Abstract
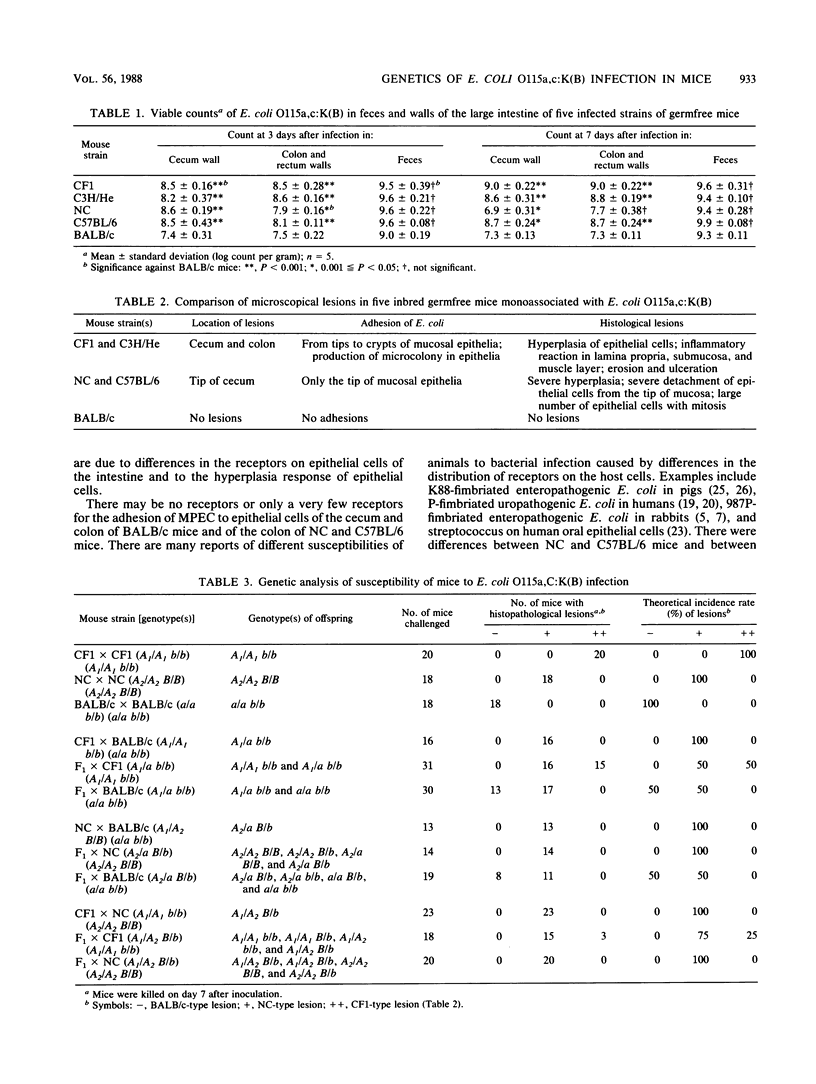
We studied the susceptibility of five germfree inbred strains of mice to oral infection by murine pathogenic Escherichia coli O115a,c:K(B) (MPEC), the causative agent of mouse megaenteron. Although MPEC colonized all strains of mice at 10(9)/g of feces, the mouse strains could be divided into three groups according to their intestinal lesions. In CF1 and C3H/He mice, intestinal lesions were produced in the cecum and colon with hyperplasia of epithelial cells accompanied by severe inflammatory reactions and erosion. The lesions in NC and C57BL/6 mice were restricted to the tip of the cecum, and hyperplasia of epithelial cells was more severe in these mice than in CF1 or C3H/He mice. BALB/c mice had no lesions. Analysis of F1 hybrids of CF1, NC, and BALB/c mice and offsprings from backcrosses of F1 mice to parental strains showed that susceptibility to MPEC seemed to be controlled genetically by a single locus which may be related to the receptors on epithelial cells for MPEC adherence. However, the differences in lesions between CF1 and NC mice suggest that a combination of this locus and another locus to which it may be related regulates the hyperplasia of intestinal epithelial cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bouhours J. F., Glickman R. M. Rat intestinal glycolipids. II. Distribution and biosynthesis of glycolipids and ceramide in villus and crypt cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jul 20;441(1):123–133. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(76)90287-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheers C., McKenzie I. F. Resistance and susceptibility of mice to bacterial infection: genetics of listeriosis. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):755–762. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.755-762.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. S., Arruda J. C., Williams T. J., Laux D. C. Adhesion of a human fecal Escherichia coli strain to mouse colonic mucus. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):139–145. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.139-145.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis J., Turk J. L. Resistance to subcutaneous infection with Mycobacterium lepraemurium is controlled by more than one gene. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):925–930. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.925-930.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean E. A., Isaacson R. E. In vitro adhesion of piliated Escherichia coli to small intestinal villous epithelial cells from rabbits and the identification of a soluble 987P pilus receptor-containing fraction. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1192–1198. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1192-1198.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean E. A., Isaacson R. E. Location and distribution of a receptor for the 987P pilus of Escherichia coli in small intestines. Infect Immun. 1985 Feb;47(2):345–348. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.2.345-348.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean E. A., Isaacson R. E. Purification and characterization of a receptor for the 987P pilus of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):98–105. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.98-105.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forget A., Skamene E., Gros P., Miailhe A. C., Turcotte R. Differences in response among inbred mouse strains to infection with small doses of Mycobacterium bovis BCG. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):42–47. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.42-47.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glickman R. M., Bouhours J. F. Characterization, distribution and biosynthesis of the major ganglioside of rat intestinal mucosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jan 22;424(1):17–25. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(76)90045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto Y., Nakamura R. M., Takahashi H., Tokunaga T. Genetic control of resistance to Mycobacterium intracellulare infection in mice. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):135–140. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.135-140.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gros P., Skamene E., Forget A. Genetic control of natural resistance to Mycobacterium bovis (BCG) in mice. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2417–2421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst R. G., Wallace M. E. Inherited resistance to Corynebacterium kutscheri in mice. Infect Immun. 1976 Aug;14(2):475–482. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.2.475-482.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hormaeche C. E. Genetics of natural resistance to salmonellae in mice. Immunology. 1979 Jun;37(2):319–327. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hormaeche C. E. Natural resistance to Salmonella typhimurium in different inbred mouse strains. Immunology. 1979 Jun;37(2):311–318. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh K., Maejima K., Ueda K., Fujiwara K. Difference in susceptibility of mice raised under barrier-sustained (SPF) or conventional conditions to infectious megaenteron. Microbiol Immunol. 1979;23(9):909–913. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1979.tb02824.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh K., Maejima K., Ueda K., Fujiwara K. Effect of intestinal flora on megaenteron of mice. Microbiol Immunol. 1978;22(11):661–672. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1978.tb00419.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh K., Ueda K., Fujiwara K. Susceptibility of germ-free mice to infectious megaenteron. Microbiol Immunol. 1980;24(4):281–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1980.tb02831.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Källenius G., Svenson S., Möllby R., Cedergren B., Hultberg H., Winberg J. Structure of carbohydrate part of receptor on human uroepithelial cells for pyelonephritogenic Escherichia coli. Lancet. 1981 Sep 19;2(8247):604–606. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92743-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muto T., Nakagawa M., Isobe Y., Saito M., Nakano T. Infectious megaenteron of mice. I. Manifestation and pathological observation. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1969 Dec;22(6):363–374. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.22.363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa M., Sakazaki R., Muto T., Saito M., Hagiwara T. Infectious megaenteron of mice. II. Detection of coliform organisms of an unusual biotype as the primary cause. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1969 Dec;22(6):375–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Beachey E. H., Eyal F., Morrison J. C. Postnatal development of binding of streptococci and lipoteichoic acid by oral mucosal cells of humans. J Infect Dis. 1977 Feb;135(2):267–274. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.2.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant J., Glynn A. A. Genetics of resistance to infection with Salmonella typhimurium in mice. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jan;133(1):72–78. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.1.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellwood R. Genetic and immune factors in the susceptibility of piglets to Escherichia coli diarrhoea. Ann Rech Vet. 1983;14(4):512–518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellwood R., Gibbons R. A., Jones G. W., Rutter J. M. Adhesion of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to pig intestinal brush borders: the existence of two pig phenotypes. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Aug;8(3):405–411. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-3-405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skamene E., Kongshavn P. A., Sachs D. H. Resistance to Listeria monocytogenes in mice: genetic control by genes that are not linked to the H-2 complex. J Infect Dis. 1979 Feb;139(2):228–231. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.2.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welkos S. L., Keener T. J., Gibbs P. H. Differences in susceptibility of inbred mice to Bacillus anthracis. Infect Immun. 1986 Mar;51(3):795–800. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.3.795-800.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]