Abstract
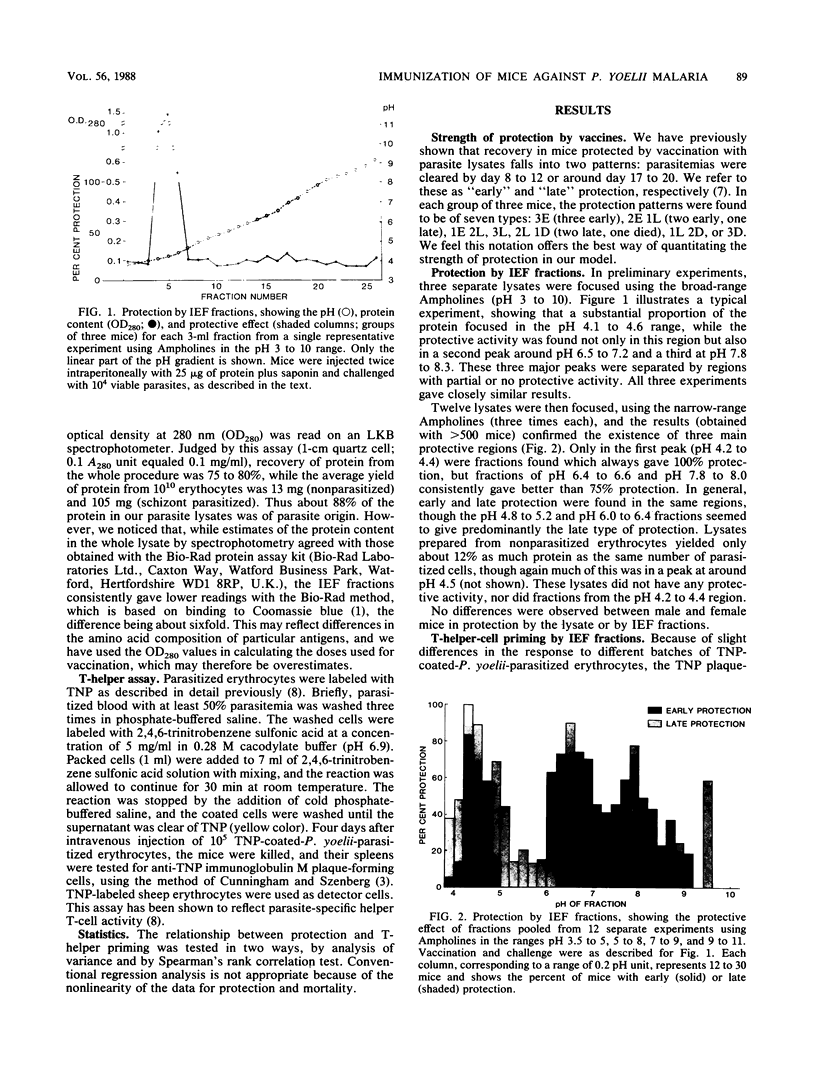
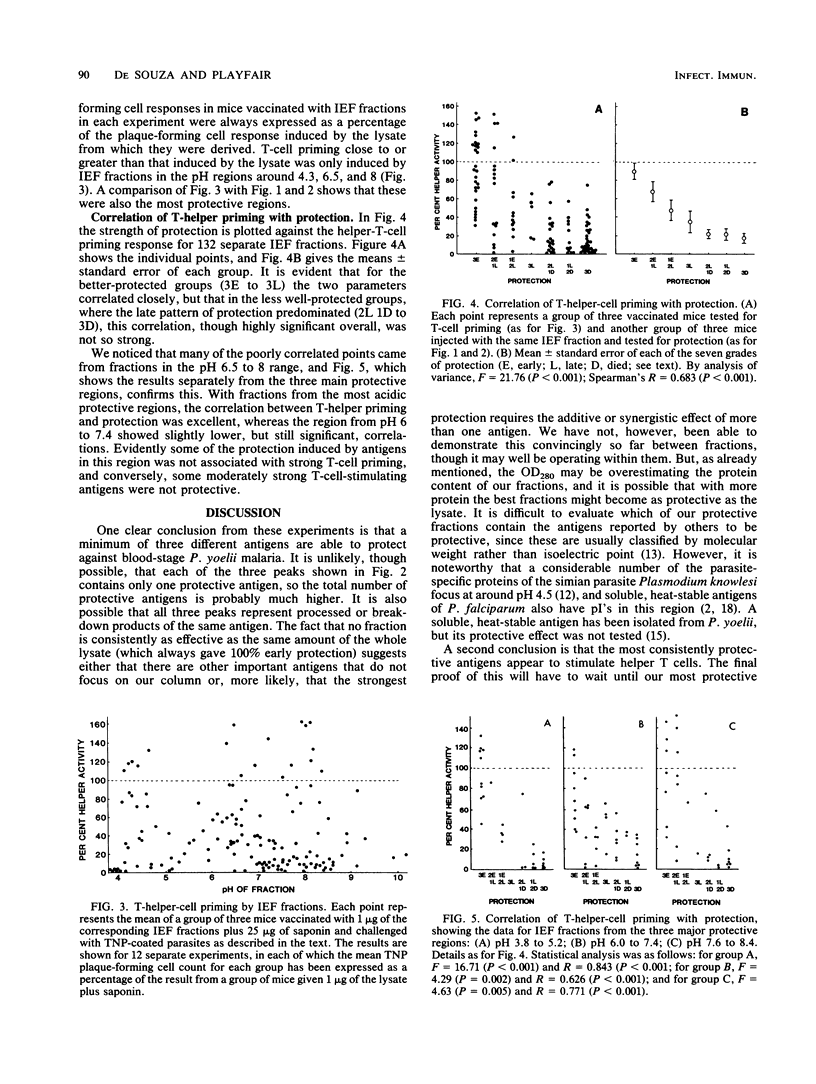
Mice were immunized with lethal Plasmodium yoelii blood-stage malaria antigens that had been fractionated by isoelectric focusing using a variety of Ampholines over the range pH 3 to 10. Fractions were tested for their ability to protect against live challenge and to prime for parasite-specific T-cell help. Both activities exhibited three major peaks in the pH regions 4.5, 6.5, and 8, the pH 4.5 peak being the most consistently protective. There was a significant correlation between protection and T-helper-cell priming, particularly with antigens from the first peak, suggesting that T-cell priming represents an important component of the function of some protective malaria vaccines.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppel R. L., Cowman A. F., Lingelbach K. R., Brown G. V., Saint R. B., Kemp D. J., Anders R. F. Isolate-specific S-antigen of Plasmodium falciparum contains a repeated sequence of eleven amino acids. Nature. 1983 Dec 22;306(5945):751–756. doi: 10.1038/306751a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham A. J., Szenberg A. Further improvements in the plaque technique for detecting single antibody-forming cells. Immunology. 1968 Apr;14(4):599–600. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahey J. R., Spitalny G. L. Immunity to Plasmodium yoelii: kinetics of the generation of T and B lymphocytes that passively transfer protective immunity against virulent challenge. Cell Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;98(2):486–495. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(86)90307-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton B., Walker A., Walliker D. Protein variation in clones of Plasmodium falciparum detected by two dimensional electrophoresis. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1985 Aug;16(2):173–183. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(85)90085-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good M. F., Maloy W. L., Lunde M. N., Margalit H., Cornette J. L., Smith G. L., Moss B., Miller L. H., Berzofsky J. A. Construction of synthetic immunogen: use of new T-helper epitope on malaria circumsporozoite protein. Science. 1987 Feb 27;235(4792):1059–1062. doi: 10.1126/science.2434994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Playfair J. H., De Souza J. B., Cottrell B. J. Protection of mice against malaria by a killed vaccine: differences in effectiveness against P. yoelii and P. berghei. Immunology. 1977 Oct;33(4):507–515. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Playfair J. H., De Souza J. B., Cottrell B. J. Reactivity and crossreactivity of mouse helper T cells to malaria parasites. Immunology. 1977 May;32(5):681–687. