Abstract
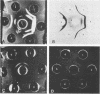
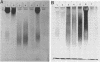
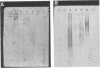
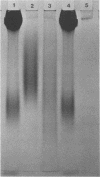
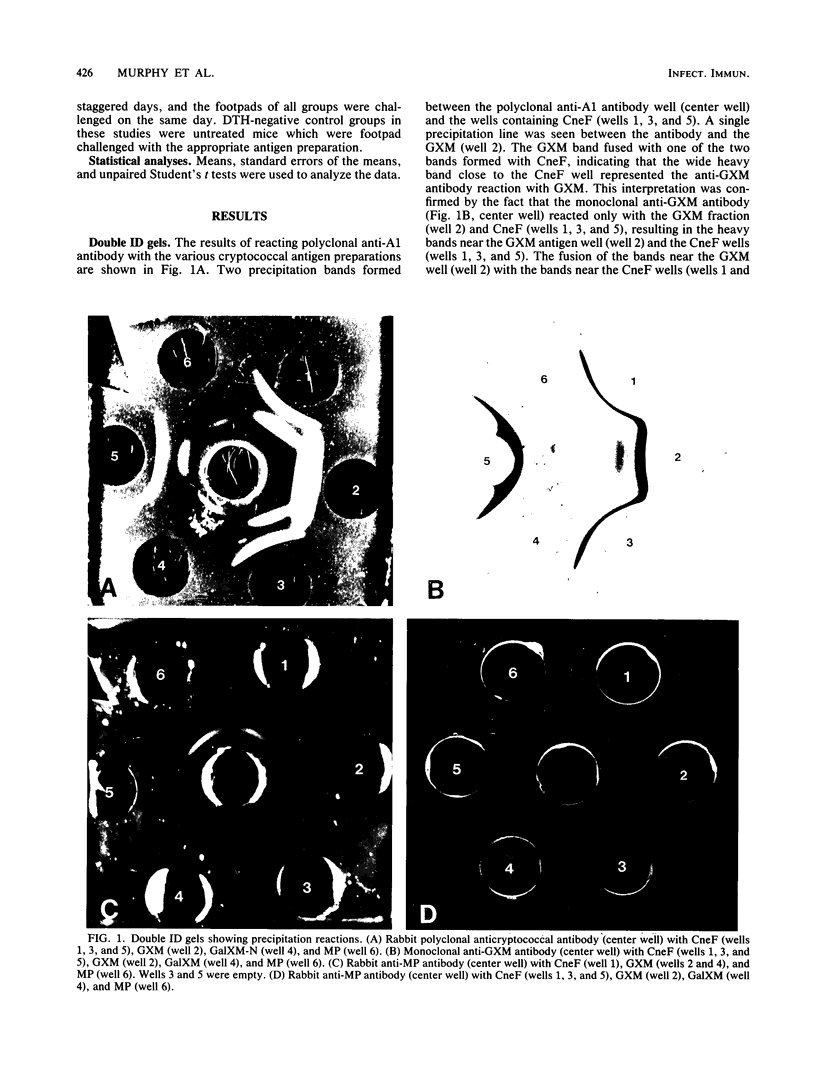
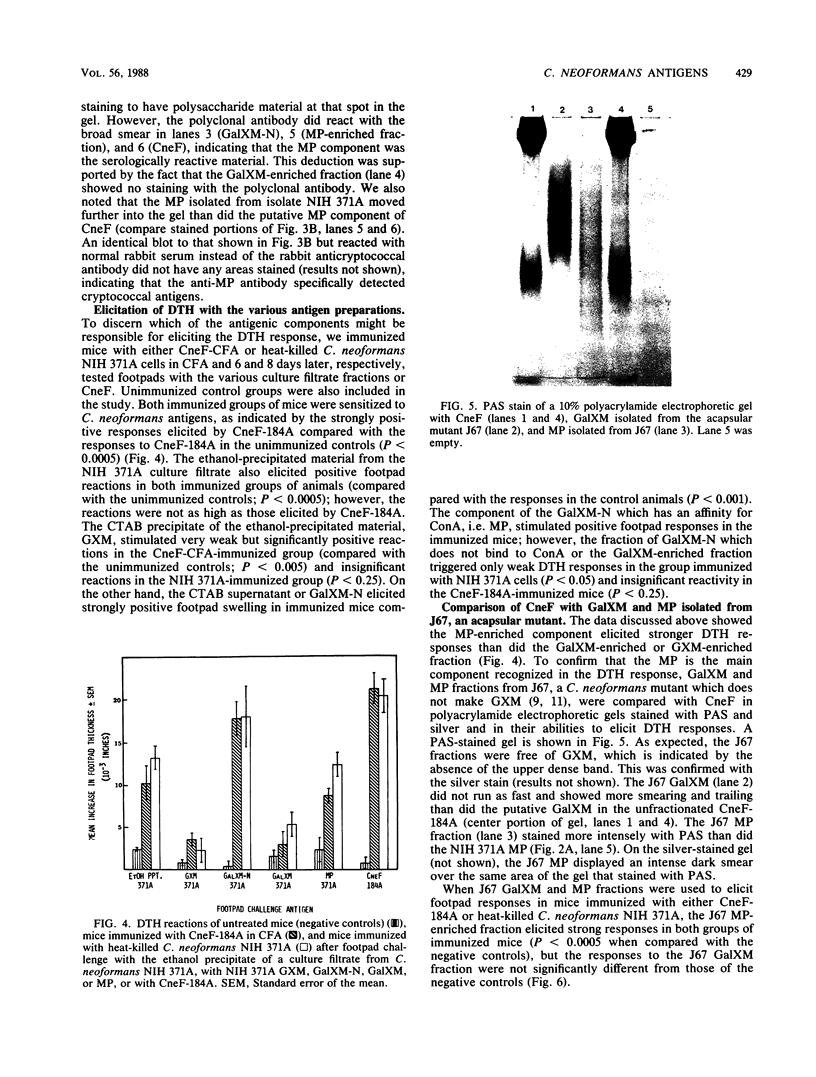
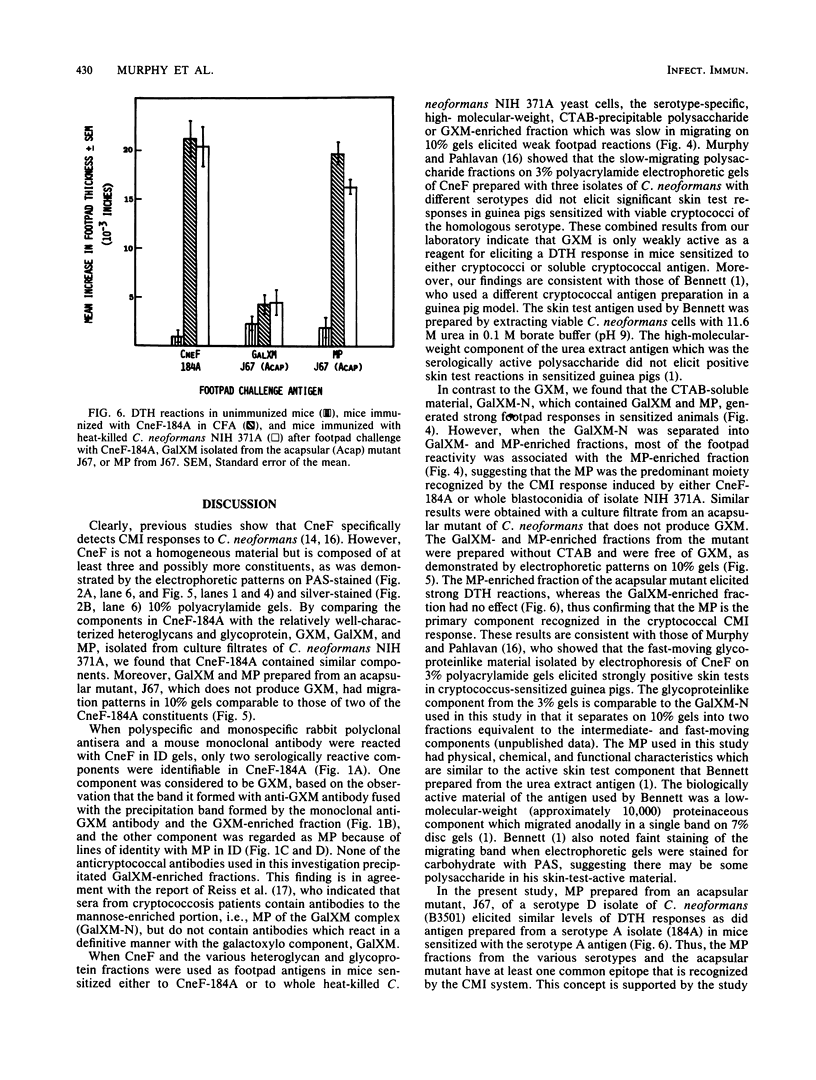
We compared a cryptococcal culture filtrate antigen referred to as CneF with chemically defined cryptococcal antigen fractions isolated by Cherniak and co-workers by using double immunodiffusion gels, polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, immunoblots, and footpad reactivity of immunized mice. The three previously described components of cryptococcal culture filtrates are a high-molecular-weight glucuronoxylo-mannan (GXM), which is the major constituent, a galactoxylomannan (GaIXM), and a mannoprotein (MP). In this study we demonstrated that CneF contained components which were serologically and electrophoretically similar to the three previously described cryptococcal culture filtrate fractions. The MP fraction elicited significantly stronger delayed-type hypersensitivity responses than did the GXM or GaIXM fraction when used in mice immunized either with the CneF in complete Freund adjuvant or whole heat-killed Cryptococcus neoformans yeast cells. These findings were confirmed when the footpads of immunized mice were challenged with GaIXM and MP preparations from a culture filtrate of a C. neoformans acapsular mutant that does not produce GXM. Thus, we concluded that the MP was the primary component recognized by the anticryptococcal cell-mediated immune response in mice.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett J. E. Cryptococcal skin test antigen: preparation variables and characterization. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):373–380. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.373-380.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharjee A. K., Bennett J. E., Bundle D. R., Glaudemans C. P. Anticryptococcal type D antibodies raised in rabbits. Mol Immunol. 1983 Apr;20(4):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(83)90016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cauley L. K., Murphy J. W. Response of congenitally athymic (nude) and phenotypically normal mice to Cryptococcus neoformans infection. