Abstract
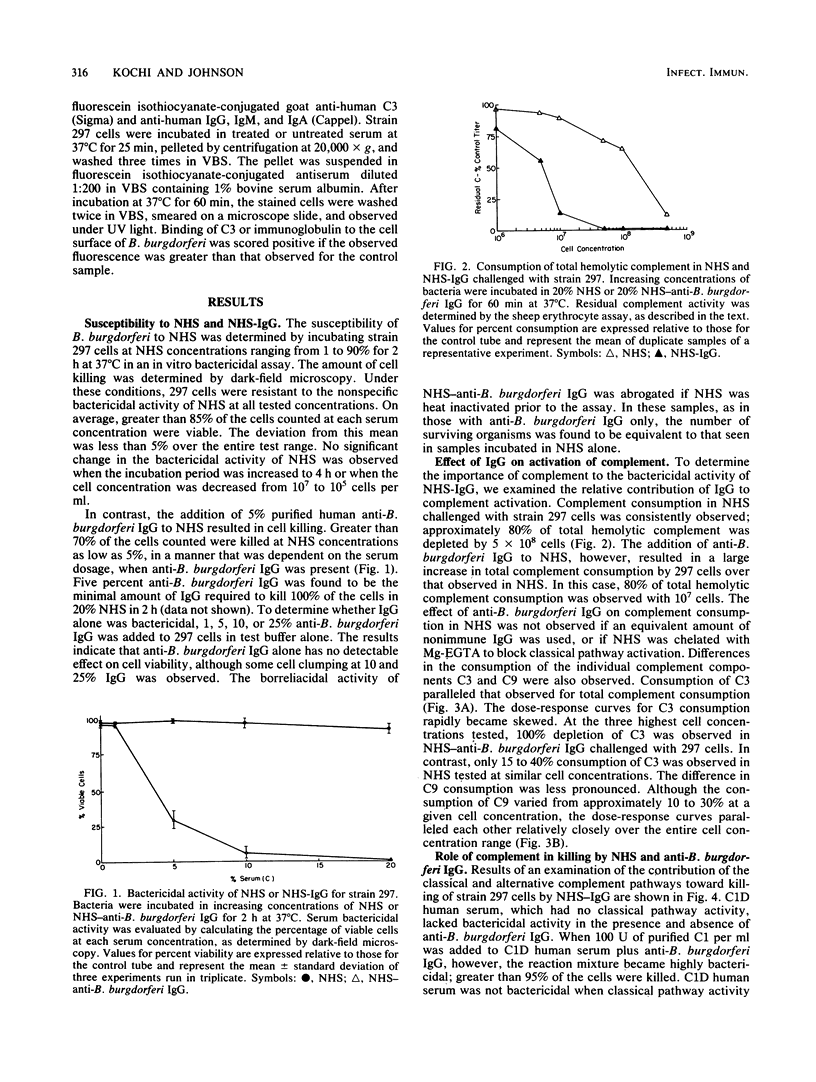
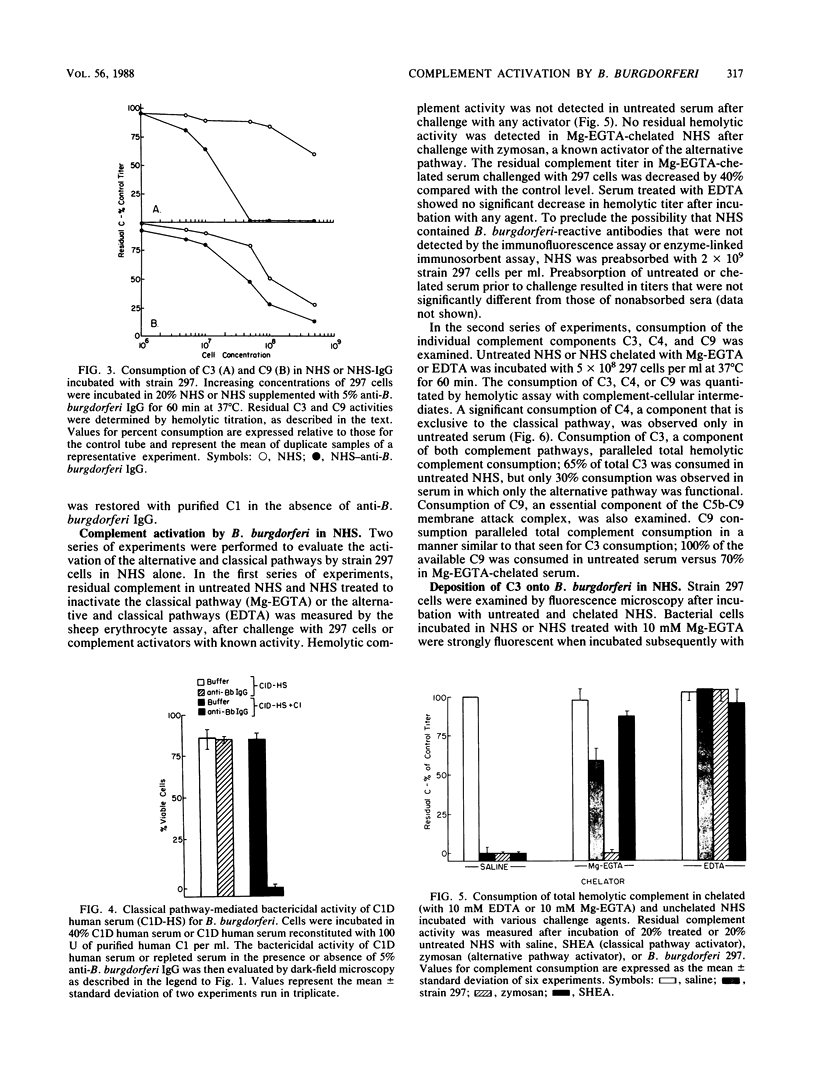
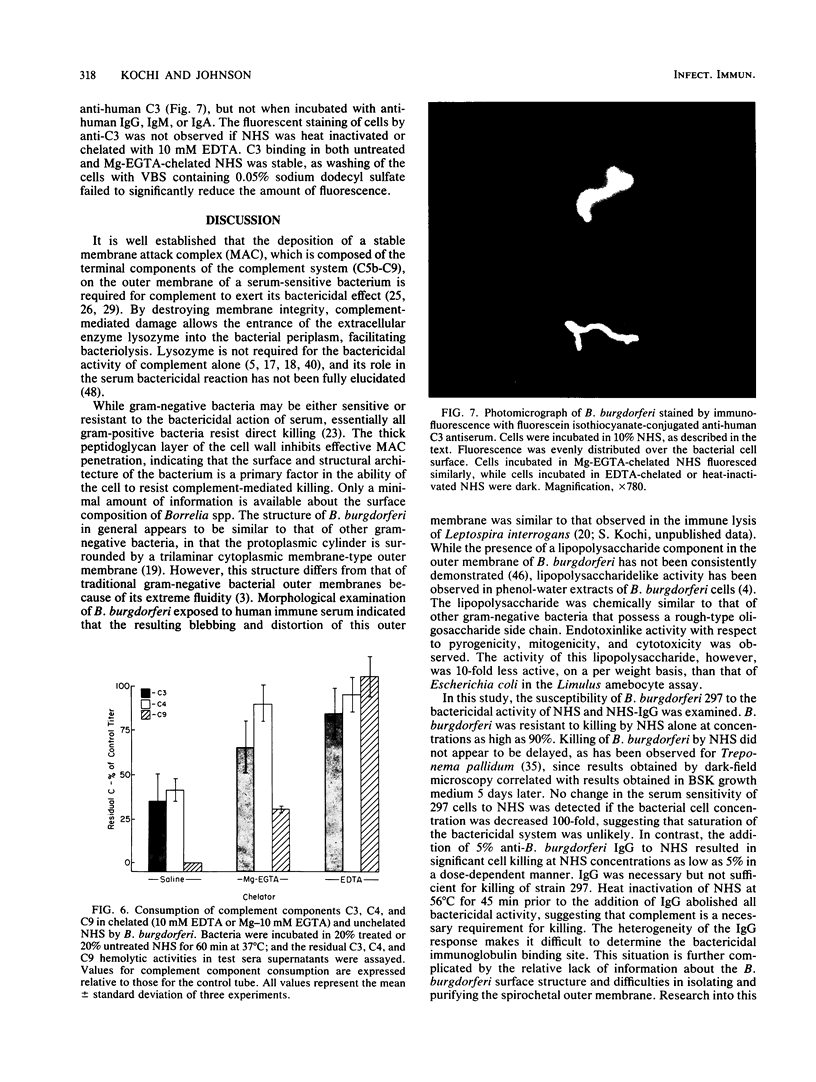
The antibody and complement requirements for killing of Borrelia burgdorferi 297 by normal human serum (NHS) and NHS plus immunoglobulin G (IgG) were examined. B. burgdorferi activated both the alternative and classical complement pathways in NHS. In NHS chelated with 10 mM ethylene glycol-bis(beta-aminoethyl ether)-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid plus 4 mM MgCl2 (Mg-EGTA) to block classical pathway activation, consumption (activation) of total hemolytic complement, complement component 3 (C3), and C9 by B. burgdorferi was observed. Furthermore, challenge of unchelated NHS with 297 cells resulted in the consumption of C4, in addition to an increase in C3 and C9 consumption over that observed in chelated serum. In spite of complement activation, B. burgdorferi was resistant to the nonspecific bactericidal activity of NHS. The addition of human anti-B. burgdorferi IgG to NHS, however, resulted in the complete killing of 297 cells. Bactericidal activity of this serum was abrogated if NHS was immunochemically depleted of C1, indicating that killing was mediated by the classical pathway. The manifestation of bactericidal activity was accompanied by a large increase in total complement and C3 consumption over that observed in NHS alone. Under similar conditions, only a minimal increase in C9 consumption was observed. No increase in total complement consumption was observed if NHS plus anti-B. burgdorferi IgG was treated with Mg-EGTA prior to challenge. The results of these experiments demonstrate that B. burgdorferi is resistant to the nonspecific bactericidal activity of NHS, in spite of classical and alternative complement pathway activation. B. burgdorferi is sensitive to serum, however, in the presence of IgG, which mediates bacterial killing through the classical complement pathway.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. L., Johnson R. C. Electron microscopy of immune disruption of leptospires: action of complement and lysozyme. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2293–2309. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2293-2309.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F. Biology of Borrelia species. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Dec;50(4):381–400. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.4.381-400.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck G., Habicht G. S., Benach J. L., Coleman J. L. Chemical and biologic characterization of a lipopolysaccharide extracted from the Lyme disease spirochete (Borrelia burgdorferi). J Infect Dis. 1985 Jul;152(1):108–117. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.1.108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloch E. F., Schmetz M. A., Foulds J., Hammer C. H., Frank M. M., Joiner K. A. Multimeric C9 within C5b-9 is required for inner membrane damage to Escherichia coli J5 during complement killing. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 1;138(3):842–848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. J., Berger M., Joiner K. A., Frank M. M. Classical complement pathway activation by antipneumococcal antibodies leads to covalent binding of C3b to antibody molecules. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):594–598. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.594-598.