Abstract
Co-infection of syphilis and AIDS has profound implications for the African American community. The purpose of this review is to: evaluate the historical background of HIV and syphilis and their similarities in pathogenesis; review the epidemiology of syphilis and HIV co-infection, and implications for continued prevention efforts; examine the effect of syphilis on HIV transmission and acquisition; and, to examine the effects of HIV infection on syphilis transmission, diagnostic and serologic changes, clinical course, and treatment. The prevalence of HIV is higher in those with syphilis; moreover, the prevalence of HIV and syphilis co-infection is highest in African Americans. There may be humoral and cellular immune similarities. HIV may affect the transmission of syphilis, alter its serologic diagnosis, and accelerate and change the clinical course and response to treatment. In conclusion, combined infection of HIV and syphilis may alter the clinical presentation and course of either disease. There are historical and immunologic similarities and the high prevalence in African Americans compared to other groups is of great importance for prevention efforts.
Full text
PDF














Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allason-Jones E. The gay bowel syndrome. Br J Hosp Med. 1987 Nov;38(5):397–397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K. C., Boyd A. W., Fisher D. C., Slaughenhoupt B., Groopman J. E., O'Hara C. J., Daley J. F., Schlossman S. F., Nadler L. M. Isolation and functional analysis of human B cell populations. I. Characterization of the B1+B2+ and B1+B2- subsets. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):820–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Augenbraun M. H., DeHovitz J. A., Feldman J., Clarke L., Landesman S., Minkoff H. M. Biological false-positive syphilis test results for women infected with human immunodeficiency virus. Clin Infect Dis. 1994 Dec;19(6):1040–1044. doi: 10.1093/clinids/19.6.1040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
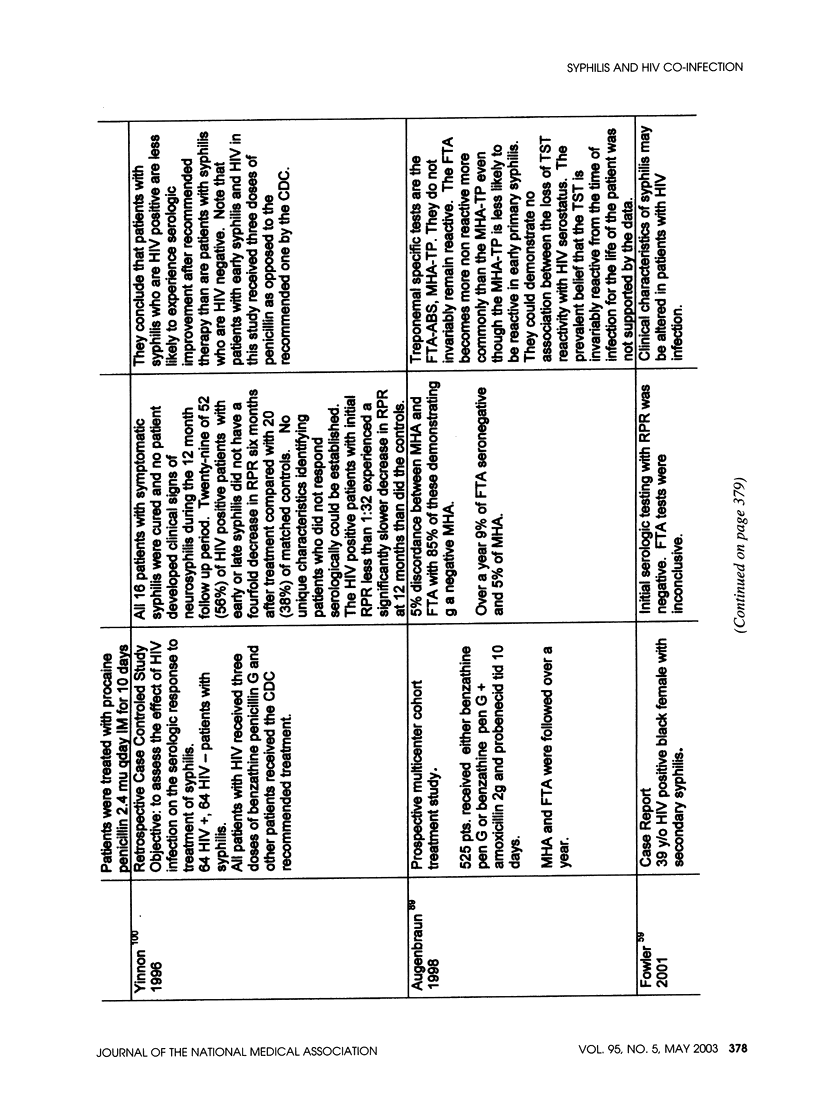
- Augenbraun M., Rolfs R., Johnson R., Joesoef R., Pope V. Treponemal specific tests for the serodiagnosis of syphilis. Syphilis and HIV Study Group. Sex Transm Dis. 1998 Nov;25(10):549–552. doi: 10.1097/00007435-199811000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azim T., Islam M. N., Bogaerts J., Mian M. A., Sarker M. S., Fattah K. R., Simmonds P., Jenkins C., Choudhury M. R., Mathan V. I. Prevalence of HIV and syphilis among high-risk groups in Bangladesh. AIDS. 2000 Jan 28;14(2):210–211. doi: 10.1097/00002030-200001280-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azim Tasnim, Bogaerts Jozef, Yirrell David L., Banerjea Akhil C., Sarker Mohammed S., Ahmed Giasuddin, Amin Mian M. M., Rahman Abu S. M. M., Hussain Abu M. Z. Injecting drug users in Bangladesh: prevalence of syphilis, hepatitis, HIV and HIV subtypes. AIDS. 2002 Jan 4;16(1):121–123. doi: 10.1097/00002030-200201040-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baughn R. E., Tung K. S., Musher D. M. Detection of circulating immune complexes in the sera of rabbits with experimental syphilis: possible role in immunoregulation. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):575–582. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.575-582.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
