Abstract
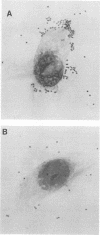
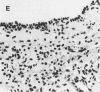
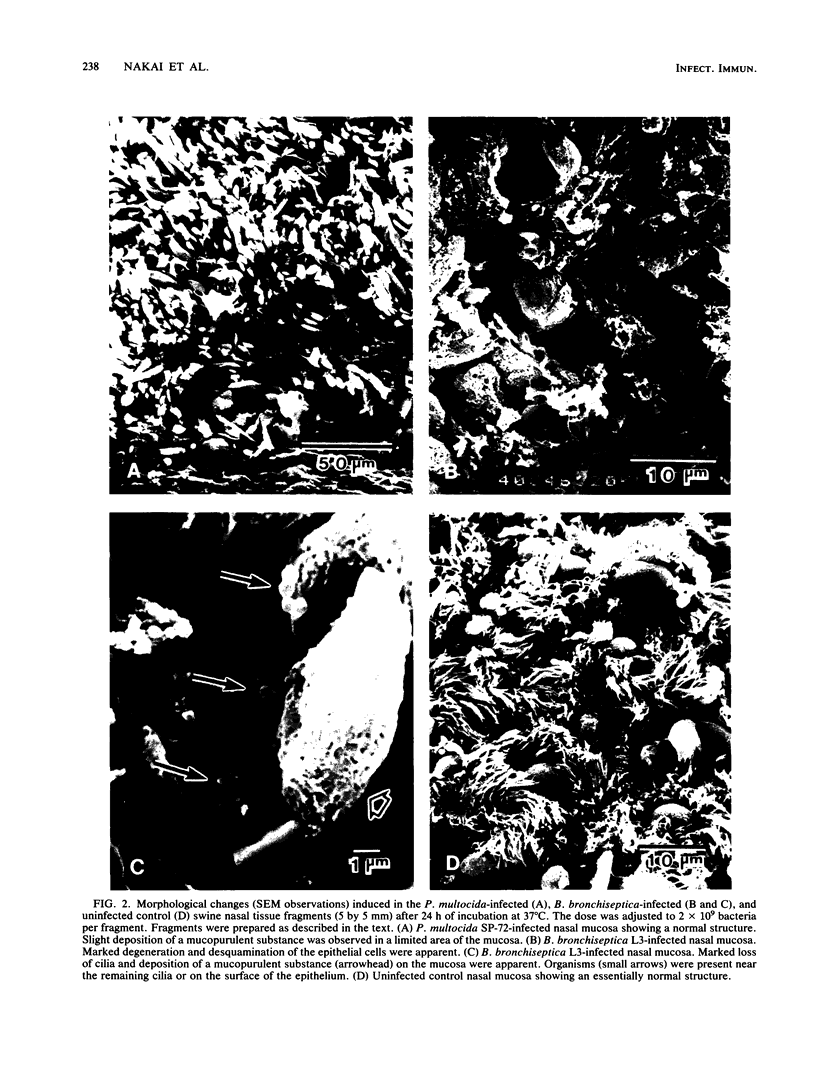
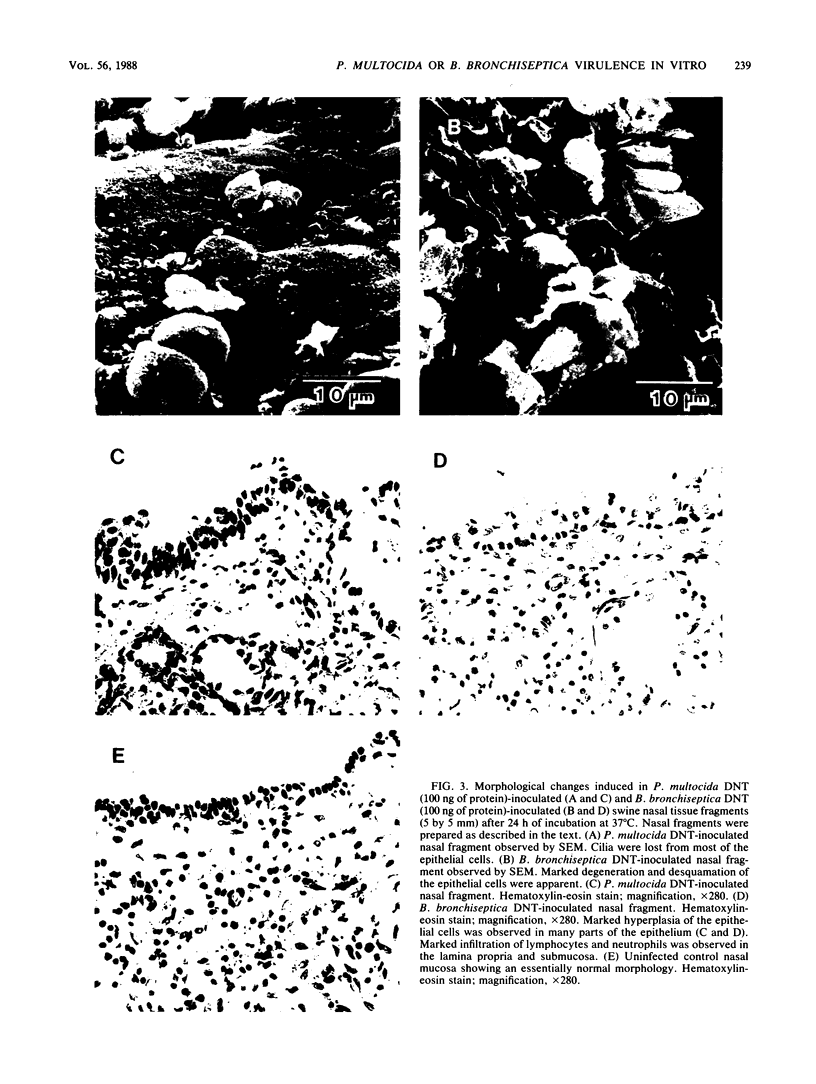
The interaction of Bordetella bronchiseptica or Pasteurella multocida with swine nasal epithelial cells was studied in vitro. The mean number of B. bronchiseptica organisms adhered per cell was about three times as high as that of P. multocida (P less than 0.01), and the adherence was specifically inhibited by the homologous antiserum prepared with the whole-cell antigen of each bacterium. The poor affinity of P. multocida to the swine nasal mucosa as compared with that of B. bronchiseptica was also demonstrated in the cultured fragments of the nasal mucosa. When observed with a scanning electron microscope, B. bronchiseptica organisms colonized the fragments, whereas few P. multocida organisms adhered. Morphologically, the P. multocida-infected fragments had an essentially normal structure, whereas marked degeneration and marked desquamation of the epithelial cells and severe inflammatory reactions were observed in many areas of the B. bronchiseptica-infected fragments. These morphological observations were consistent with those for the nasal mucosa of P. multocida- or B. bronchiseptica-infected neonatal pigs (T. Nakai, K. Kume, H. Yoshikawa, T. Oyamada, and T. Yoshikawa, Jpn. J. Vet. Sci. 48:693-701, 1986; T. Oyamada, T. Yoshikawa, H. Yoshikawa, M. Shimizu, T. Nakai, and K. Kume, Jpn. J. Vet. Sci. 48:377-387, 1986). Cultured swine nasal fragments, however, were equally injured when they were incubated in a medium containing purified dermonecrotic toxin (DNT) preparations of B. bronchiseptica or P. multocida. Therefore, these DNT preparations can induce morphological damage closely resembling that induced in vivo. Hence, colonization of B. bronchiseptica and production of its DNT on the swine nasal mucosa appear to result in the production of mucosal damage. On the other hand, P. multocida seems to lack the ability to colonize normal swine nasal mucosa, thus resulting in no production or the slight production of DNT to such an extent as to produce mucosal damage. The present data support our previous hypothesis (Nakai et al.; Oyamada et al.) that B. bronchiseptica induces swine atrophic rhinitis, whereas P. multocida does not.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brassinne M., Dewaele A., Gouffaux M. Intranasal infection with Bordetella bronchiseptica in gnotobiotic piglets. Res Vet Sci. 1976 Mar;20(2):162–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARTER G. R. Studies on Pasteurella multocida. I. A hemagglutination test for the identification of serological types. Am J Vet Res. 1955 Jul;16(60):481–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan J. R., Ross R. F., Switzer W. P., Ramsey F. K. Pathology of experimental Bordetella bronchiseptica infection in swine: atrophic rhinitis. Am J Vet Res. 