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Benach J. L., Grunwaldt E., Davis J. P. Lyme disease-a tick-borne spirochetosis? Science. 1982 Jun 18;216(4552):1317–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.7043737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderon J., Schreiber R. D. Activation of the alternative and classical complement pathways by Entamoeba histolytica. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):560–565. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.560-565.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craft J. E., Fischer D. K., Shimamoto G. T., Steere A. C. Antigens of Borrelia burgdorferi recognized during Lyme disease. Appearance of a new immunoglobulin M response and expansion of the immunoglobulin G response late in the illness. J Clin Invest. 1986 Oct;78(4):934–939. doi: 10.1172/JCI112683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine D. P. Comparison of ethyleneglycoltetraacetic acid and its magnesium salt as reagents for studying alternative complement pathway function. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):124–128. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.124-128.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine D. P., Marney S. R., Jr, Colley D. G., Sergent J. S., Des Prez R. M. C3 shunt activation in human serum chelated with EGTA. J Immunol. 1972 Oct;109(4):807–809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fries L. F., Gaither T. A., Hammer C. H., Frank M. M. C3b covalently bound to IgG demonstrates a reduced rate of inactivation by factors H and I. J Exp Med. 1984 Dec 1;160(6):1640–1655. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.6.1640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gee A. P. Molecular titration of components of the classical complement pathway. Methods Enzymol. 1983;93:339–375. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)93052-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harriman G. R., Podack E. R., Braude A. I., Corbeil L. C., Esser A. F., Curd J. G. Activation of complement by serum-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Assembly of the membrane attack complex without subsequent cell death. J Exp Med. 1982 Oct 1;156(4):1235–1249. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.4.1235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue K., Yonemasu K., Takamizawa A., Amano T. [Studies on the immune bacteriolysis. XIV. Requirement of all nine components of complement for immune bacteriolysis]. Biken J. 1968 Sep;11(3):203–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Harris V. G. Antileptospiral activity of serum. II. Leptospiral virulence factor. J Bacteriol. 1967 Feb;93(2):513–519. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.2.513-519.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Marek N., Kodner C. Infection of Syrian hamsters with Lyme disease spirochetes. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Dec;20(6):1099–1101. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.6.1099-1101.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C. The spirochetes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:89–106. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.000513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner K. A., Goldman R. C., Hammer C. H., Leive L., Frank M. M. Studies on the mechanism of bacterial resistance to complement-mediated killing. VI. IgG increases the bactericidal efficiency of C5b-9 for E. coli 0111B4 by acting at a step before C5 cleavage. