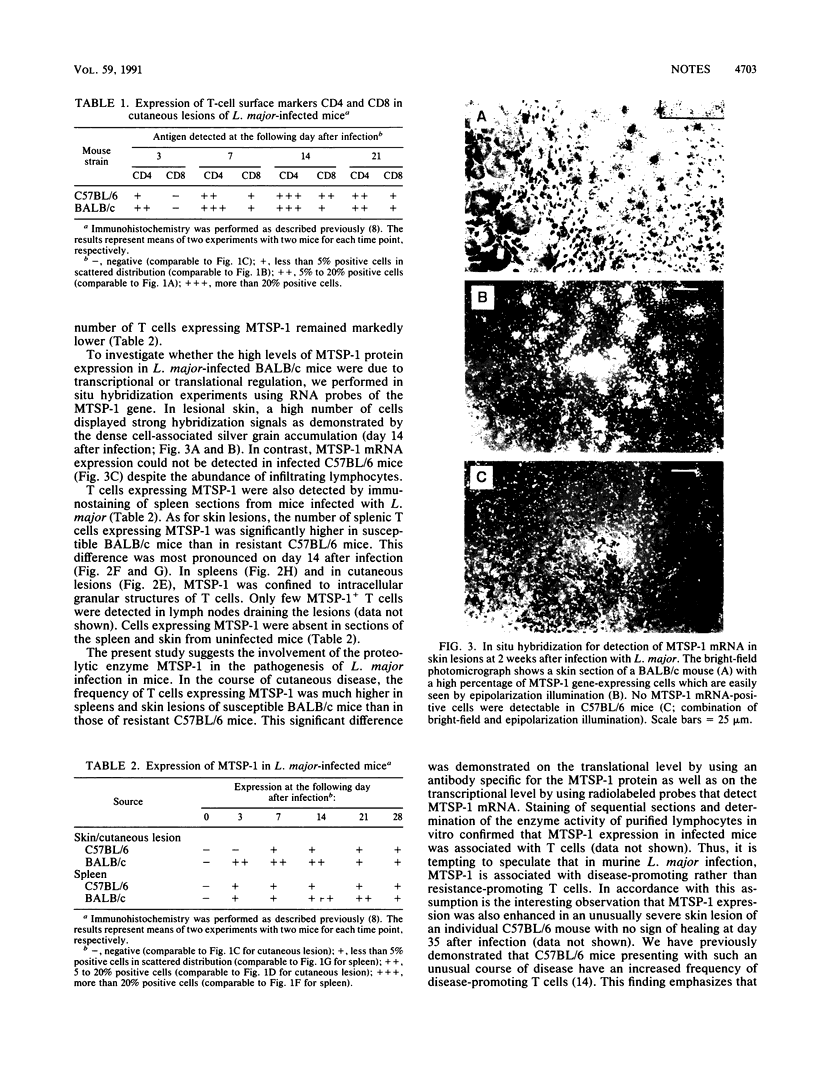


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brunner G., Simon M. M., Kramer M. D. Activation of pro-urokinase by the human T cell-associated serine proteinase HuTSP-1. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jan 15;260(1):141–144. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80087-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper C. L., Mueller C., Sinchaisri T. A., Pirmez C., Chan J., Kaplan G., Young S. M., Weissman I. L., Bloom B. R., Rea T. H. Analysis of naturally occurring delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions in leprosy by in situ hybridization. J Exp Med. 1989 May 1;169(5):1565–1581. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.5.1565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebnet K., Chluba-de Tapia J., Hurtenbach U., Kramer M. D., Simon M. M. In vivo primed mouse T cells selectively express T cell-specific serine proteinase-1 and the proteinase-like molecules granzyme B and C. Int Immunol. 1991 Jan;3(1):9–19. doi: 10.1093/intimm/3.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fruth U., Nerz G., Prester M., Simon H. G., Kramer M. D., Simon M. M. Determination of frequency of T cells expressing the T cell-specific serine proteinase 1 (TSP-1) reveals two types of L3T4+ T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1988 May;18(5):773–781. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershenfeld H. K., Weissman I. L. Cloning of a cDNA for a T cell-specific serine protease from a cytotoxic T lymphocyte. Science. 1986 May 16;232(4752):854–858. doi: 10.1126/science.2422755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinzel F. P., Sadick M. D., Holaday B. J., Coffman R. L., Locksley R. M. Reciprocal expression of interferon gamma or interleukin 4 during the resolution or progression of murine leishmaniasis. Evidence for expansion of distinct helper T cell subsets. J Exp Med. 1989 Jan 1;169(1):59–72. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinzel F. P., Sadick M. D., Locksley R. M. Leishmania major: analysis of lymphocyte and macrophage cellular phenotypes during infection of susceptible and resistant mice. Exp Parasitol. 1988 Apr;65(2):258–268. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(88)90130-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer M. D., Fruth U., Simon H. G., Simon M. M. Expression of cytoplasmic granules with T cell-associated serine proteinase-1 activity in Ly-2+(CD8+) T lymphocytes responding to lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus in vivo. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Jan;19(1):151–156. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., Herzenberg L. A. Xenogeneic monoclonal antibodies to mouse lymphoid differentiation antigens. Immunol Rev. 1979;47:63–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liew F. Y., Hale C., Howard J. G. Immunologic regulation of experimental cutaneous leishmaniasis. V. Characterization of effector and specific suppressor T cells. J Immunol. 1982 Apr;128(4):1917–1922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C. C., Rafii S., Granelli-Piperno A., Trapani J. A., Young J. D. Perforin and serine esterase gene expression in stimulated human T cells. Kinetics, mitogen requirements, and effects of cyclosporin A. J Exp Med. 1989 Dec 1;170(6):2105–2118. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.6.2105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson D., Nabholz M., Estrade C., Tschopp J. Granules of cytolytic T-lymphocytes contain two serine esterases. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1595–1600. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04401.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McElrath M. J., Kaplan G., Nusrat A., Cohn Z. A. Cutaneous leishmaniasis. The defect in T cell influx in BALB/c mice. J Exp Med. 1987 Feb 1;165(2):546–559. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.2.546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll H., Mitchell G. F. Analysis of variables associated with promotion of resistance and its abrogation in T cell-reconstituted nude mice infected with Leishmania major. J Parasitol. 