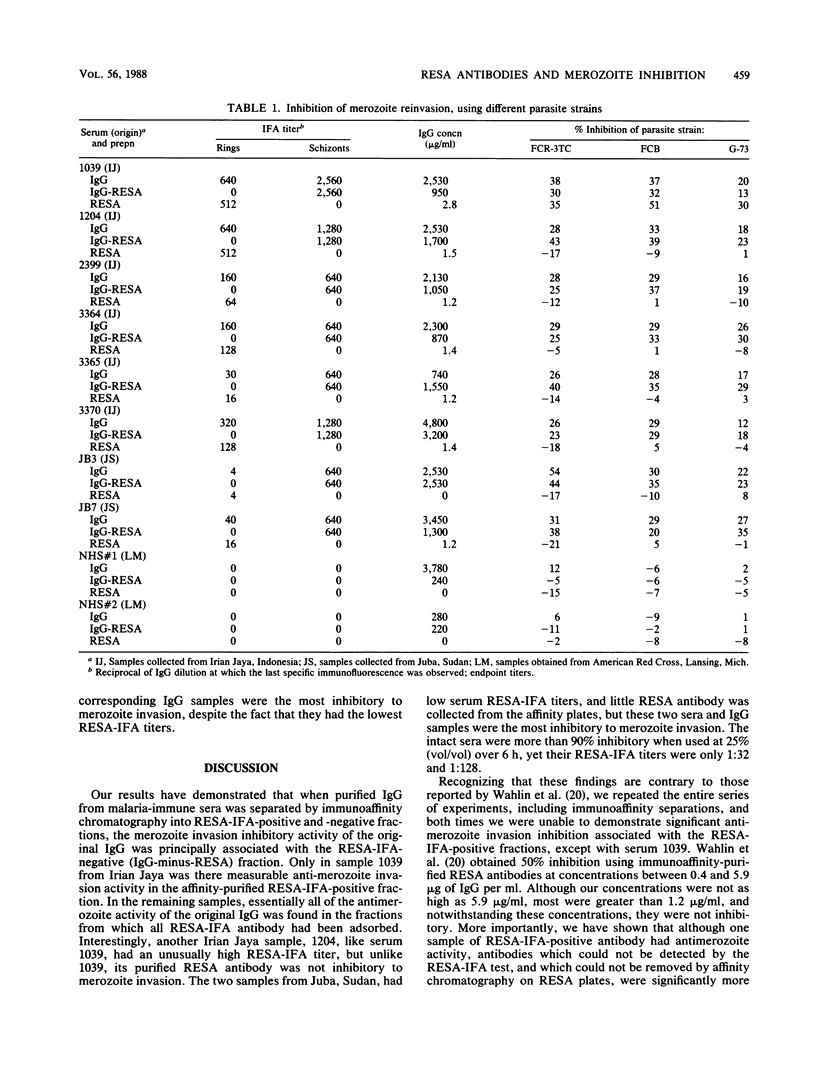
Abstract
We affinity purified, from malaria-immune serum, antibody to the ring-infected erythrocyte surface antigen (RESA), using petri dishes containing a monolayer of Plasmodium falciparum ring-infected erythrocytes. Except for one out of eight samples, the purified antibody positive by RESA-immunofluorescent assay was not inhibitory to the in vitro invasion of merozoites into erythrocytes in three geographically distinct strains of P. falciparum. However, the initial high level of merozoite-inhibiting antibodies of the intact serum samples remained in the immunoglobulin G fraction from which the RESA antibodies had been removed by affinity chromatography. These results suggest that, although in some cases RESA-immunofluorescent assay-positive antibodies may be inhibitory to merozoite invasion, there are more important antibodies capable of merozoite invasion inhibition.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown G. V., Culvenor J. G., Crewther P. E., Bianco A. E., Coppel R. L., Saint R. B., Stahl H. D., Kemp D. J., Anders R. F. Localization of the ring-infected erythrocyte surface antigen (RESA) of Plasmodium falciparum in merozoites and ring-infected erythrocytes. J Exp Med. 1985 Aug 1;162(2):774–779. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.2.774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chulay J. D., Aikawa M., Diggs C., Haynes J. D. Inhibitory effects of immune monkey serum on synchronized Plasmodium falciparum cultures. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1981 Jan;30(1):12–19. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1981.30.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins W. E., Anders R. F., Pappaioanou M., Campbell G. H., Brown G. V., Kemp D. J., Coppel R. L., Skinner J. C., Andrysiak P. M., Favaloro J. M. Immunization of Aotus monkeys with recombinant proteins of an erythrocyte surface antigen of Plasmodium falciparum. Nature. 1986 Sep 18;323(6085):259–262. doi: 10.1038/323259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppel R. L., Cowman A. F., Anders R. F., Bianco A. E., Saint R. B., Lingelbach K. R., Kemp D. J., Brown G. V. Immune sera recognize on erythrocytes Plasmodium falciparum antigen composed of repeated amino acid sequences. 1984 Aug 30-Sep 5Nature. 310(5980):789–792. doi: 10.1038/310789a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowman A. F., Coppel R. L., Saint R. B., Favaloro J., Crewther P. E., Stahl H. D., Bianco A. E., Brown G. V., Anders R. F., Kemp D. J. The ring-infected erythrocyte surface antigen (RESA) polypeptide of Plasmodium falciparum contains two separate blocks of tandem repeats encoding antigenic epitopes that are naturally immunogenic in man. Mol Biol Med. 1984 Jun;2(3):207–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Divo A. A., Geary T. G., Jensen J. B. Oxygen- and time-dependent effects of antibiotics and selected mitochondrial inhibitors on Plasmodium falciparum in culture. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jan;27(1):21–27. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green T. J., Morhardt M., Brackett R. G., Jacobs R. L. Serum inhibition of merozoite dispersal from Plasmodium falciparum schizonts: indicator of immune status. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1203–1208. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1203-1208.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadley T. J. Invasion of erythrocytes by malaria parasites: a cellular and molecular overview. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:451–477. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.002315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. L., Haynes J. D., Chulay J. D., Diggs C. L. Cultured Plasmodium falciparum used as antigen in a malaria indirect fluorescent antibody test. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1978 Sep;27(5):849–852. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1978.27.849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen J. B., Boland M. T., Hayes M., Akood M. A. Plasmodium falciparum: rapid assay for in vitro inhibition due to human serum from residents of malarious areas. Exp Parasitol. 1982 Dec;54(3):416–424. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(82)90051-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen J. B. Concentration from continuous culture of erythrocytes infected with trophozoites and schizonts of Plasmodium falciparum. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1978 Nov;27(6):1274–1276. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1978.27.1274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen J. B., Trager W. Plasmodium falciparum in culture: use of outdated erthrocytes and description of the candle jar method. J Parasitol. 1977 Oct;63(5):883–886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp D. J., Coppel R. L., Stahl H. D., Bianco A. E., Corcoran L. M., McIntyre P., Langford C. J., Favaloro J. M., Crewther P. E., Brown G. V. The Wellcome Trust lecture. Genes for antigens of Plasmodium falciparum. Parasitology. 1986;92 (Suppl):S83–108. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000085711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambros C., Vanderberg J. P. Synchronization of Plasmodium falciparum erythrocytic stages in culture. J Parasitol. 1979 Jun;65(3):418–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon J. A., Haynes J. D., Diggs C. L., Chulay J. D., Pratt-Rossiter J. M. Plasmodium falciparum antigens synthesized by schizonts and stabilized at the merozoite surface by antibodies when schizonts mature in the presence of growth inhibitory immune serum. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 15;136(6):2252–2258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. H., Aikawa M., Dvorak J. A. Malaria (Plasmodium knowlesi) merozoites: immunity and the surface coat. J Immunol. 1975 Apr;114(4):1237–1242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann H., Berzins K., Wahlgren M., Carlsson J., Björkman A., Patarroyo M. E., Perlmann P. Antibodies in malarial sera to parasite antigens in the membrane of erythrocytes infected with early asexual stages of Plasmodium falciparum. J Exp Med. 1984 Jun 1;159(6):1686–1704. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.6.1686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vande Waa J. A., Jensen J. B., Akood M. A., Bayoumi R. Longitudinal study on the in vitro immune response to Plasmodium falciparum in Sudan. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):505–510. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.505-510.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahlgren M., Björkman A., Perlmann H., Berzins K., Perlmann P. Anti-Plasmodium falciparum antibodies acquired by residents in a holoendemic area of Liberia during development of clinical immunity. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1986 Jan;35(1):22–29. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1986.35.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wåhlin B., Wahlgren M., Perlmann H., Berzins K., Björkman A., Patarroyo M. E., Perlmann P. Human antibodies to a Mr 155,000 Plasmodium falciparum antigen efficiently inhibit merozoite invasion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7912–7916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