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2570–2575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner K. A., Hammer C. H., Brown E. J., Cole R. J., Frank M. M. Studies on the mechanism of bacterial resistance to complement-mediated killing. I. Terminal complement components are deposited and released from Salmonella minnesota S218 without causing bacterial death. J Exp Med. 1982 Mar 1;155(3):797–808. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.3.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner K. A., Hammer C. H., Brown E. J., Frank M. M. Studies on the mechanism of bacterial resistance to complement-mediated killing. II. C8 and C9 release C5b67 from the surface of Salmonella minnesota S218 because the terminal complex does not insert into the bacterial outer membrane. J Exp Med. 1982 Mar 1;155(3):809–819. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.3.809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner K. A., Schmetz M. A., Goldman R. C., Leive L., Frank M. M. Mechanism of bacterial resistance to complement-mediated killing: inserted C5b-9 correlates with killing for Escherichia coli O111B4 varying in O-antigen capsule and O-polysaccharide coverage of lipid A core oligosaccharide. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):113–117. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.113-117.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner K. A., Warren K. A., Brown E. J., Swanson J., Frank M. M. Studies on the mechanism of bacterial resistance to complement-mediated killing. IV. C5b-9 forms high molecular weight complexes with bacterial outer membrane constituents on serum-resistant but not on serum-sensitive Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Immunol. 1983 Sep;131(3):1443–1451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner K., Brown E., Hammer C., Warren K., Frank M. Studies on the mechanism of bacterial resistance to complement-mediated killing. III. C5b-9 deposits stably on rough and type 7 S. pneumoniae without causing bacterial killing. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):845–849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll H. P., Bhakdi S., Taylor P. W. Membrane changes induced by exposure of Escherichia coli to human serum. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):1055–1066. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.1055-1066.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy N. J., Kasper D. L. Antibody-independent and -dependent opsonization of group B Streptococcus requires the first component of complement C1. Infect Immun. 1985 Jul;49(1):19–24. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.1.19-24.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medicus R. G., Chapuis R. M. The first component of complement. I. Purification and properties of native C1. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):390–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neoh S. H., Gordon T. P., Roberts-Thomson P. J. A simple one-step procedure for preparation of C1-deficient human serum. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Apr 27;69(2):277–280. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90325-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platts-Mills T. A., Ishizaka K. Activation of the alternate pathway of human complements by rabbit cells. J Immunol. 