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):644–651. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.644-651.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherniak R., Reiss E., Slodki M. E., Plattner R. D., Blumer S. O. Structure and antigenic activity of the capsular polysaccharide of Cryptococcus neoformans serotype A. Mol Immunol. 1980 Aug;17(8):1025–1032. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(80)90096-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS E. E., KESSEL J. F. The antigenic composition of Cryptococcus neoformans. II. Serologic studies with the capsular polysaccharide. J Immunol. 1951 Aug;67(2):109–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert T. F., Kozel T. R. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies specific for Cryptococcus neoformans capsular polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1987 Aug;55(8):1895–1899. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.8.1895-1899.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromtling R. A., Shadomy H. J., Jacobson E. S. Decreased virulence in stable, acapsular mutants of cryptococcus neoformans. Mycopathologia. 1982 Jul 23;79(1):23–29. doi: 10.1007/BF00636177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda R., Shinoda T., Fukazawa Y., Kaufman L. Antigenic characterization of Cryptococcus neoformans serotypes and its application to serotyping of clinical isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jul;16(1):22–29. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.1.22-29.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson E. S., Ayers D. J., Harrell A. C., Nicholas C. C. Genetic and phenotypic characterization of capsule mutants of Cryptococcus neoformans. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jun;150(3):1292–1296. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.3.1292-1296.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. W., Cozad G. C. Immunological unresponsiveness induced by cryptococcal capsular polysaccharide assayed by the hemolytic plaque technique. Infect Immun. 1972 Jun;5(6):896–901. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.6.896-901.