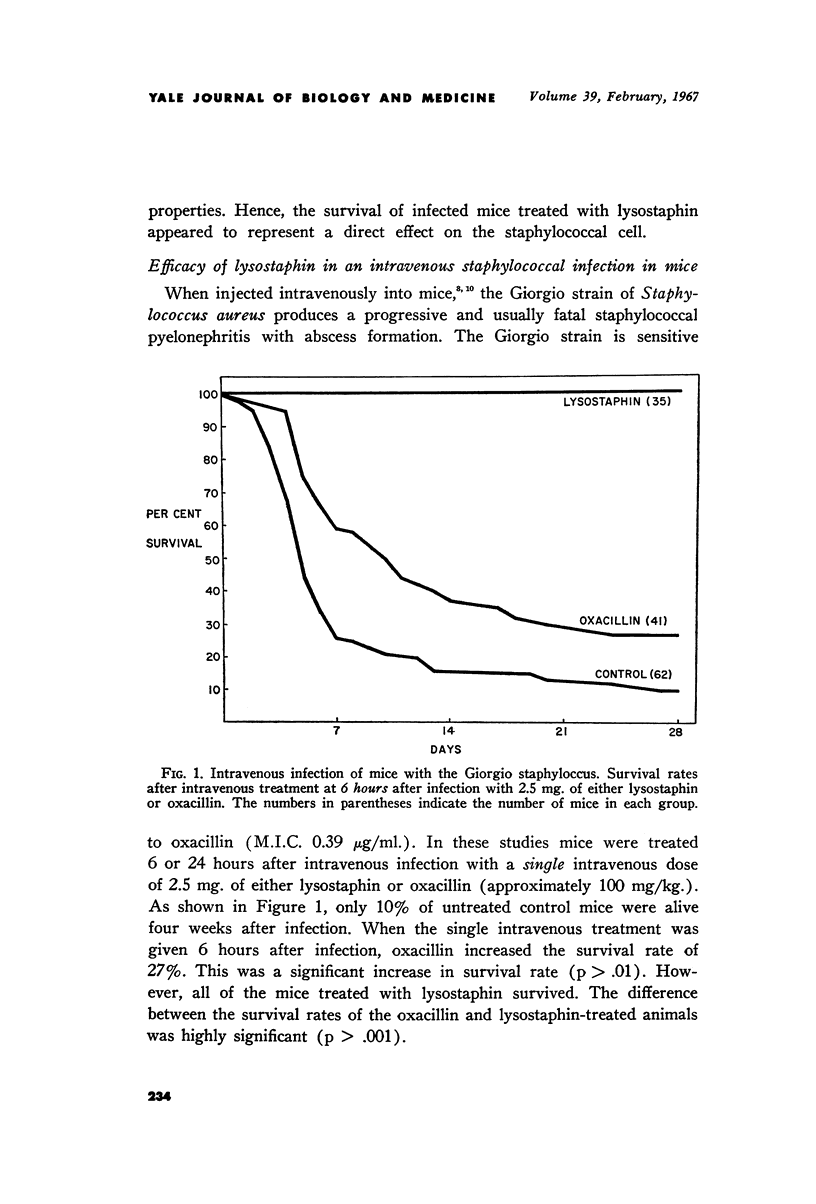
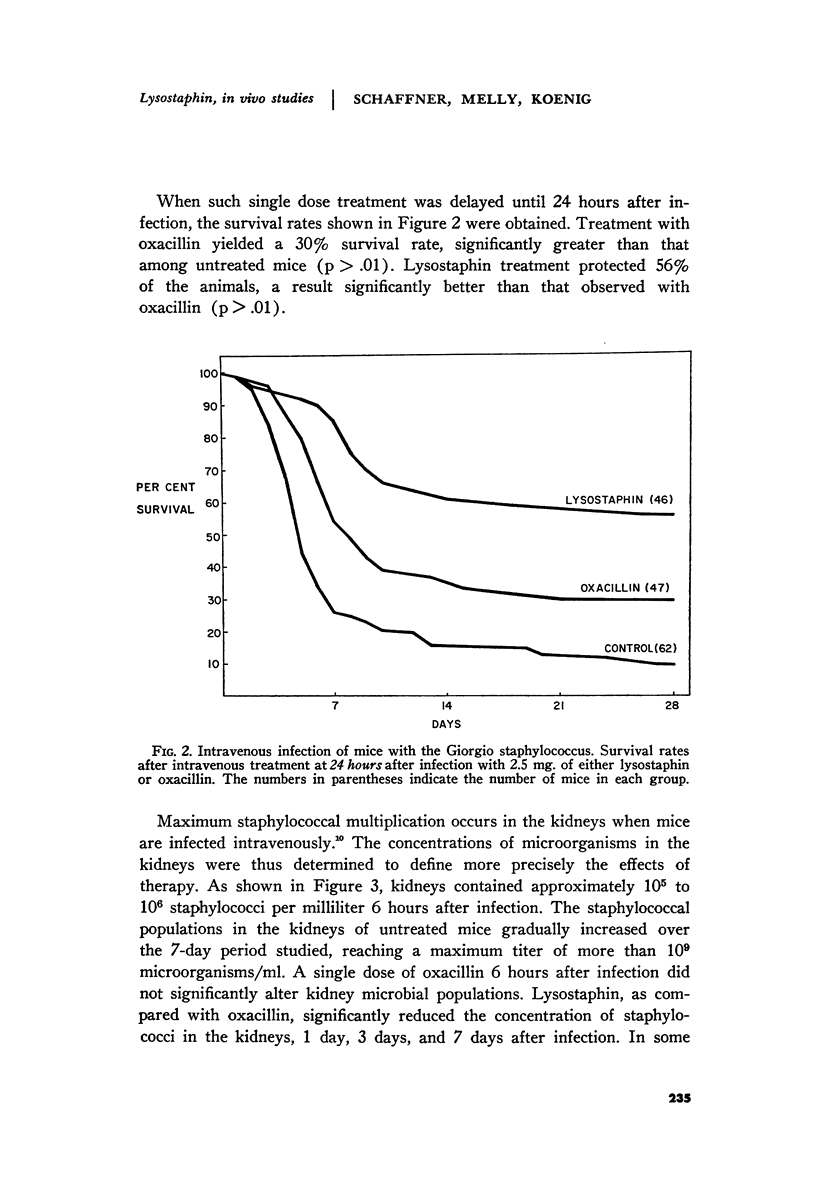
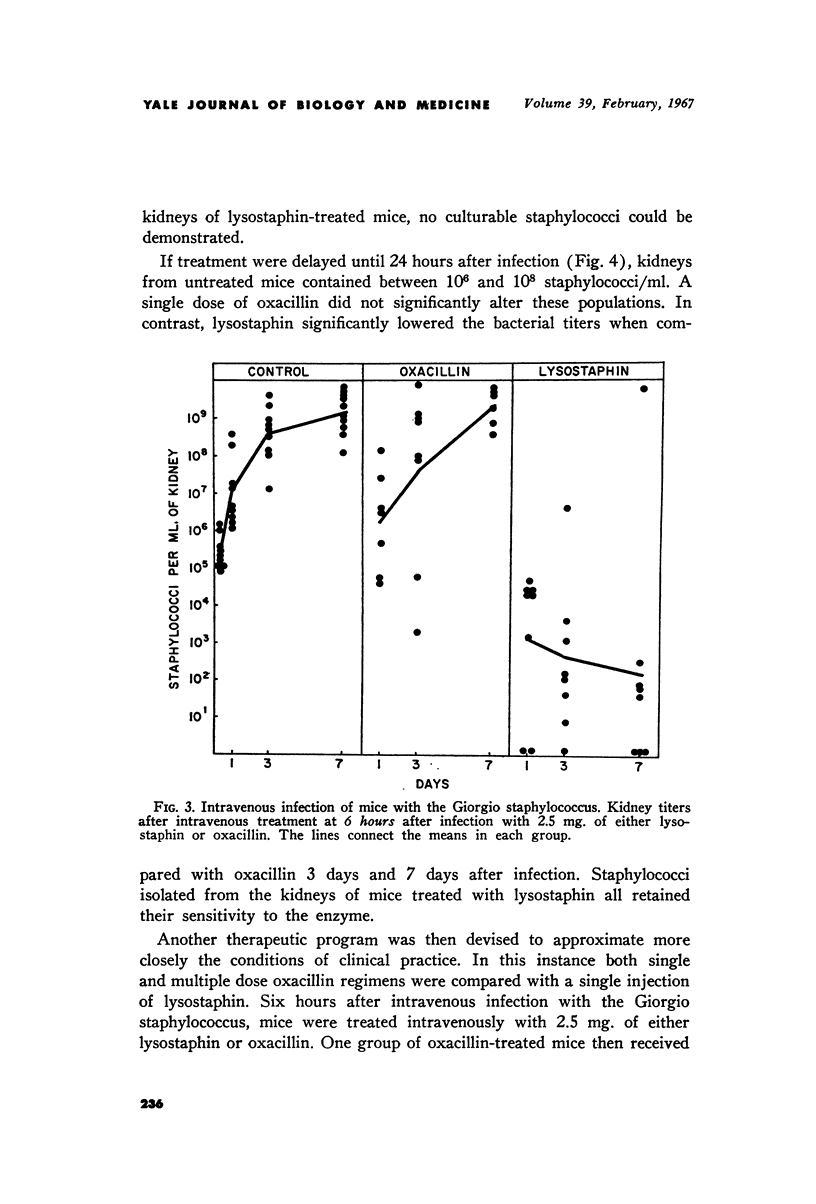
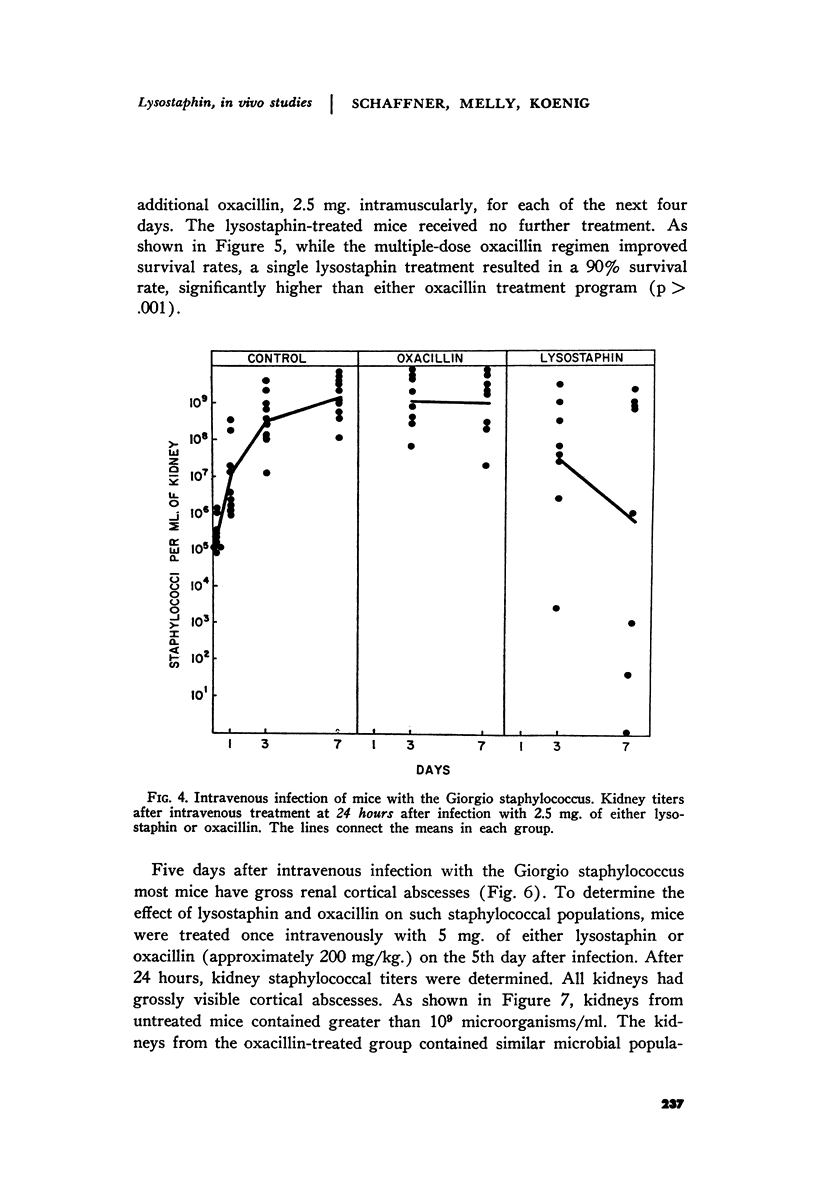
Full text
PDF


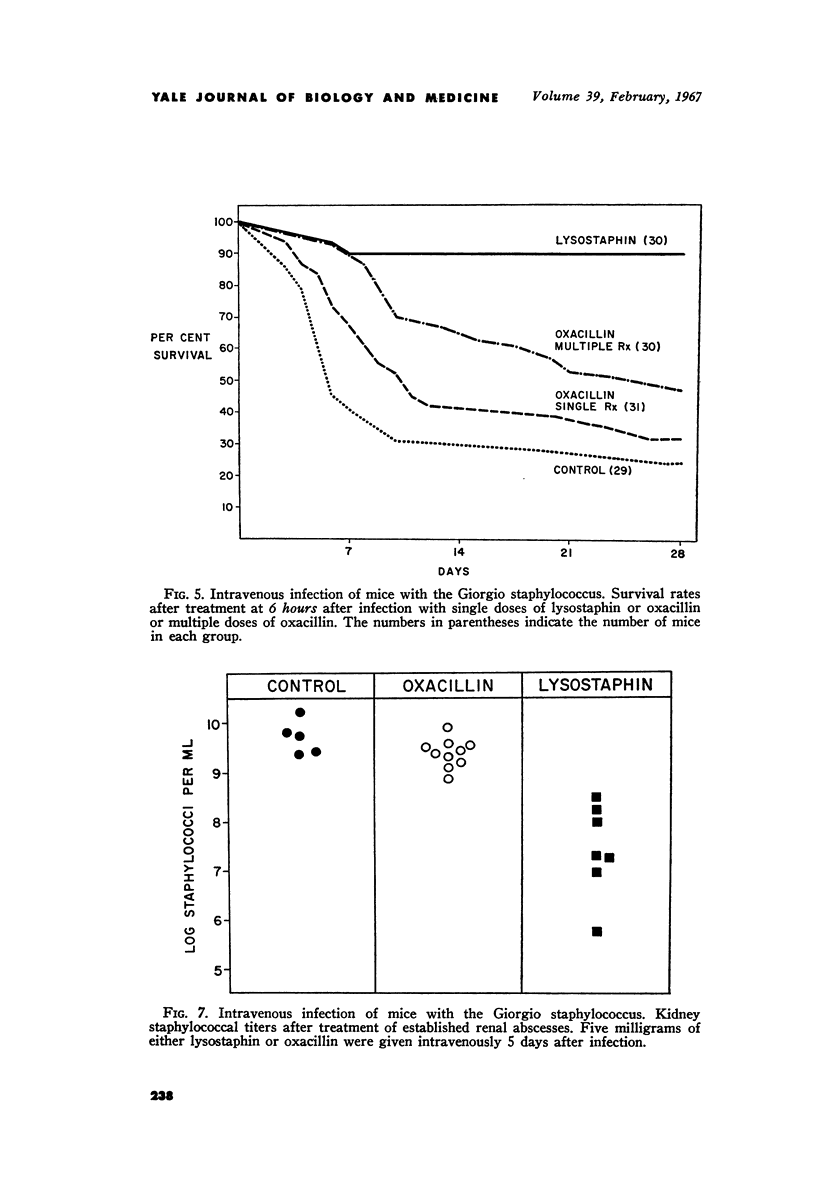
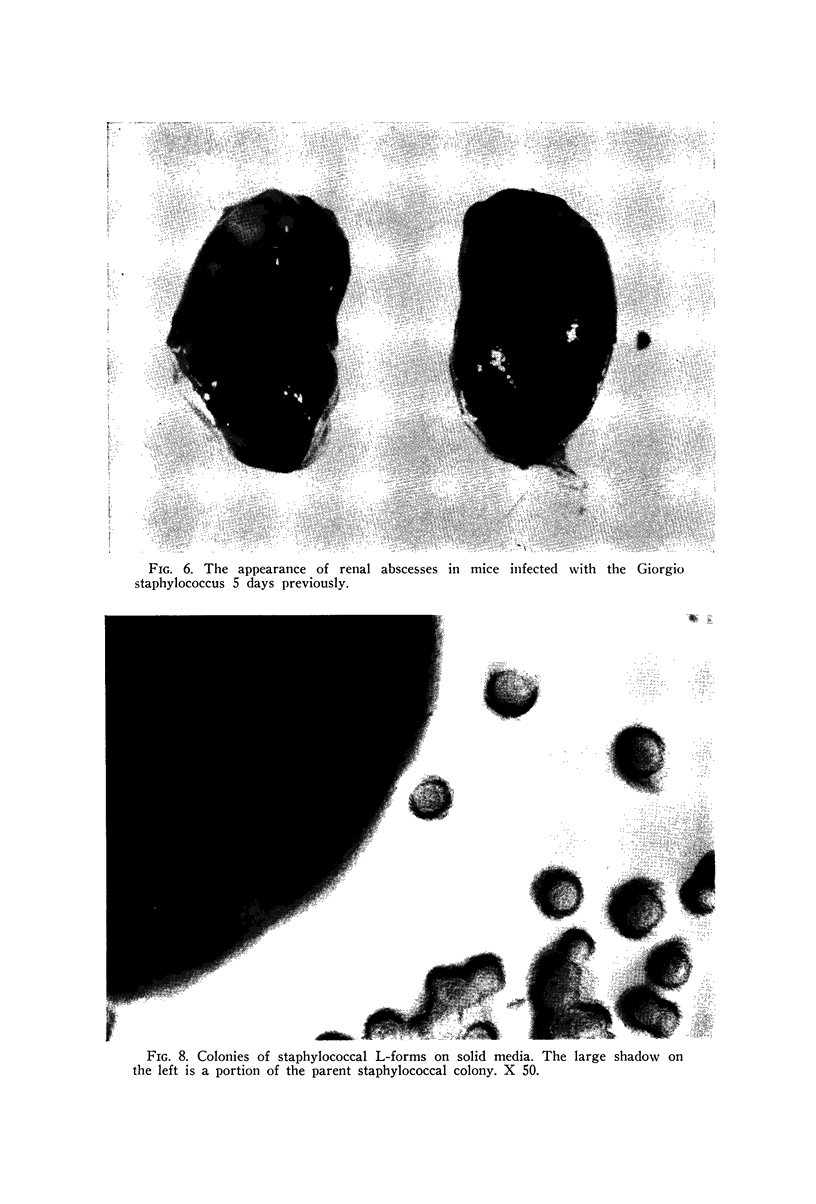
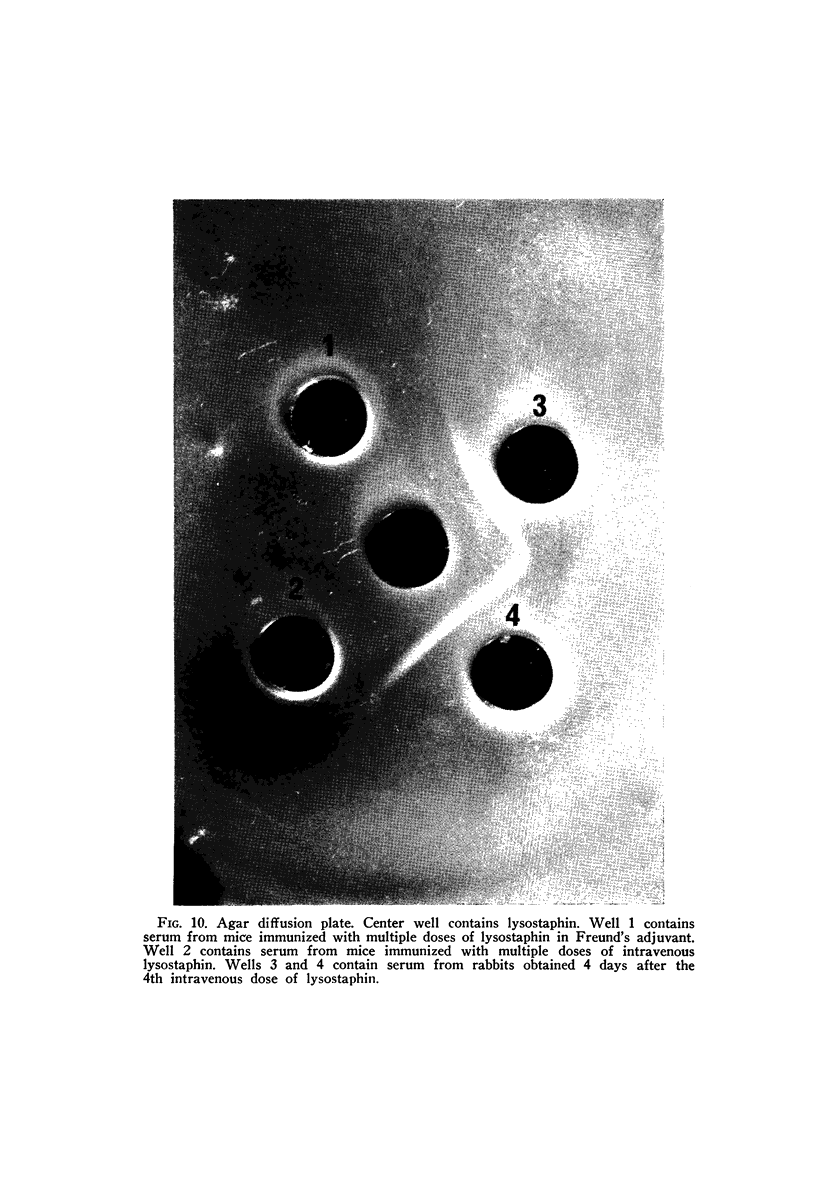
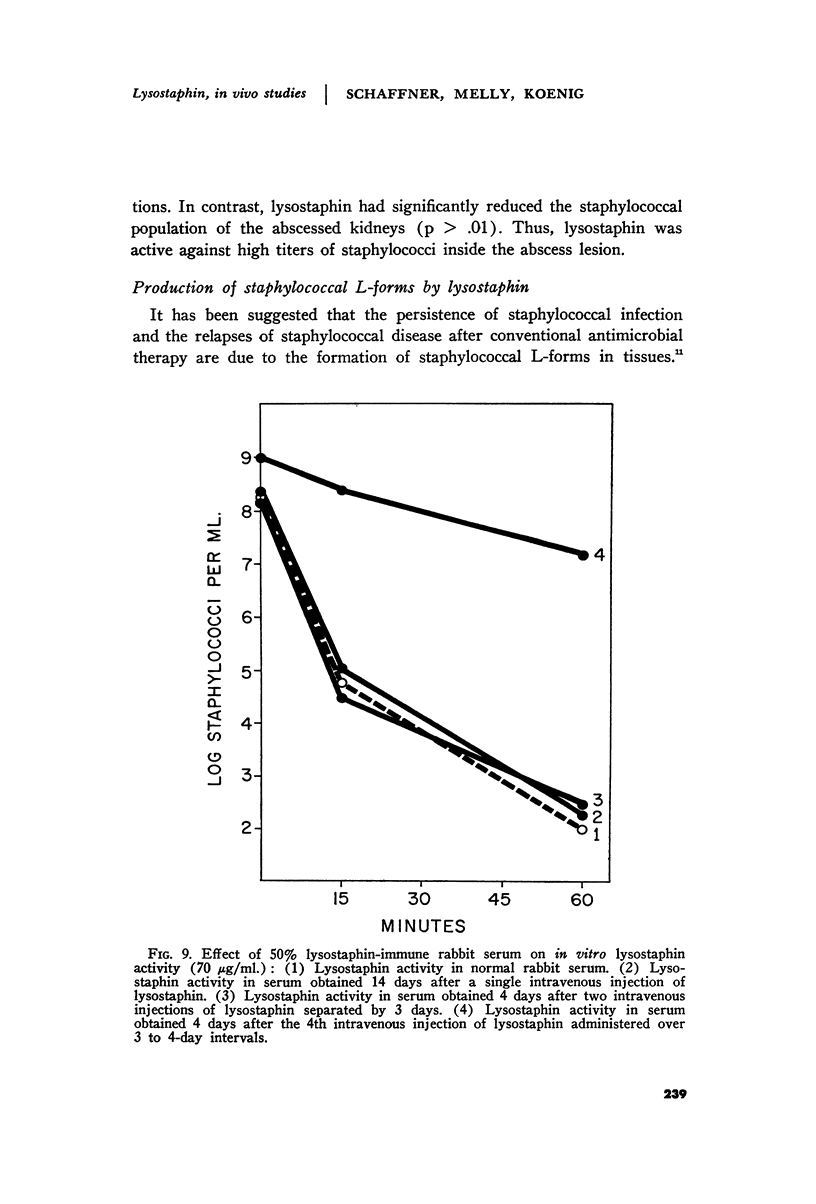





