Abstract
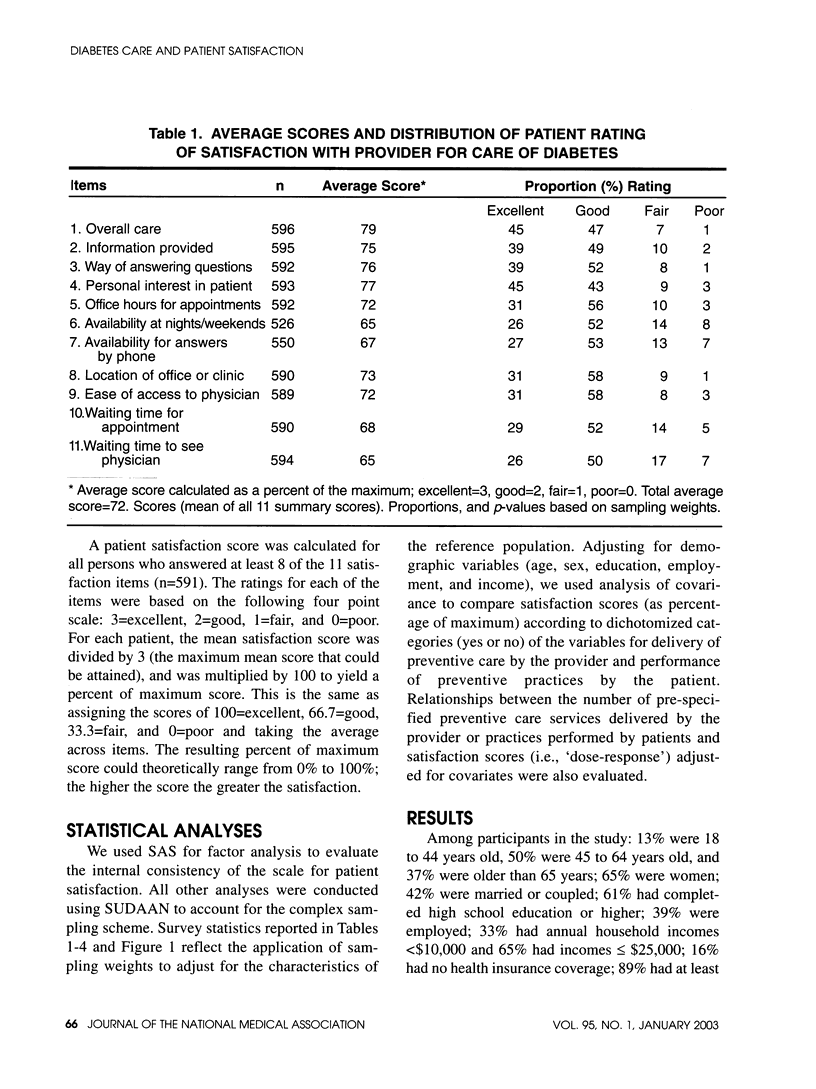
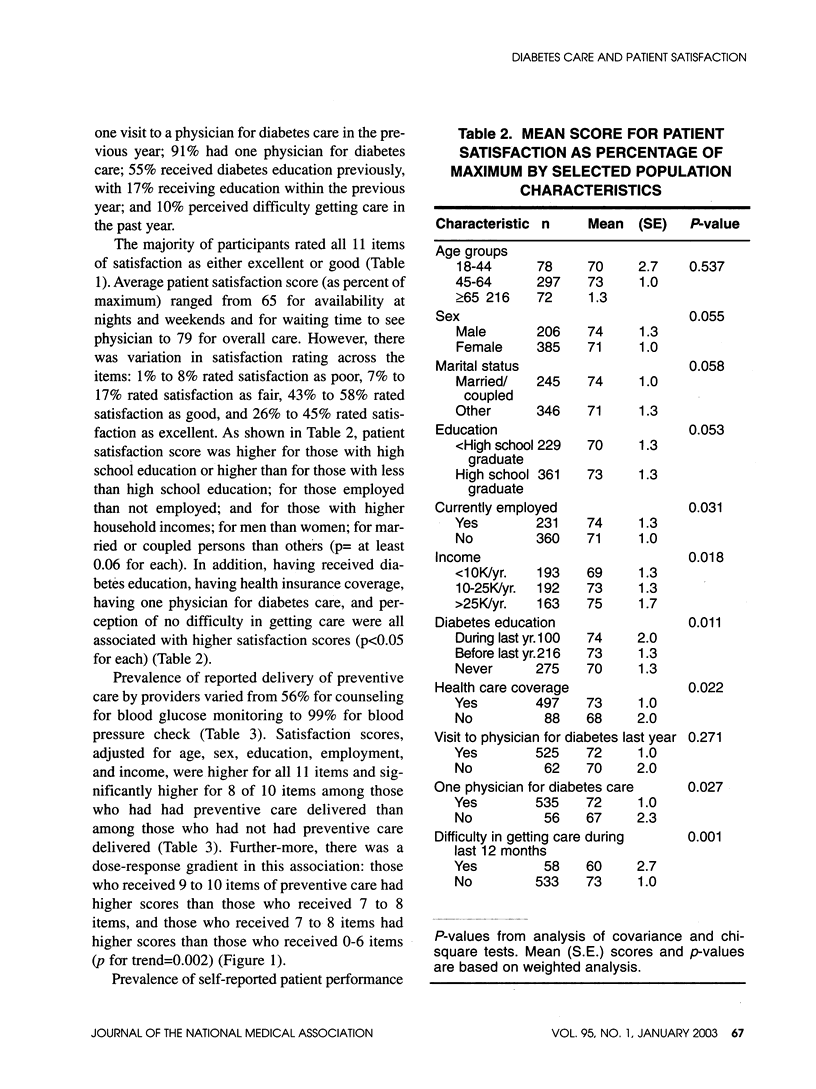
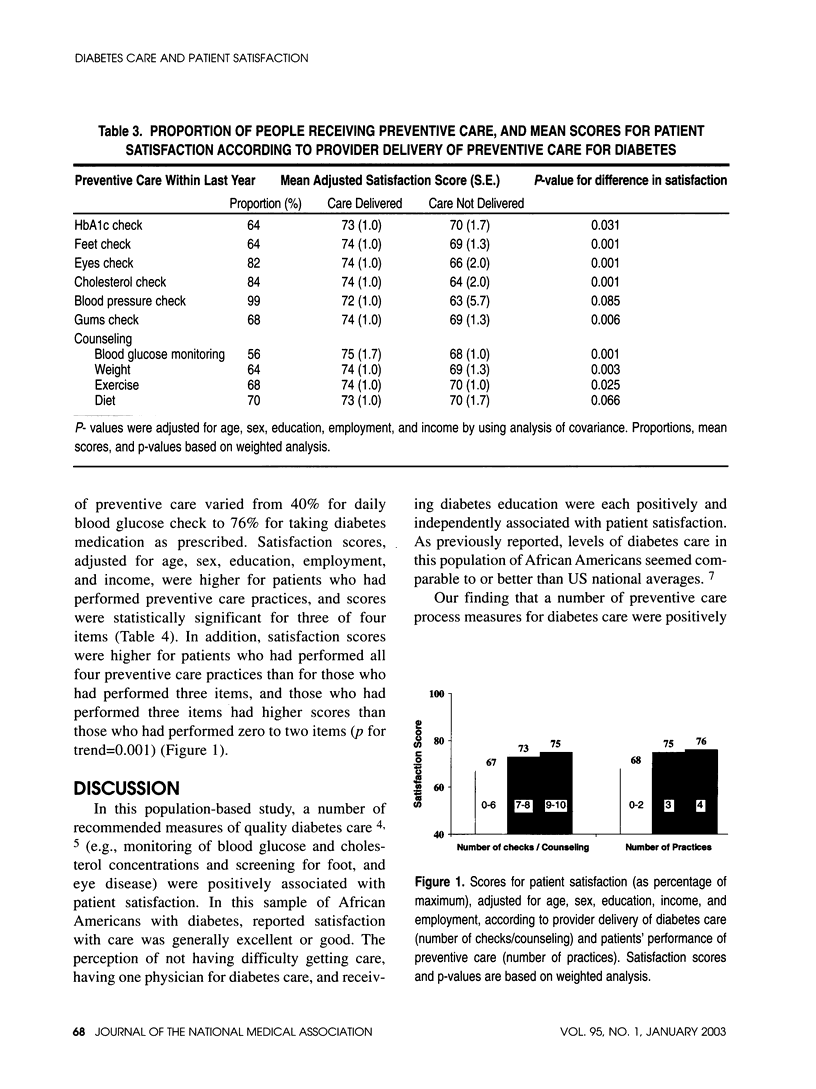
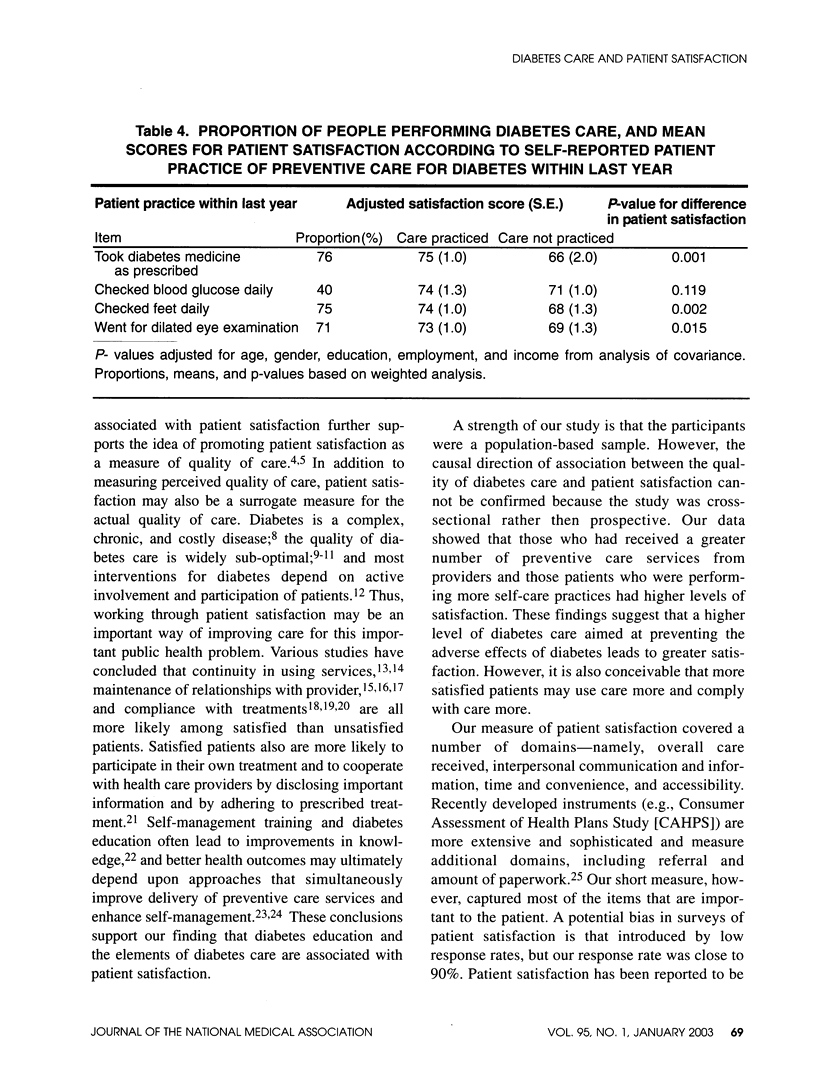
OBJECTIVE: Patient satisfaction is regarded as a component of the quality of medical care. We examined the association between quality of care and patient satisfaction. DESIGN: Cross-sectional study. SETTING: Population-based random sample in North Carolina, United States, 1997. PARTICIPANTS: 591 African-Americans aged > or = 18 years with self-reported diabetes were interviewed for providers' delivery of 10 preventive measures and patients' performance of four preventive measures for diabetes care. MAIN OUTCOME MEASURES: Satisfaction with health care providers with respect to 11 items, on a 4-point scale (excellent, good, fair, and poor). Average satisfaction scores were compared according to levels of quality of care. RESULTS: Patient satisfaction was positively associated with income, employment, diabetes education, ease of getting care during the last year, having health care coverage and having one physician for diabetes care (P < 0.05 for each). Adjusted for age, sex, education, employment, and income, 8 of 10 preventive care practices by providers during the previous year--monitoring of concentrations of glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) and cholesterol; performing eye, foot, and gum examinations; and physician counseling on self-monitoring of blood glucose concentrations, exercise, and weight reduction--were associated with higher satisfaction scores (P < 0.05). Patients' performance of three of four preventive practices--taking medications for diabetes as prescribed, performing daily self-examination of the feet, and going for an eye examination with dilation of the pupils--were also associated with higher satisfaction scores (P < 0.05). CONCLUSION: Quality of diabetes care was positively associated with patient satisfaction with provider of care. Prospective studies are needed to confirm this association and its direction.