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. W., Gregory J. A., Larsh H. W. Skin testing of guinea pigs and footpad testing of mice with a new antigen for detecting delayed hypersensitivity to Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1974 Feb;9(2):404–409. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.2.404-409.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. W., Moorhead J. W. Regulation of cell-mediated immunity in cryptococcosis. I. Induction of specific afferent T suppressor cells by cryptococcal antigen. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):276–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. W., Pahlavan N. Cryptococcal culture filtrate antigen for detection of delayed-type hypersensitivity in cryptococcosis. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):284–292. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.284-292.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss E., Cherniak R., Eby R., Kaufman L. Enzyme immunoassay detection of IgM to galactoxylomannan of Cryptococcus neoformans. Diagn Immunol. 1984;2(2):109–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner S. H., Cherniak R., Reiss E. Fractionation and characterization of galactoxylomannan from Cryptococcus neoformans. Carbohydr Res. 1984 Feb 15;125(2):343–349. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(84)85172-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeke B. A manual of quantitative immunoelectrophoresis. Methods and applications. 1. General remarks on principles, equipment, reagents and procedures. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:15–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb03776.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. E., Bennett J. E., Bailey J. W. Serologic grouping of Cryptococcus neoformans. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Mar;127(3):820–823. doi: 10.3181/00379727-127-32812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacharius R. M., Zell T. E., Morrison J. H., Woodlock J. J. Glycoprotein staining following electrophoresis on acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1969 Jul;30(1):148–152. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90383-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]