1966 Mar;27(117):457–466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gois M., Barnes H. J., Ross R. F. Potentiation of turbinate atrophy in pigs by long-term nasal colonization with Pasteurella multocida. Am J Vet Res. 1983 Mar;44(3):372–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanada M., Shimoda K., Tomita S., Nakase Y., Nishiyama Y. Production of lesions similar to naturally occurring swine atrophic rhinitis by cell-free sonicated extract of Bordetella bronchiseptica. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1979 Feb;41(1):1–8. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.41.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimman T. G., Kamp E. M. Induced atrophic rhinitis in rats. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Nov;47(11):2426–2430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kume K., Nakai T., Samejima Y., Sugimoto C. Properties of dermonecrotic toxin prepared from sonic extracts Bordetella bronchiseptica. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):370–377. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.370-377.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda M., Shimizu T. Nasal infection of Alcaligenes bronchisepticus (Bordetella bronchiseptica) and lesions in newborn rabbits. Natl Inst Anim Health Q (Tokyo) 1975 Spring;15(1):29–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miniats O. P., Johnson J. A. Experimental atrophic rhinitis in gnotobiotic pigs. Can J Comp Med. 1980 Oct;44(4):358–365. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muse K. E., Collier A. M., Baseman J. B. Scanning electron microscopic study of hamster tracheal organ cultures infected with Bordetella pertussis. J Infect Dis. 1977 Dec;136(6):768–777. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.6.768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAMIOKA S., MURATA M. Serological studies on Pasteurella multocida. I. A simplified method for capsule typing of the organism. Cornell Vet. 1961 Oct;51:498–521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa M., Shimizu T., Motoi Y. Pathology of experimental atrophic rhinitis in swine infected with Alcaligenes bronchisepticus or Pasteurella multocida. Natl Inst Anim Health Q (Tokyo) 1974 Summer;14(2):61–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai T., Kume K., Yoshikawa H., Oyamada T., Yoshikawa T. Changes in the nasal mucosa of specific-pathogen-free neonatal pigs infected with Pasteurella multocida or Bordetella bronchiseptica. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1986 Aug;48(4):693–701. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.48.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai T., Sawata A., Kume K. Intracellular locations of dermonecrotic toxins in Pasteurella multocida and in Bordetella bronchiseptica. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Apr;46(4):870–874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai T., Sawata A., Tsuji M., Kume K. Characterization of dermonecrotic toxin produced by serotype D strains of Pasteurella multocida. Am J Vet Res. 1984 Nov;45(11):2410–2413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai T., Sawata A., Tsuji M., Samejima Y., Kume K. Purification of dermonecrotic toxin from a sonic extract of Pasteurella multocida SP-72 serotype D. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):429–434. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.429-434.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oyamada T., Yoshikawa T., Yoshikawa H., Shimizu M., Nakai T., Kume K. Lesions induced in the nasal turbinates of neonatal pigs inoculated with Pasteurella multocia and/or Bordetella bronchiseptica. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1986 Apr;48(2):377–387. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.48.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen K. B., Barfod K. The aetiological significance of Bordetella bronchiseptica and Pasteurella multocida in atrophic rhinitis of swine. Nord Vet Med. 1981 Dec;33(12):513–522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen K. B., Elling F. The pathogenesis of atrophic rhinitis in pigs induced by toxigenic Pasteurella multocida. J Comp Pathol. 1984 Apr;94(2):203–214. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(84)90041-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutter J. M., Luther P. D. Cell culture assay for toxigenic Pasteurella multocida from atrophic rhinitis of pigs. Vet Rec. 1984 Apr 21;114(16):393–396. doi: 10.1136/vr.114.16.393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutter J. M. Virulence of Pasteurella multocida in atrophic rhinitis of gnotobiotic pigs infected with Bordetella bronchiseptica. Res Vet Sci. 1983 May;34(3):287–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawata A., Kume K. Nasal turbinate atrophy in young mice inoculated with Bordetella bronchiseptica of pig origin. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Oct;43(10):1845–1847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawata A., Nakai T., Kume K., Yoshikawa H., Yoshikawa T. Intranasal inoculation of chickens with encapsulated or nonencapsulated variants of Haemophilus paragallinarum: electron microscopic evaluation of the nasal mucosa. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Nov;46(11):2346–2353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu T., Nakagawa M., Shibata S., Suzuki K. Atrophic rhinitis produced by intranasal inoculation of Bordetella bronchiseptica in hysterectomy produced colostrum-deprived pigs. Cornell Vet. 1971 Oct;61(4):696–705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokomizo Y., Shimizu T. Adherence of Bordetella bronchiseptica to swine nasal epithelial cells and its possible role in virulence. Res Vet Sci. 1979 Jul;27(1):15–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]