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aharony L., Strasser S. Patient satisfaction: what we know about and what we still need to explore. Med Care Rev. 1993 Spring;50(1):49–79. doi: 10.1177/002570879305000104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aubert R. E., Herman W. H., Waters J., Moore W., Sutton D., Peterson B. L., Bailey C. M., Koplan J. P. Nurse case management to improve glycemic control in diabetic patients in a health maintenance organization. A randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 1998 Oct 15;129(8):605–612. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-129-8-199810150-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett E. E., Grayson M., Barker R., Levine D. M., Golden A., Libber S. The effects of physician communications skills on patient satisfaction; recall, and adherence. J Chronic Dis. 1984;37(9-10):755–764. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(84)90044-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMatteo M. R., Prince L. M., Taranta A. Patients' percentions of physicians' behavior: determinants of patient commitment to the therapeutic relationship. J Community Health. 1979 Summer;4(4):280–290. doi: 10.1007/BF01319022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelgau M. M., Narayan K. M., Geiss L. S., Thompson T. J., Beckles G. L., Lopez L., Hartwell T., Visscher W., Liburd L. A project to reduce the burden of diabetes in the African-American Community: Project DIRECT. J Natl Med Assoc. 1998 Oct;90(10):605–613. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregg E. W., Geiss L. S., Saaddine J., Fagot-Campagna A., Beckles G., Parker C., Visscher W., Hartwell T., Liburd L., Narayan K. M. Use of diabetes preventive care and complications risk in two African-American communities. Am J Prev Med. 2001 Oct;21(3):197–202. doi: 10.1016/s0749-3797(01)00351-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris M. I., Eastman R. C., Cowie C. C., Flegal K. M., Eberhardt M. S. Racial and ethnic differences in glycemic control of adults with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 1999 Mar;22(3):403–408. doi: 10.2337/diacare.22.3.