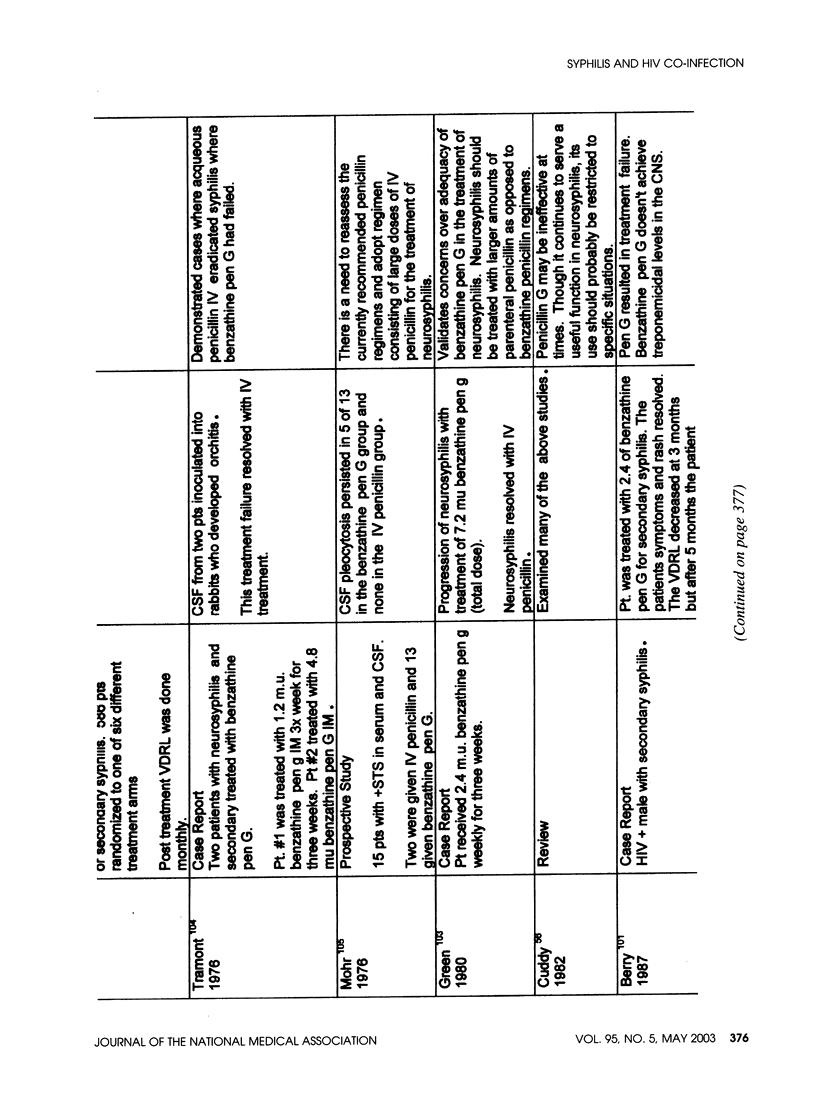
- Berry C. D., Hooton T. M., Collier A. C., Lukehart S. A. Neurologic relapse after benzathine penicillin therapy for secondary syphilis in a patient with HIV infection. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jun 18;316(25):1587–1589. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198706183162507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum N. R., Goldschmidt R. H., Buffett W. O. Resolving the common clinical dilemmas of syphilis. Am Fam Physician. 1999 Apr 15;59(8):2233-40, 2245-6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blocker M. E., Levine W. C., St Louis M. E. HIV prevalence in patients with syphilis, United States. Sex Transm Dis. 2000 Jan;27(1):53–59. doi: 10.1097/00007435-200001000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. T., Zaidi A., Larsen S. A., Reynolds G. H. Serological response to syphilis treatment. A new analysis of old data. JAMA. 1985 Mar 1;253(9):1296–1299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARK E. G., DANBOLT N. The Oslo study of the natural history of untreated syphilis; an epidemiologic investigation based on a restudy of the Boeck-Bruusgaard material; a review and appraisal. J Chronic Dis. 1955 Sep;2(3):311–344. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(55)90139-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control (CDC) Kaposi's sarcoma and Pneumocystis pneumonia among homosexual men--New York City and California. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1981 Jul 3;30(25):305–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control (CDC) Recommendations for diagnosing and treating syphilis in HIV-infected patients. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1988 Oct 7;37(39):600-2, 607-8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) HIV and AIDS--United States, 1981-2000. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2001 Jun 1;50(21):430–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Primary and secondary syphilis--United States, 1999. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2001 Feb 23;50(7):113–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chemtai A. K. Immunology of HIV infection and AIDS: a review. East Afr Med J. 1989 Dec;66(12):837–843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuddy P. G. Benzathine penicillin G in the treatment of neurosyphilis. Drug Intell Clin Pharm. 