Abstract
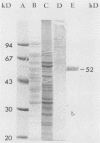
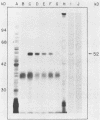
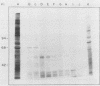
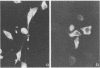
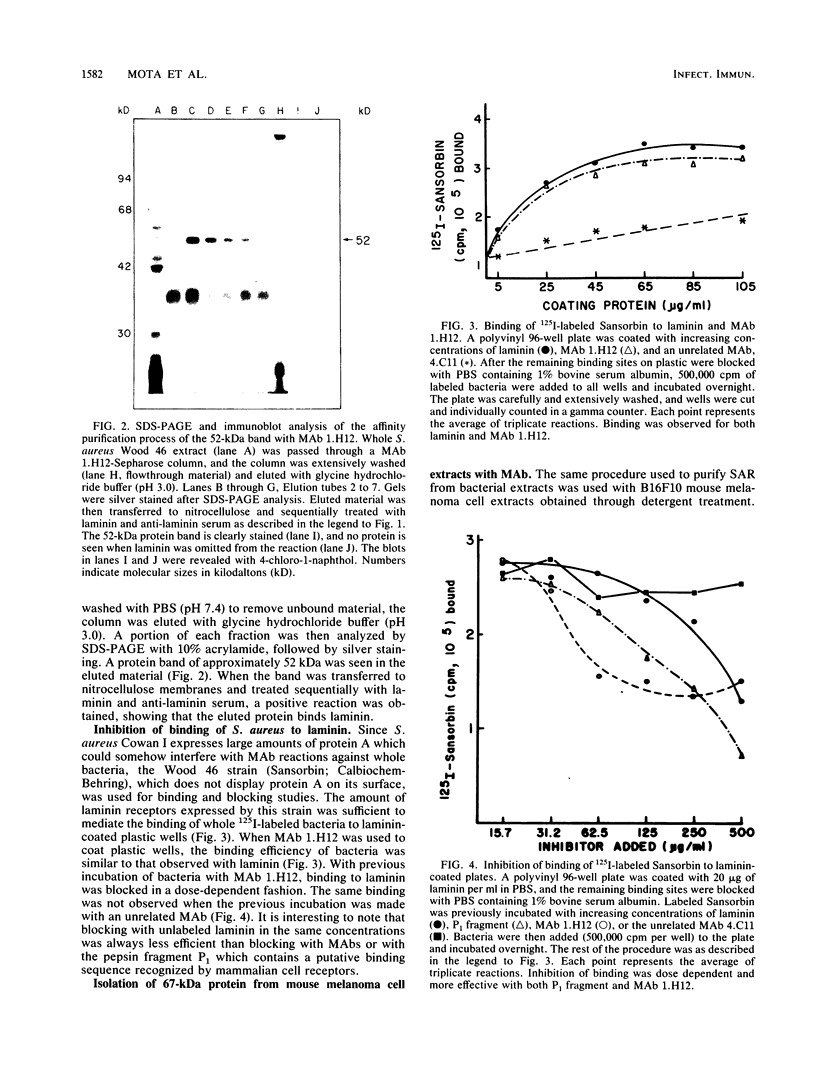
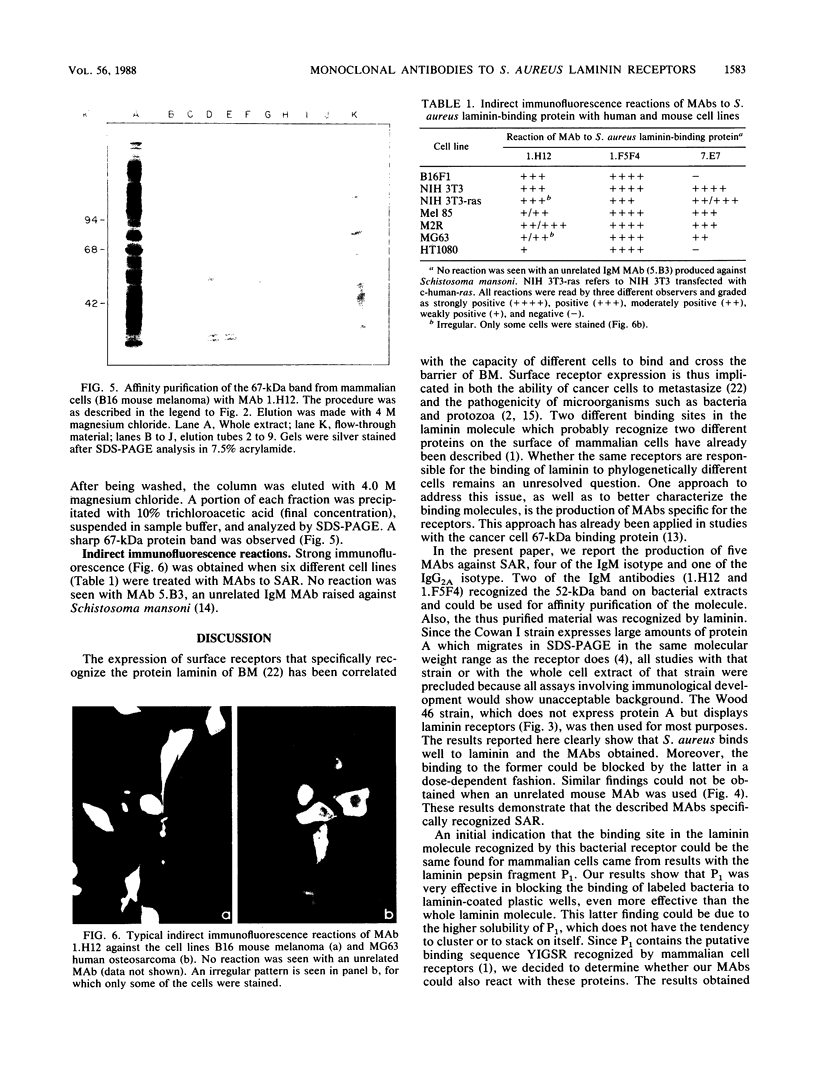
We and others have previously shown that some microorganisms, including bacteria, express on their surfaces receptors that specifically recognize extracellular matrix proteins, such as laminin, fibronectin, or both. The ability of microorganisms to adhere and to invade might depend on the existence of receptors which could, thus, be correlated with pathogenicity. In the present paper, we report the isolation of five stable cell lines that were producers of monoclonal antibodies to Staphylococcus aureus laminin receptors. One of these antibodies, which was of the immunoglobulin M isotype, blocked the binding of laminin to bacteria before and after fixation and recognized the putative 52-kilodalton laminin-binding protein in whole bacterial extracts. Also, purified receptor was isolated by immunoaffinity chromatography and shown to bind laminin. Furthermore, the same antibodies bound the 67-kilodalton putative receptor from mouse melanoma cells and gave positive immunofluorescence reactions against mammalian tumor cells. These data strongly suggest either the evolutionary conservation of at least some sequences in both procaryotic and eucaryotic laminin-binding proteins or convergent evolution and positive selection of epitopes cross-reacting with laminin. Some of these antibodies to the procaryotic protein could therefore become useful markers for the expression of laminin receptors by cancer cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aumailley M., Nurcombe V., Edgar D., Paulsson M., Timpl R. The cellular interactions of laminin fragments. Cell adhesion correlates with two fragment-specific high affinity binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11532–11538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretaña A., Avila J. L., Arias-Flores M., Contreras M., Tapia F. J. Trypanosoma cruzi and American Leishmania spp: immunocytochemical localization of a laminin-like protein in the plasma membrane. Exp Parasitol. 1986 Apr;61(2):168–175. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(86)90149-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant G., Rao C. N., Brentani M., Martins W., Lopes J. D., Martin S. E., Liotta L. A., Schiffmann E. A role for the laminin receptor in leukocyte chemotaxis. J Leukoc Biol. 1987 Mar;41(3):220–227. doi: 10.1002/jlb.41.3.220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung A. L., Bayer A. S., Peters J., Ward J. I. Analysis by gel electrophoresis, Western blot, and peptide mapping of protein A heterogeneity in Staphylococcus aureus strains. Infect Immun. 1987 Apr;55(4):843–847. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.4.843-847.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E. Enzyme immunoassay ELISA and EMIT. Methods Enzymol. 1980;70(A):419–439. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)70067-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ey P. L., Prowse S. J., Jenkin C. R. Isolation of pure IgG1, IgG2a and IgG2b immunoglobulins from mouse serum using protein A-sepharose. Immunochemistry. 1978 Jul;15(7):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Repesh L. A., Blanco D. R., Miller J. N. Attachment of Treponema pallidum to fibronectin, laminin, collagen IV, and collagen I, and blockage of attachment by immune rabbit IgG. Br J Vener Dis. 1984 Dec;60(6):357–363. doi: 10.1136/sti.60.6.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding J. W. Use of staphylococcal protein A as an immunological reagent. J Immunol Methods. 