Abstract
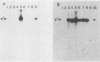
The cbbE' gene codes for the E' protein of Coxiella burnetii and was detected in genomic DNA from all known human isolates of the biotzere strain but not in DNA from the other five strains of C. burnetti. The biotzere strain is strictly associated with chronic disease in humans. Extrinsic iodination of biotzere strain cells radiolabeled a 55-kDa protein which comigrated on sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis with the E' protein synthesized in vitro from recombinants containing the cbbE' gene. The 125I-labeled 55-kDa protein was immunoprecipitated with polyclonal anti-E' antiserum, confirming its identity as E'. Predicted secondary structure of the E' polypeptide shows six regions of beta-sheet structure and an alpha-helix near the C terminus with adequate lengths to span a membrane. The predicted hydropathy profile of E' is similar to profiles of known outer membrane proteins and corroborates the biochemical data, indicating that the protein is located in the outer membrane of C. burnetii.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams G. A., Rose J. K. Structural requirements of a membrane-spanning domain for protein anchoring and cell surface transport. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):1007–1015. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;47:45–148. doi: 10.1002/9780470122921.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emini E. A., Hughes J. V., Perlow D. S., Boger J. Induction of hepatitis A virus-neutralizing antibody by a virus-specific synthetic peptide. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):836–839. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.836-839.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulig P. A., Curtiss R., 3rd Plasmid-associated virulence of Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):2891–2901. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.2891-2901.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackett J., Misra R., Reeves P. The TolC protein of Escherichia coli K12 is synthesised in a precursor form. FEBS Lett. 1983 Jun 13;156(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80518-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackstadt T. Antigenic variation in the phase I lipopolysaccharide of Coxiella burnetii isolates. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):337–340. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.337-340.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heffernan E. J., Fierer J., Chikami G., Guiney D. Natural history of oral Salmonella dublin infection in BALB/c mice: effect of an 80-kilobase-pair plasmid on virulence. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jun;155(6):1254–1259. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.6.1254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrix L. R., Samuel J. E., Mallavia L. P. Differentiation of Coxiella burnetii isolates by analysis of restriction-endonuclease-digested DNA separated by SDS-PAGE. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Feb;137(2):269–276. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-2-269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jameson B. A., Wolf H. The antigenic index: a novel algorithm for predicting antigenic determinants. Comput Appl Biosci. 1988 Mar;4(1):181–186. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/4.1.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimbrough R. C., 3rd, Ormsbee R. A., Peacock M., Rogers W. R., Bennetts R. W., Raaf J., Krause A., Gardner C. Q fever endocarditis in the United States. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Sep;91(3):400–402. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-3-400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallavia L. P., Whiting L. L., Minnick M. F., Heinzen R., Reschke D., Foreman M., Baca O. G., Frazier M. E. Strategy for detection and differentiation of Coxiella burnetii strains using the polymerase chain reaction. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;590:572–581. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb42268.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A. A new solid-state reagent to iodinate proteins. I. Conditions for the efficient labeling of antiserum. Anal Biochem. 1982 Sep 15;125(2):427–432. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurelli A. T., Baudry B., d'Hauteville H., Hale T. L., Sansonetti P. J. Cloning of plasmid DNA sequences involved in invasion of HeLa cells by Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1985 Jul;49(1):164–171. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.1.164-171.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minnick M. F., Heinzen R. A., Douthart R., Mallavia L. P., Frazier M. E. Analysis of QpRS-specific sequences from Coxiella burnetii. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;590:514–522. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb42261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minnick M. F., Heinzen R. A., Frazier M. E., Mallavia L. P. Characterization and expression of the cbbE' gene of Coxiella burnetii. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Jun;136(6):1099–1107. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-6-1099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moos A., Hackstadt T. Comparative virulence of intra- and interstrain lipopolysaccharide variants of Coxiella burnetii in the guinea pig model. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1144–1150. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1144-1150.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nau C. D., Konisky J. Evolutionary relationship between the TonB-dependent outer membrane transport proteins: nucleotide and amino acid sequences of the Escherichia coli colicin I receptor gene. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):1041–1047. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.1041-1047.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen T. T., Postle K., Bertrand K. P. Sequence homology between the tetracycline-resistance determinants of Tn10 and pBR322. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(1):83–92. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90170-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postle K., Skare J. T. Escherichia coli TonB protein is exported from the cytoplasm without proteolytic cleavage of its amino terminus. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):11000–11007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai T., Sasakawa C., Makino S., Kamata K., Yoshikawa M. Molecular cloning of a genetic determinant for Congo red binding ability which is essential for the virulence of Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):476–482. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.476-482.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel J. E., Frazier M. E., Kahn M. L., Thomashow L. S., Mallavia L. P. Isolation and characterization of a plasmid from phase I Coxiella burnetii. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):488–493. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.488-493.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel J. E., Frazier M. E., Mallavia L. P. Correlation of plasmid type and disease caused by Coxiella burnetii. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):775–779. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.775-779.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasakawa C., Kamata K., Sakai T., Murayama S. Y., Makino S., Yoshikawa M. Molecular alteration of the 140-megadalton plasmid associated with loss of virulence and Congo red binding activity in Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):470–475. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.470-475.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savinelli E. A., Mallavia L. P. Comparison of Coxiella burnetii plasmids to homologous chromosomal sequences present in a plasmidless endocarditis-causing isolate. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;590:523–533. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb42262.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small P. L., Falkow S. Identification of regions on a 230-kilobase plasmid from enteroinvasive Escherichia coli that are required for entry into HEp-2 cells. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):225–229. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.225-229.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vodkin M. H., Williams J. C., Stephenson E. H. Genetic heterogeneity among isolates of Coxiella burnetii. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Feb;132(2):455–463. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-2-455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeaman M. R., Mitscher L. A., Baca O. G. In vitro susceptibility of Coxiella burnetii to antibiotics, including several quinolones. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jul;31(7):1079–1084. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.7.1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeaman M. R., Roman M. J., Baca O. G. Antibiotic susceptibilities of two Coxiella burnetii isolates implicated in distinct clinical syndromes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jul;33(7):1052–1057. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.7.1052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]