1988 Dec;74(6):993–998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll H., Röllinghoff M. Resistance to murine cutaneous leishmaniasis is mediated by TH1 cells, but disease-promoting CD4+ cells are different from TH2 cells. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Sep;20(9):2067–2074. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll H., Scollay R., Mitchell G. F. Resistance to cutaneous leishmaniasis in nude mice injected with L3T4+ T cells but not with Ly-2+ T cells. Immunol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;66(Pt 1):57–63. doi: 10.1038/icb.1988.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller C., Gershenfeld H. K., Lobe C. G., Okada C. Y., Bleackley R. C., Weissman I. L. A high proportion of T lymphocytes that infiltrate H-2-incompatible heart allografts in vivo express genes encoding cytotoxic cell-specific serine proteases, but do not express the MEL-14-defined lymph node homing receptor. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):1124–1136. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.1124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller C., Kägi D., Aebischer T., Odermatt B., Held W., Podack E. R., Zinkernagel R. M., Hengartner H. Detection of perforin and granzyme A mRNA in infiltrating cells during infection of mice with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Jul;19(7):1253–1259. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojcius D. M., Young J. D. Cell-mediated killing: effector mechanisms and mediators. Cancer Cells. 1990 May;2(5):138–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternack M. S., Verret C. R., Liu M. A., Eisen H. N. Serine esterase in cytolytic T lymphocytes. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):740–743. doi: 10.1038/322740a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierres A., Naquet P., Van Agthoven A., Bekkhoucha F., Denizot F., Mishal Z., Schmitt-Verhulst A. M., Pierres M. A rat anti-mouse T4 monoclonal antibody (H129.19) inhibits the proliferation of Ia-reactive T cell clones and delineates two phenotypically distinct (T4+, Lyt-2,3-, and T4-, Lyt-2,3+) subsets among anti-Ia cytolytic T cell clones. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):2775–2782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. M., Hoschützky H., Fruth U., Simon H. G., Kramer M. D. Purification and characterization of a T cell specific serine proteinase (TSP-1) from cloned cytolytic T lymphocytes. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3267–3274. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04638.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. M., Prester M., Nerz G., Kramer M. D., Fruth U. Release of biologically active fragments from human plasma-fibronectin by murine T cell-specific proteinase 1 (TSP-1). Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1988 May;369 (Suppl):107–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. M., Simon H. G., Fruth U., Epplen J., Müller-Hermelink H. K., Kramer M. D. Cloned cytolytic T-effector cells and their malignant variants produce an extracellular matrix degrading trypsin-like serine proteinase. Immunology. 1987 Feb;60(2):219–230. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A. Interleukin 2. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:319–333. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Cohn Z. A. Cell-mediated killing: a common mechanism? Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):641–642. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90336-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Leong L. G., Liu C. C., Damiano A., Wall D. A., Cohn Z. A. Isolation and characterization of a serine esterase from cytolytic T cell granules. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):183–194. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90441-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]