Abstract
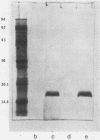
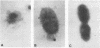
P6, a 16,600-dalton protein present in the outer membranes of both typeable and nontypeable strains, may be an important antigen in immunity to Haemophilus influenzae. The gene encoding P6 of a nontypeable strain of H. influenzae was cloned by using bacteriophage lambda gt11. Four recombinant phages were detected by screening plaques with monoclonal antibodies and a polyclonal antiserum. One recombinant phage, clone O, produced a full-length gene product which was expressed at a high yield. The DNA insert contained within this phage was cloned into the plasmid vector pUC18 to create the recombinant plasmid pBUD1. An Escherichia coli transformant containing this plasmid produced a protein which had an apparent molecular weight identical to that of H. influenzae P6, as determined by Western blot (immunoblot) analyses. Expression of the P6 polypeptide by both clone 0 and the transformant was independent of induction of the lac operon by isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactopyranoside, suggesting that transcription was from the promoter of the P6 gene. Immunoelectron microscopy using a monoclonal antibody with specificity for a P6 surface epitope detected the presence of P6 on the surface of the transformant. The insert in pBUD1 was cut down in size to approximately 800 base pairs. The resultant plasmid, pBUD5, also coded for a full-length gene product. DNA sequence analysis revealed that the P6 gene contains transcriptional and translational sequences resembling those recognized in E. coli and a signal sequence characteristic of procaryotic membrane proteins. In addition, the carboxy terminus of this signal sequence shares homology with a common sequence found in bacterial lipoproteins, suggesting that P6 is a lipoprotein. Posttranslational proteolytic cleavage of the signal sequence would result in a protein composed of 134 amino acids.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apicella M. A., Dudas K. C., Campagnari A., Rice P., Mylotte J. M., Murphy T. F. Antigenic heterogeneity of lipid A of Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):9–14. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.9-14.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barenkamp S. J., Munson R. S., Jr, Granoff D. M. Outer membrane protein and biotype analysis of pathogenic nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):535–540. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.535-540.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray G. L., Smith D. H., Baldridge J. S., Harkins R. N., Vasil M. L., Chen E. Y., Heyneker H. L. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression in Escherichia coli of the exotoxin A structural gene of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2645–2649. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmans P. L., Loftus T. A., Hansen E. J. Cloning and surface expression in Escherichia coli of a structural gene encoding a surface protein of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):236–242. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.236-242.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb M. R., Smith D. H. Outer membrane protein composition in disease isolates of Haemophilus influenzae: pathogenic and epidemiological implications. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):709–717. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.709-717.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson R. S., Jr, Granoff D. M. Purification and partial characterization of outer membrane proteins P5 and P6 from Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):544–549. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.544-549.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Apicella M. A. Nontypable Haemophilus influenzae: a review of clinical aspects, surface antigens, and the human immune response to infection. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jan-Feb;9(1):1–15. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Bartos L. C., Rice P. A., Nelson M. B., Dudas K. C., Apicella M. A. Identification of a 16,600-dalton outer membrane protein on nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae as a target for human serum bactericidal antibody. J Clin Invest. 1986 Oct;78(4):1020–1027. doi: 10.1172/JCI112656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Dudas K. C., Mylotte J. M., Apicella M. A. A subtyping system for nontypable Haemophilus influenzae based on outer-membrane proteins. J Infect Dis. 1983 May;147(5):838–846. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.5.838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Nelson M. B., Dudas K. C., Mylotte J. M., Apicella M. A. Identification of a specific epitope of Haemophilus influenzae on a 16,600-dalton outer membrane protein. J Infect Dis. 1985 Dec;152(6):1300–1307. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.6.1300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson E. N., Jr, McGee Z. A., Kaplan J., Hammond M. E., Larson J. K., Buchanan T. M., Schoolnik G. K. Ultrastructural localization of specific gonococcal macromolecules with antibody-gold sphere immunological probes. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):361–366. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.361-366.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas W. R., Rossi A. A. Molecular cloning of DNA coding for outer membrane proteins of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1986 Jun;52(3):812–817. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.3.812-817.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson M. E. Compilation of published signal sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5145–5164. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. C., Tokunaga M. Biogenesis of lipoproteins in bacteria. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;125:127–157. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71251-7_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Yeast RNA polymerase II genes: isolation with antibody probes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):778–782. doi: 10.1126/science.6356359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]