Abstract
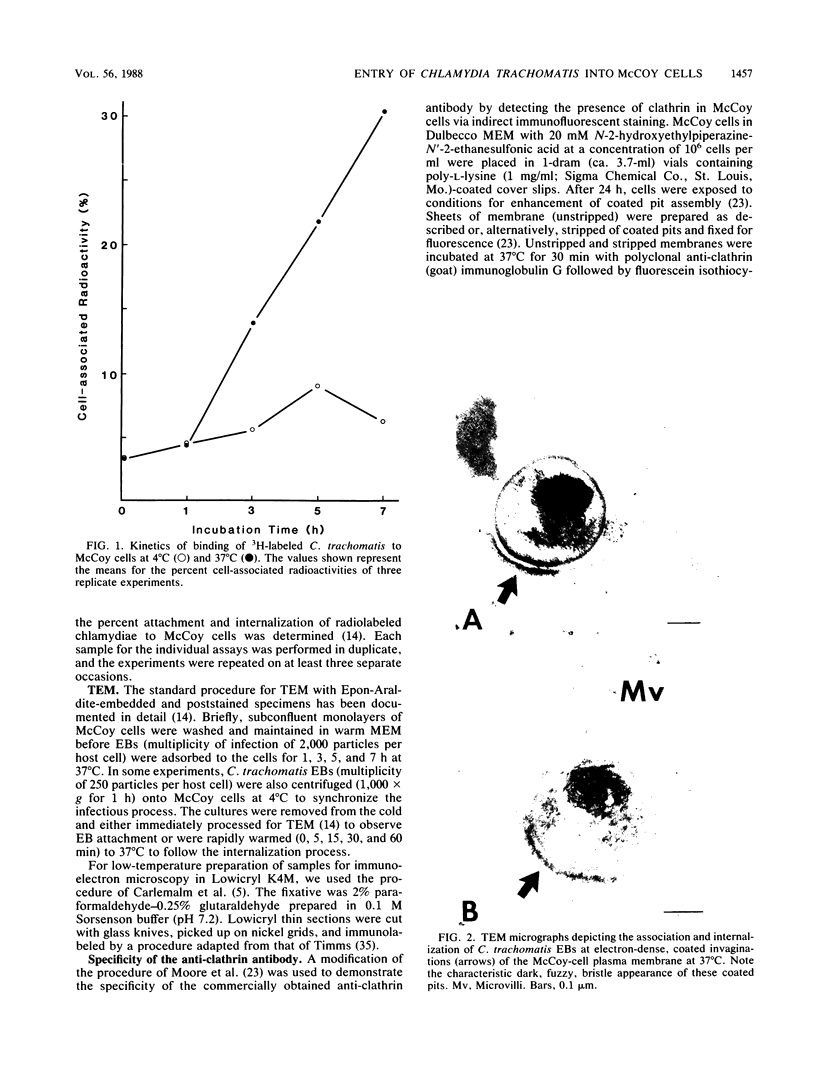
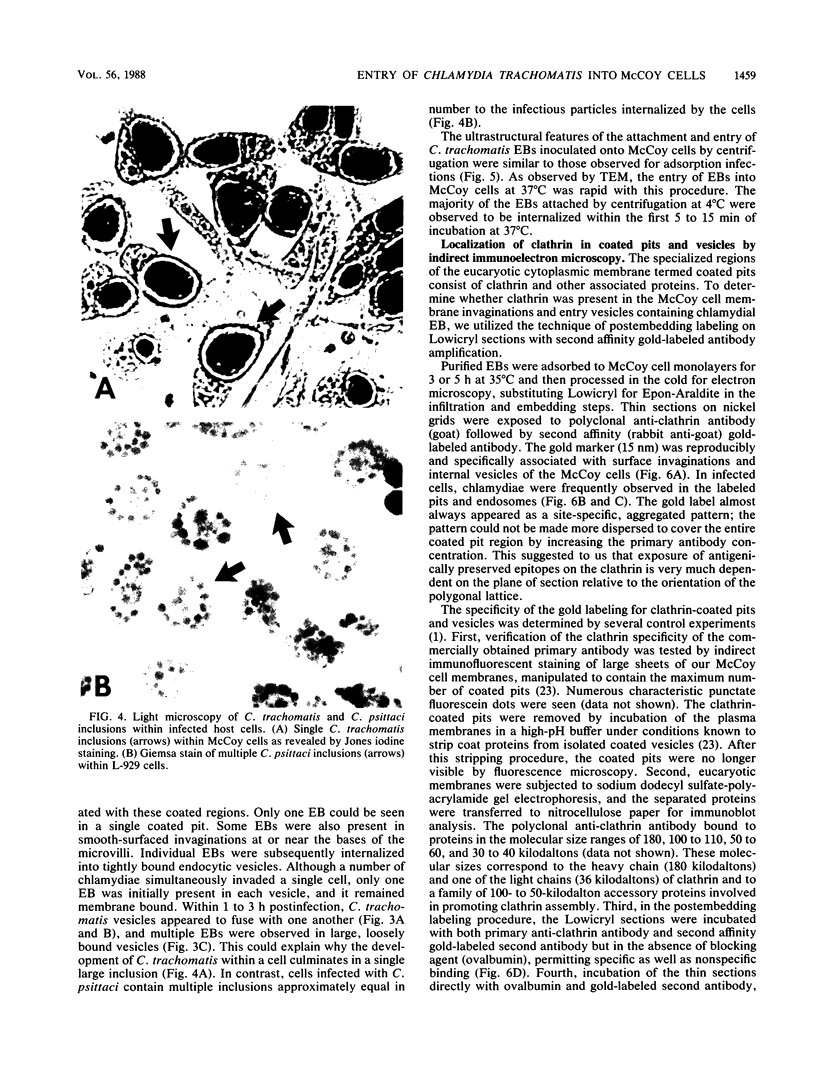
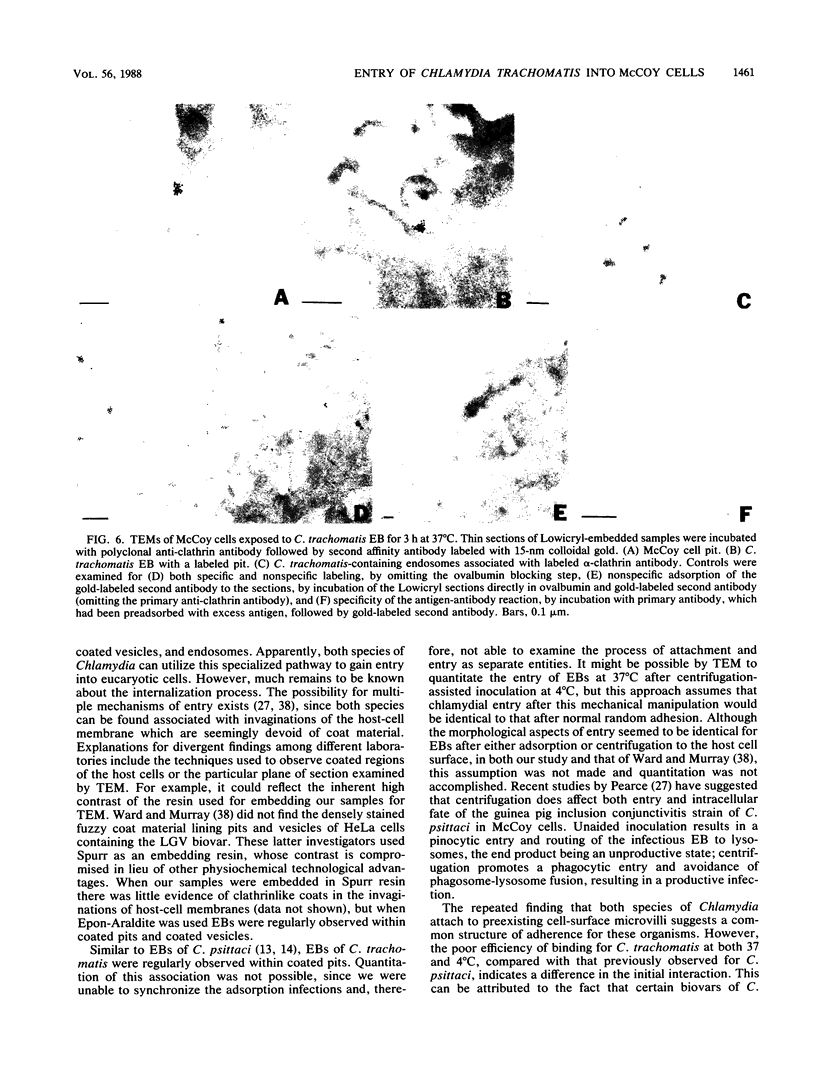
The entry of Chlamydia trachomatis into McCoy cells (fibroblasts) was studied by transmission electron microscopy. On adsorption of elementary bodies (EBs) to host cells at 37 degrees C, the EBs were bound primarily to preexisting cell-surface microvilli. They were also observed in coated pits located at the bases of the microvilli and along smooth surfaces of the host cells and were internalized within coated vesicles at this temperature. Postembedding immunogold labeling on Lowicryl thin sections with anti-clathrin antibody as the primary reagent revealed the gold marker localized in pits and vesicles containing chlamydiae. Some EBs were present in smooth-surfaced invaginations at or near the bases of microvilli and in vesicles devoid of distinguishable coat material. A similar entry process was observed with centrifugation-assisted inoculation of EBs onto the McCoy cells. Individual EBs were initially internalized into tightly bound endocytic vesicles. However, within 1 to 3 h postinfection, multiple C. trachomatis EBs were observed in large, loosely bound vesicles. Evidence suggests that vesicles containing C. trachomatis may have fused with one another early in the infectious process. These results indicate that chlamydiae can exploit the specific process of adsorptive endocytosis for entry into host cells and for translocation to a given intracellular destination, which may be different for each species.