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hays R. D., Shaul J. A., Williams V. S., Lubalin J. S., Harris-Kojetin L. D., Sweeny S. F., Cleary P. D. Psychometric properties of the CAHPS 1.0 survey measures. Consumer Assessment of Health Plans Study. Med Care. 1999 Mar;37(3 Suppl):MS22–MS31. doi: 10.1097/00005650-199903001-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulka B. S., Cassel J. C., Kupper L. L., Burdette J. A. Communication, compliance, and concordance between physicians and patients with prescribed medications. Am J Public Health. 1976 Sep;66(9):847–853. doi: 10.2105/ajph.66.9.847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassirer J. P. Incorporating patients' preferences into medical decisions. N Engl J Med. 1994 Jun 30;330(26):1895–1896. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199406303302611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little P., Everitt H., Williamson I., Warner G., Moore M., Gould C., Ferrier K., Payne S. Observational study of effect of patient centredness and positive approach on outcomes of general practice consultations. BMJ. 2001 Oct 20;323(7318):908–911. doi: 10.1136/bmj.323.7318.908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray-García J. L., Selby J. V., Schmittdiel J., Grumbach K., Quesenberry C. P., Jr Racial and ethnic differences in a patient survey: patients' values, ratings, and reports regarding physician primary care performance in a large health maintenance organization. Med Care. 2000 Mar;38(3):300–310. doi: 10.1097/00005650-200003000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayan K. M., Gregg E. W., Engelgau M. M., Moore B., Thompson T. J., Williamson D. F., Vinicor F. Translation research for chronic disease: the case of diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2000 Dec;23(12):1794–1798. doi: 10.2337/diacare.23.12.1794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris S. L., Engelgau M. M., Narayan K. M. Effectiveness of self-management training in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Care. 2001 Mar;24(3):561–587. doi: 10.2337/diacare.24.3.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roghmann K. J., Hengst A., Zastowny T. R. Satisfaction with medical care: its measurement and relation to utilization. Med Care. 1979 May;17(5):461–479. doi: 10.1097/00005650-197905000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saaddine Jinan B., Engelgau Michael M., Beckles Gloria L., Gregg Edward W., Thompson Theodore J., Narayan K. M. Venkat. A diabetes report card for the United States: quality of care in the 1990s. Ann Intern Med. 2002 Apr 16;136(8):565–574. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-136-8-200204160-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stump T. E., Dexter P. R., Tierney W. M., Wolinsky F. D. Measuring patient satisfaction with physicians among older and diseased adults in a primary care municipal outpatient setting. An examination of three instruments. Med Care. 1995 Sep;33(9):958–972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. W., Penchansky R. Relating satisfaction with access to utilization of services. Med Care. 1984 Jun;22(6):553–568. doi: 10.1097/00005650-198406000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware J. E., Jr, Wright W. R., Snyder M. K., Chu G. C. Consumer perceptions of health care services: implications for academic medicine. J Med Educ. 1975 Sep;50(9):839–848. doi: 10.1097/00001888-197509000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wartman S. A., Morlock L. L., Malitz F. E., Palm E. A. Patient understanding and satisfaction as predictors of compliance. Med Care. 1983 Sep;21(9):886–891. doi: 10.1097/00005650-198309000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