1974 Jul;113(1):348–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluschke G., Achtman M. Degree of antibody-independent activation of the classical complement pathway by K1 Escherichia coli differs with O antigen type and correlates with virulence of meningitis in newborns. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):684–692. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.684-692.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice M., Fitzgerald T. J. Immune immobilization of Treponema pallidum: antibody and complement interactions revisited. Can J Microbiol. 1985 Dec;31(12):1147–1151. doi: 10.1139/m85-216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller N. L., Alazard M. J., Borowski R. S. Serum sensitivity of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa mucoid strain. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):748–755. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.748-755.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller N. L., Joiner K. A. Interaction of complement with serum-sensitive and serum-resistant strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):689–694. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.689-694.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger P. A., Duray P. H., Burke B. A., Steere A. C., Stillman M. T. Maternal-fetal transmission of the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Jul;103(1):67–68. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-103-1-67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoolnik G. K., Ochs H. D., Buchanan T. M. Immunoglobulin class responsible for gonococcal bactericidal activity of normal human sera. J Immunol. 1979 May;122(5):1771–1779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber R. D., Pangburn M. K., Lesavre P. H., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Initiation of the alternative pathway of complement: recognition of activators by bound C3b and assembly of the entire pathway from six isolated proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3948–3952. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott E. N., Muchmore H. G., Fine D. P. Activation of the alternative complement pathway by Sporothrix schenckii. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):6–9. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.6-9.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Grodzicki R. L., Kornblatt A. N., Craft J. E., Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W., Schmid G. P., Johnson E., Malawista S. E. The spirochetal etiology of Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 31;308(13):733–740. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303313081301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Hardin J. A., Ruddy S., Mummaw J. G., Malawista S. E. Lyme arthritis: correlation of serum and cryoglobulin IgM with activity, and serum IgG with remission. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 May;22(5):471–483. doi: 10.1002/art.1780220506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama K., Rothenberg R. J., Barbour A. G. Absence of lipopolysaccharide in the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2311–2313. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2311-2313.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarr P. I., Hosea S. W., Brown E. J., Schneerson R., Sutton A., Frank M. M. The requirement of specific anticapsular IgG for killing of Haemophilus influenzae by the alternative pathway of complement activation. J Immunol. 1982 Apr;128(4):1772–1775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]