Full text
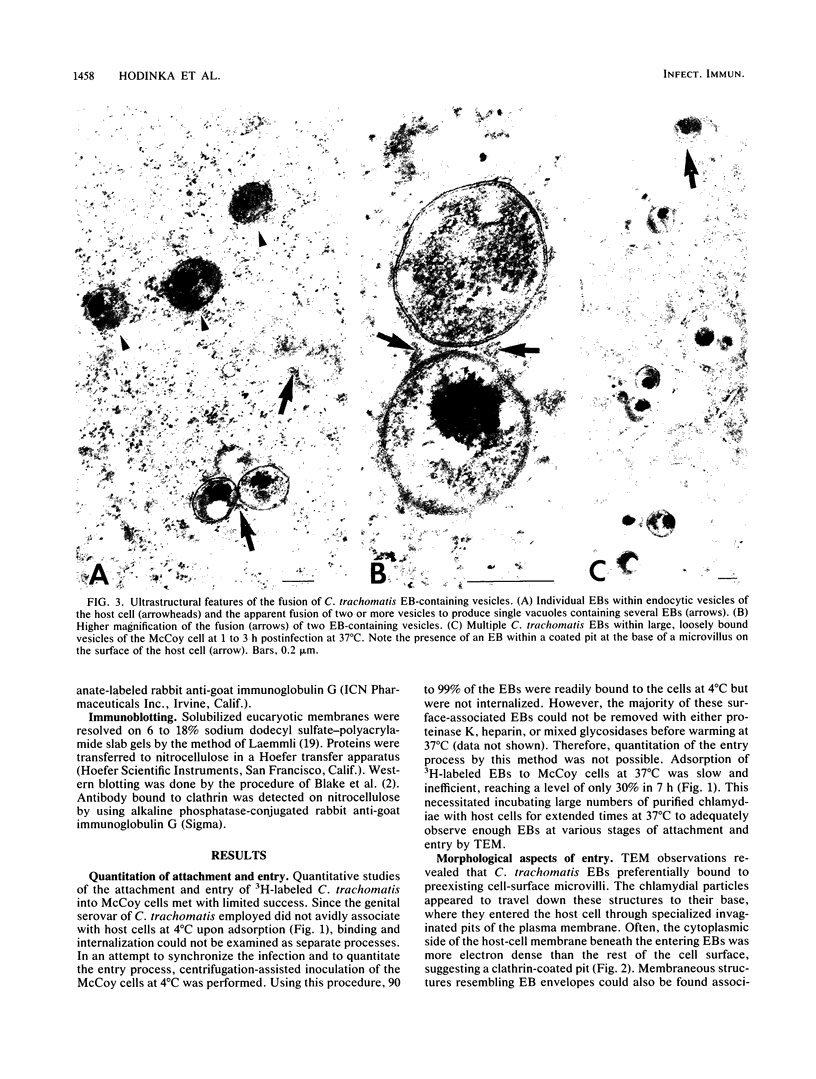
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blake M. S., Johnston K. H., Russell-Jones G. J., Gotschlich E. C. A rapid, sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-antibody on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownridge E., Wyrick P. B. Interaction of Chlamydia psittaci reticulate bodies with mouse peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):697–700. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.697-700.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne G. I., Moulder J. W. Parasite-specified phagocytosis of Chlamydia psittaci and Chlamydia trachomatis by L and HeLa cells. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):598–606. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.598-606.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eissenberg L. G., Wyrick P. B., Davis C. H., Rumpp J. W. Chlamydia psittaci elementary body envelopes: ingestion and inhibition of phagolysosome fusion. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):741–751. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.741-751.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eissenberg L. G., Wyrick P. B. Inhibition of phagolysosome fusion is localized to Chlamydia psittaci-laden vacuoles. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):889–896. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.889-896.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friis R. R. Interaction of L cells and Chlamydia psittaci: entry of the parasite and host responses to its development. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):706–721. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.706-721.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Anderson R. G., Brown M. S. Coated pits, coated vesicles, and receptor-mediated endocytosis. Nature. 1979 Jun 21;279(5715):679–685. doi: 10.1038/279679a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackstadt T. Identification and properties of chlamydial polypeptides that bind eucaryotic cell surface components. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jan;165(1):13–20. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.1.13-20.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Kartenbeck J., Simons K., Fries E. On the entry of Semliki forest virus into BHK-21 cells. J Cell Biol. 1980 Feb;84(2):404–420. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.2.404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodinka R. L., Wyrick P. B. Ultrastructural study of mode of entry of Chlamydia psittaci into L-929 cells. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):855–863. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.855-863.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. B., Mammel J. B., Shepard M. K., Fisher R. R. Recovery of Chlamydia trachomatis from the endometrium of women at risk for chlamydial infection. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1986 Jul;155(1):35–39. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(86)90073-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraaipoel R. J., van Duin A. M. Isoelectric focusing of Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):775–778. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.775-778.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. C., Grayston T. Interaction of Chlamydia trachomatis organisms and HeLa 229 cells. Infect Immun. 1976 Apr;13(4):1103–1109. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.4.1103-1109.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. C., Wang S. P., Grayston J. T. Effect of polycations, polyanions and neuraminidase on the infectivity of trachoma-inclusin conjunctivitis and lymphogranuloma venereum organisms HeLa cells: sialic acid residues as possible receptors for trachoma-inclusion conjunction. Infect Immun. 1973 Jul;8(1):74–79. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.1.74-79.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. K. Interaction between a trachoma strain of Chlamydia trachomatis and mouse fibroblasts (McCoy cells) in the absence of centrifugation. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):584–591. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.584-591.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlin K. S., Reggio H., Helenius A., Simons K. Infectious entry pathway of influenza virus in a canine kidney cell line. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):601–613. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlebrook J. L., Dorland R. B. Bacterial toxins: cellular mechanisms of action. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Sep;48(3):199–221. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.3.199-221.