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BATTEN J. C., DINEEN P. A. P., MCCUNE R. M., Jr The effect of antimicrobial drugs on an experimental staphylococcal infection in mice. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1956 Aug 31;65(3):91–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1956.tb36627.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN Z. A. Determinants of infection in the peritoneal cavity. I. Response to and fate of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus albus in the mouse. Yale J Biol Med. 1962 Aug;35:12–28. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOENIG M. G. Factors relating to the virulence of staphylococci. I. Comparative studies on two colonial variants. Yale J Biol Med. 1962 Jun;34:537–559. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOENIG M. G., MELLY M. A., ROGERS D. E. Factors relating to the virulence of Staphylococci. II. Observations on four mouse-pathogenic strains. J Exp Med. 1962 Nov 1;116:589–599. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.5.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOENIG M. G., MELLY M. A., ROGERS D. E. Factors relating to the virulence of Staphylococci. III. Antibacterial versus antioxic immunity. J Exp Med. 1962 Nov 1;116:601–610. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.5.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagan B. M. Staphylococcal L-forms--ecologic perspectives. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jul 23;128(1):81–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb11631.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby W. M. Therapeutic aspects of staphylococcal disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jul 23;128(1):443–450. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb11653.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUCHTERLONY O. Antigen-antibody reactions in gels. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1949;26(4):507–515. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1949.tb00751.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH J. M., DUBOS R. J. The behavior of virulent and avirulent staphylococci in the tissues of normal mice. J Exp Med. 1956 Jan 1;103(1):87–108. doi: 10.1084/jem.103.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]