Abstract
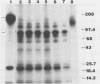
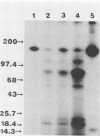
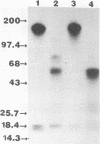
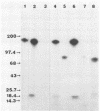
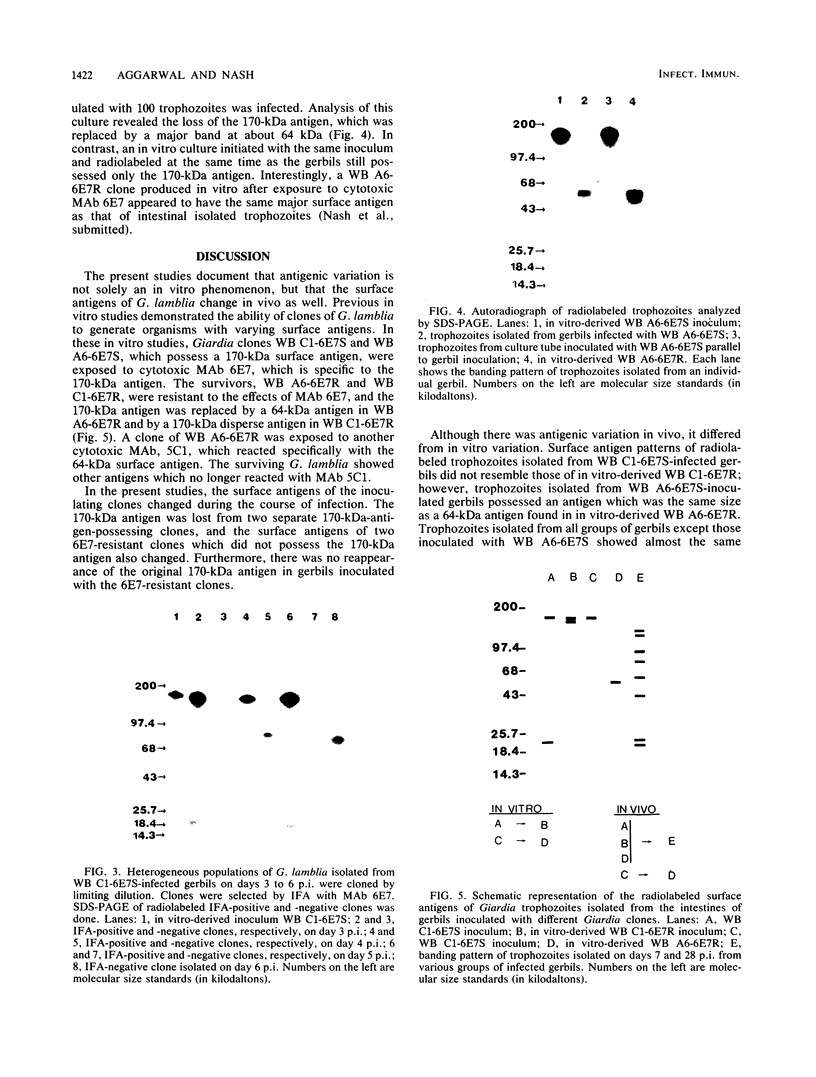
A single Giardia lamblia trophozoite can give rise in vitro to G. lamblia with varying surface antigens. To determine whether antigenic variation also occurs in vivo, gerbils were inoculated with defined G. lamblia clones and the surface antigens of the intestinal trophozoites were studied at different times during the infection. The proportion of monoclonal antibody 6E7-reacting trophozoites from WB C1-6E7S-inoculated gerbils had decreased significantly by day 3 postinoculation, indicating the presence of a heterogeneous population. On day 7, the 170-kilodalton antigen was no longer present and was replaced by a variety of antigens, including a major protein of 92 kilodaltons. With the exception of isolates from gerbils inoculated with WB A6-6E7S, the banding patterns of G. lamblia isolated from gerbils on day 7 or later were the same regardless of the clones used for inoculation. These studies show that G. lamblia changes its surface antigen(s) in vivo within 7 days following inoculation and appears to maintain the same set of surface antigens during the course of infection.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggarwal A., Nash T. E. Comparison of two antigenically distinct Giardia lamblia isolates in gerbils. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1987 Mar;36(2):325–332. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1987.36.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Suprun-Brown L., Kasmala L. Monoclonal antibody to a major surface glycoprotein immunogen differentiates isolates and subpopulations of Trichomonas vaginalis. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):70–75. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.70-75.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belosevic M., Faubert G. M., MacLean J. D., Law C., Croll N. A. Giardia lamblia infections in Mongolian gerbils: an animal model. J Infect Dis. 1983 Feb;147(2):222–226. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.2.222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehl K. S., Farmer S. G., Komorowski R. A., Knox K. K. Antigenic variation among Borrelia spp. in relapsing fever. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):899–902. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.899-902.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keister D. B. Axenic culture of Giardia lamblia in TYI-S-33 medium supplemented with bile. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1983;77(4):487–488. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(83)90120-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myler P. J., Allen A. L., Agabian N., Stuart K. Antigenic variation in clones of Trypanosoma brucei grown in immune-deficient mice. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):684–690. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.684-690.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. E., Gillin F. D., Smith P. D. Excretory-secretory products of Giardia lamblia. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):2004–2010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. E., Keister D. B. Differences in excretory-secretory products and surface antigens among 19 isolates of Giardia. J Infect Dis. 1985 Dec;152(6):1166–1171. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.6.1166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. E., McCutchan T., Keister D., Dame J. B., Conrad J. D., Gillin F. D. Restriction-endonuclease analysis of DNA from 15 Giardia isolates obtained from humans and animals. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jul;152(1):64–73. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovis L., Barbet A. F., Williams R. O. Characterisation of the surface coat of Trypanosoma congolense. Nature. 1978 Feb 16;271(5646):654–656. doi: 10.1038/271654a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. D., Gillin F. D., Kaushal N. A., Nash T. E. Antigenic analysis of Giardia lamblia from Afghanistan, Puerto Rico, Ecuador, and Oregon. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):714–719. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.714-719.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ungar B. L., Nash T. E. Cross-reactivity among different Giardia lamblia isolates using immunofluorescent antibody and enzyme immunoassay techniques. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1987 Sep;37(2):283–289. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1987.37.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. L., Wang C. C. Discovery of a specific double-stranded RNA virus in Giardia lamblia. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1986 Dec;21(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(86)90132-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A., Wang C. C., Alderete J. F. Trichomonas vaginalis phenotypic variation occurs only among trichomonads infected with the double-stranded RNA virus. J Exp Med. 1987 Jul 1;166(1):142–150. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.1.142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe M. S. Giardiasis. JAMA. 1975 Sep 29;233(13):1362–1365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yardley J. H., Bayless T. M. Giardiasis. Gastroenterology. 1967 Feb;52(2):301–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]