Abstract
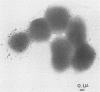
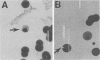
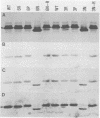
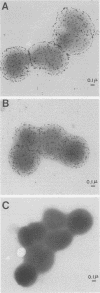
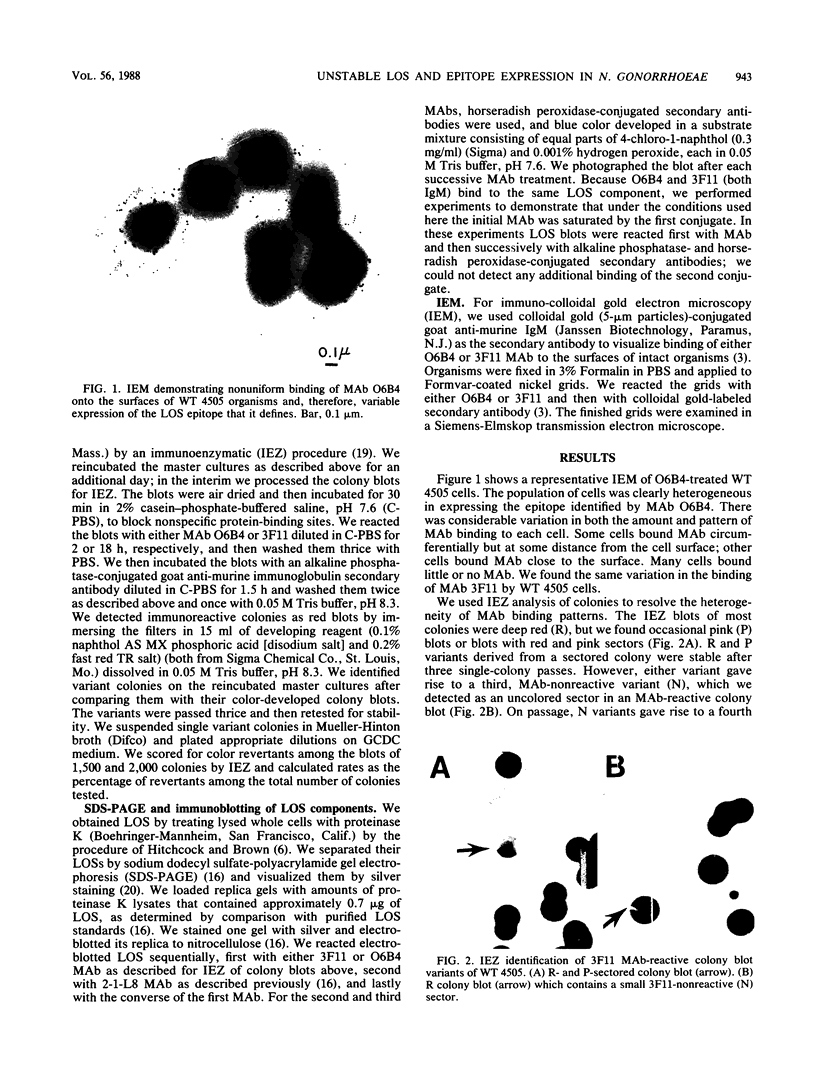
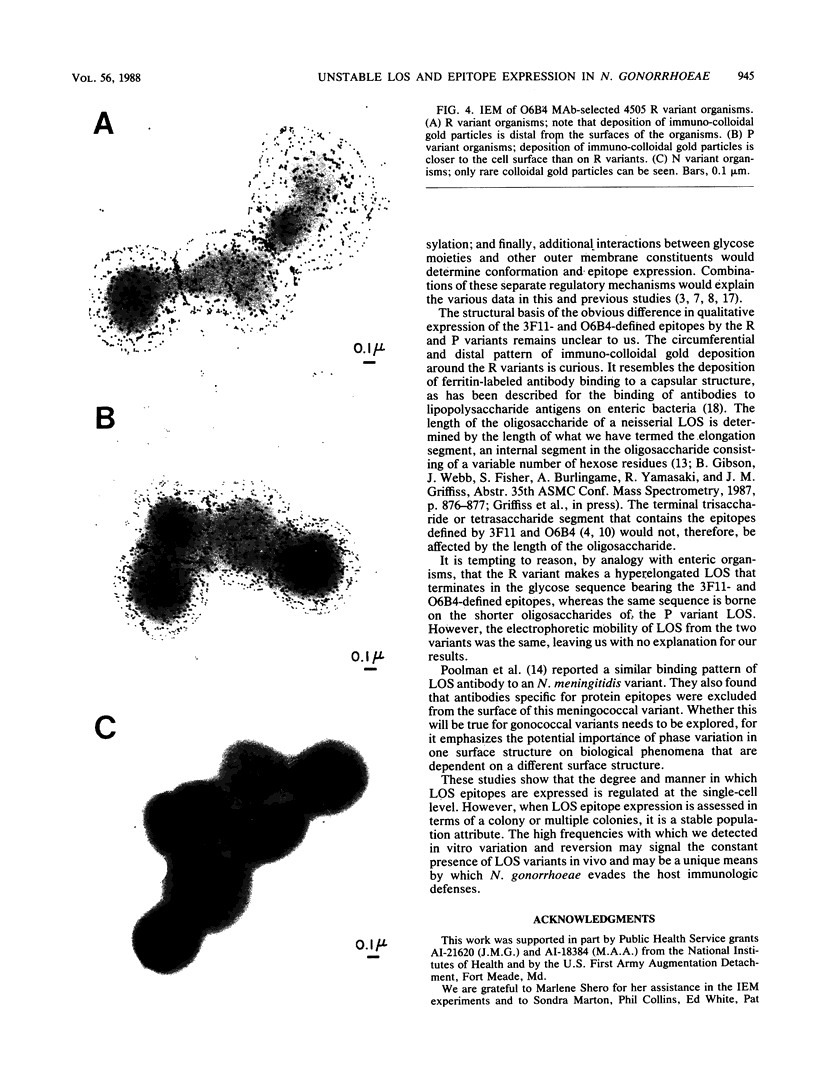
We assessed variation in the expression of lipooligosaccharide (LOS) components and their epitopes within populations of a strain of Neisseria gonorrhoeae by using the monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) O6B4 and 3F11 and immunoenzymatic, immuno-colloidal gold electron microscopic, and sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoretic procedures. Wild-type organisms varied in binding of both MAbs. We used the intensity of immunoenzymatic colony blot color to distinguish four binding variants for each MAb: red (R), pink (P), and colorless (nonreactive [N]) and an N back to R (N-R) revertant. R to P to R and R to N to R variation occurred at frequencies of 0.2% and 0.02%, respectively. The electrophoretic LOS profiles and MAb immunoblot patterns of the R, P, and N-R variants were the same as those of the wild type. LOSs of the N variants, in contrast, were of lower Mr, bound neither 3F11 nor O6B4 MAb, and contained as their major component the 3.6-kilodalton LOS that bears the L8LOS epitope of N. meningitidis. Results of immunoelectron microscopic studies were consistent with LOS binding patterns. Large number of colloidal gold particles were deposited about both R and P variants, distally from R organisms, but proximally from P organisms. N variant organisms, like their LOS, bound neither of the MAbs. N-R variant organisms were like the wild type in that they showed much variation in the amounts of MAb they bound.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apicella M. A., Bennett K. M., Hermerath C. A., Roberts D. E. Monoclonal antibody analysis of lipopolysaccharide from Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):751–756. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.751-756.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apicella M. A. Serogrouping of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: identification of four immunologically distinct acidic polysaccharides. J Infect Dis. 1976 Oct;134(4):377–383. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.4.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apicella M. A., Shero M., Jarvis G. A., Griffiss J. M., Mandrell R. E., Schneider H. Phenotypic variation in epitope expression of the Neisseria gonorrhoeae lipooligosaccharide. Infect Immun. 1987 Aug;55(8):1755–1761. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.8.1755-1761.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connelly M. C., Allen P. Z. Antigenic specificity and heterogeneity of lipopolysaccharides from pyocin-sensitive and -resistant strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1046–1055. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1046-1055.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiss J. M., O'Brien J. P., Yamasaki R., Williams G. D., Rice P. A., Schneider H. Physical heterogeneity of neisserial lipooligosaccharides reflects oligosaccharides that differ in apparent molecular weight, chemical composition, and antigenic expression. Infect Immun. 1987 Aug;55(8):1792–1800. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.8.1792-1800.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandrell R., Schneider H., Apicella M., Zollinger W., Rice P. A., Griffiss J. M. Antigenic and physical diversity of Neisseria gonorrhoeae lipooligosaccharides. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):63–69. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.63-69.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald I. J., Adams G. A. Influence of cultural conditions on the lipopolysaccharide composition of Neisseria sicca. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Feb;65(2):201–207. doi: 10.1099/00221287-65-2-201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse S. A., Apicella M. A. Isolation of a lipopolysaccharide mutant of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: an analysis of the antigenic and biologic difference. J Infect Dis. 1982 Feb;145(2):206–216. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.2.206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse S. A., Mintz C. S., Sarafian S. K., Bartenstein L., Bertram M., Apicella M. A. Effect of dilution rate on lipopolysaccharide and serum resistance of Neisseria gonorrhoeae grown in continuous culture. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):74–82. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.74-82.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider H., Griffiss J. M., Mandrell R. E., Jarvis G. A. Elaboration of a 3.6-kilodalton lipooligosaccharide, antibody against which is absent from human sera, is associated with serum resistance of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):672–677. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.672-677.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider H., Hale T. L., Zollinger W. D., Seid R. C., Jr, Hammack C. A., Griffiss J. M. Heterogeneity of molecular size and antigenic expression within lipooligosaccharides of individual strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):544–549. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.544-549.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider H., Hammack C. A., Shuman B. A., Griffiss J. M. Stability of expression of Neisseria gonorrhoeae lipooligosaccharides. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):924–927. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.924-927.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shands J. W. Localization of somatic antigen on gram-negative bacteria using ferritin antibody conjugates. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jun 30;133(2):292–298. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb52372.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidberry H., Kaufman B., Wright D. C., Sadoff J. Immunoenzymatic analysis by monoclonal antibodies of bacterial lipopolysaccharides after transfer to nitrocellulose. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Feb 11;76(2):299–305. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90307-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein D. C., Petricoin E. F., Griffiss J. M., Schneider H. Use of transformation to construct Neisseria gonorrhoeae strains with altered lipooligosaccharides. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):762–765. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.762-765.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zollinger W. D., Mandrell R. E. Importance of complement source in bactericidal activity of human antibody and murine monoclonal antibody to meningococcal group B polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):257–264. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.257-264.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]