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. S., Mahaffey D. T., Brodsky F. M., Anderson R. G. Assembly of clathrin-coated pits onto purified plasma membranes. Science. 1987 May 1;236(4801):558–563. doi: 10.1126/science.2883727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moorman D. R., Sixbey J. W., Wyrick P. B. Interaction of Chlamydia trachomatis with human genital epithelium in culture. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Apr;132(4):1055–1067. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-4-1055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris R. E., Gerstein A. S., Bonventre P. F., Saelinger C. B. Receptor-mediated entry of diphtheria toxin into monkey kidney (Vero) cells: electron microscopic evaluation. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):721–727. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.721-727.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newhall W. J., Batteiger B., Jones R. B. Analysis of the human serological response to proteins of Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1982 Dec;38(3):1181–1189. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.3.1181-1189.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce J. H. Early events in chlamydial infection. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 May-Jun;137A(3):325–332. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(86)80043-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachter J., Caldwell H. D. Chlamydiae. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:285–309. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein S. C., Steinman R. M., Cohn Z. A. Endocytosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:669–722. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.003321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons K., Garoff H., Helenius A. How an animal virus gets into and out of its host cell. Sci Am. 1982 Feb;246(2):58–66. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0282-58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderlund G., Kihlström E. Physicochemical surface properties of elementary bodies from different serotypes of chlamydia trachomatis and their interaction with mouse fibroblasts. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):893–899. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.893-899.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. E., Washington A. E. Epidemiology of sexually transmitted Chlamydia trachomatis infections. Epidemiol Rev. 1983;5:96–123. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timms B. G. Postembedding immunogold labeling for electron microscopy using "LR White" resin. Am J Anat. 1986 Feb-Mar;175(2-3):267–275. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001750211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd W. J., Caldwell H. D. The interaction of Chlamydia trachomatis with host cells: ultrastructural studies of the mechanism of release of a biovar II strain from HeLa 229 cells. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jun;151(6):1037–1044. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.6.1037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward M. E. Chlamydial classification, development and structure. Br Med Bull. 1983 Apr;39(2):109–115. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward M. E., Murray A. Control mechanisms governing the infectivity of Chlamydia trachomatis for HeLa cells: mechanisms of endocytosis. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Jul;130(7):1765–1780. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-7-1765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenman W. M., Meuser R. U. Chlamydia trachomatis elementary bodies possess proteins which bind to eucaryotic cell membranes. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):602–607. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.602-607.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyrick P. B., Brownridge E. A. Growth of Chlamydia psittaci in macrophages. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):1054–1060. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.1054-1060.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyrick P. B., Brownridge E. A., Ivins B. E. Interaction of Chlamydia psittaci with mouse peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):1061–1067. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.1061-1067.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeichhardt H., Wetz K., Willingmann P., Habermehl K. O. Entry of poliovirus type 1 and Mouse Elberfeld (ME) virus into HEp-2 cells: receptor-mediated endocytosis and endosomal or lysosomal uncoating. J Gen Virol. 1985 Mar;66(Pt 3):483–492. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-3-483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]