1978;20:241–253. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(78)90259-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf J., Iwamoto Y., Sasaki M., Martin G. R., Kleinman H. K., Robey F. A., Yamada Y. Identification of an amino acid sequence in laminin mediating cell attachment, chemotaxis, and receptor binding. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):989–996. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90707-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huard T. K., Malinoff H. L., Wicha M. S. Macrophages express a plasma membrane receptor for basement membrane laminin. Am J Pathol. 1986 May;123(2):365–370. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta L. A., Horan Hand P., Rao C. N., Bryant G., Barsky S. H., Schlom J. Monoclonal antibodies to the human laminin receptor recognize structurally distinct sites. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Jan;156(1):117–126. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(85)90266-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopes J. D., Carneiro C. R., Vilela A. A., Camargo E. P. Production of monoclonal antibodies against Schistosoma mansoni and a trypanosomatid: a methodological report. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 1982 Nov-Dec;24(6):327–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopes J. D., dos Reis M., Brentani R. R. Presence of laminin receptors in Staphylococcus aureus. Science. 1985 Jul 19;229(4710):275–277. doi: 10.1126/science.3160113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao N. C., Barsky S. H., Terranova V. P., Liotta L. A. Isolation of a tumor cell laminin receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Mar 29;111(3):804–808. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91370-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohde H., Bächinger H. P., Timpl R. Characterization of pepsin fragments of laminin in a tumor basement membrane. Evidence for the existence of related proteins. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1980 Nov;361(11):1651–1660. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1980.361.2.1651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speziale P., Hök M., Wadström T., Timpl R. Binding of the basement membrane protein laminin to Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1982 Sep 6;146(1):55–58. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80704-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switalski L. M., Murchison H., Timpl R., Curtiss R., 3rd, Hök M. Binding of laminin to oral and endocarditis strains of viridans streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1095–1101. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1095-1101.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switalski L. M., Speziale P., Hök M., Wadström T., Timpl R. Binding of Streptococcus pyogenes to laminin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3734–3738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terranova V. P., Liotta L. A., Russo R. G., Martin G. R. Role of laminin in the attachment and metastasis of murine tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1982 Jun;42(6):2265–2269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terranova V. P., Rao C. N., Kalebic T., Margulies I. M., Liotta L. A. Laminin receptor on human breast carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):444–448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R., Rohde H., Robey P. G., Rennard S. I., Foidart J. M., Martin G. R. Laminin--a glycoprotein from basement membranes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9933–9937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]