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Playfair J. H., De Souza J. B., Freeman R. R., Holder A. A. Vaccination with a purified blood-stage malaria antigen in mice: correlation of protection with T cell mediated immunity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Oct;62(1):19–23. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Playfair J. H., De Souza J. B. Vaccination of mice against malaria with soluble antigens. I. The effect of detergent, route of injection, and adjuvant. Parasite Immunol. 1986 Sep;8(5):409–414. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1986.tb00857.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Playfair J. H., Dockrell H., Taverne J. Macrophages as effector cells in immunity to malaria. Immunol Lett. 1985;11(3-4):233–237. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(85)90173-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Ullrich R., Wallach D. F. Plasmodium knowlesi-induced antigens in membranes of parasitized rhesus monkey erythrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4949–4953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman I. W. Membrane structure and function of malaria parasites and the infected erythrocyte. Parasitology. 1985 Dec;91(Pt 3):609–645. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000062843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tait A. Analysis of protein variation in Plasmodium falciparum by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1981 Feb;2(3-4):205–218. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(81)90101-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. W., Evans C. B., Hennessy G. W., Aley S. B. Use of a two-sited monoclonal antibody assay to detect a heat-stable malarial antigen in the sera of mice infected with Plasmodium yoelii. Infect Immun. 1986 Mar;51(3):884–890. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.3.884-890.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theander T. G., Bygbjerg I. C., Jacobsen L., Jepsen S., Larsen P. B., Kharazmi A. Low parasite specific T cell response in clinically immune individuals with low grade Plasmodium falciparum parasitaemia. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1986;80(6):1000–1001. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(86)90295-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troye-Blomberg M., Andersson G., Stoczkowska M., Shabo R., Romero P., Patarroyo M. E., Wigzell H., Perlmann P. Production of IL 2 and IFN-gamma by T cells from malaria patients in response to Plasmodium falciparum or erythrocyte antigens in vitro. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3498–3504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. J., Ling I. Fractionation and characterization of Plasmodium falciparum antigens. Bull World Health Organ. 1979;57 (Suppl 1):123–133. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]