1982 Mar;16(3):205–210. doi: 10.1177/106002808201600303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czelusta A., Yen-Moore A., Van der Straten M., Carrasco D., Tyring S. K. An overview of sexually transmitted diseases. Part III. Sexually transmitted diseases in HIV-infected patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000 Sep;43(3):409–436. doi: 10.1067/mjd.2000.105158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dada A. J., Ajayi A. O., Diamondstone L., Quinn T. C., Blattner W. A., Biggar R. J. A serosurvey of Haemophilus ducreyi, syphilis, and herpes simplex virus type 2 and their association with human immunodeficiency virus among female sex workers in Lagos, Nigeria. Sex Transm Dis. 1998 May;25(5):237–242. doi: 10.1097/00007435-199805000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson M. C., Johnston J., Delea T. E., White A., Andrews E. The causal role for genital ulcer disease as a risk factor for transmission of human immunodeficiency virus. An application of the Bradford Hill criteria. Sex Transm Dis. 1996 Sep-Oct;23(5):429–440. doi: 10.1097/00007435-199609000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durack D. T. Opportunistic infections and Kaposi's sarcoma in homosexual men. N Engl J Med. 1981 Dec 10;305(24):1465–1467. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198112103052408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engering Anneke, Van Vliet Sandra J., Geijtenbeek Teunis B. H., Van Kooyk Yvette. Subset of DC-SIGN(+) dendritic cells in human blood transmits HIV-1 to T lymphocytes. Blood. 2002 Sep 1;100(5):1780–1786. doi: 10.1182/blood-2001-12-0179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairchild A. L., Bayer R. Uses and abuses of Tuskegee. Science. 1999 May 7;284(5416):919–921. doi: 10.1126/science.284.5416.919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnes S. W., Setness P. A. Serologic tests for syphilis. Postgrad Med. 1990 Feb 15;87(3):37-41, 45-6. doi: 10.1080/00325481.1990.11704578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming D. T., Levine W. C., Trees D. L., Tambe P., Toomey K., St Louis M. E. Syphilis in Atlanta during an era of declining incidence. Sex Transm Dis. 2000 Feb;27(2):68–73. doi: 10.1097/00007435-200002000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming D. T., Wasserheit J. N. From epidemiological synergy to public health policy and practice: the contribution of other sexually transmitted diseases to sexual transmission of HIV infection. Sex Transm Infect. 1999 Feb;75(1):3–17. doi: 10.1136/sti.75.1.3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler V. G., Jr, Maxwell G. L., Myers S. A., Shea C. R., Livengood C. N., 3rd, Prieto V. G., Hicks C. B. Failure of benzathine penicillin in a case of seronegative secondary syphilis in a patient with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: case report and review of the literature. Arch Dermatol. 2001 Oct;137(10):1374–1376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamble V. N. Under the shadow of Tuskegee: African Americans and health care. Am J Public Health. 1997 Nov;87(11):1773–1778. doi: 10.2105/ajph.87.11.1773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
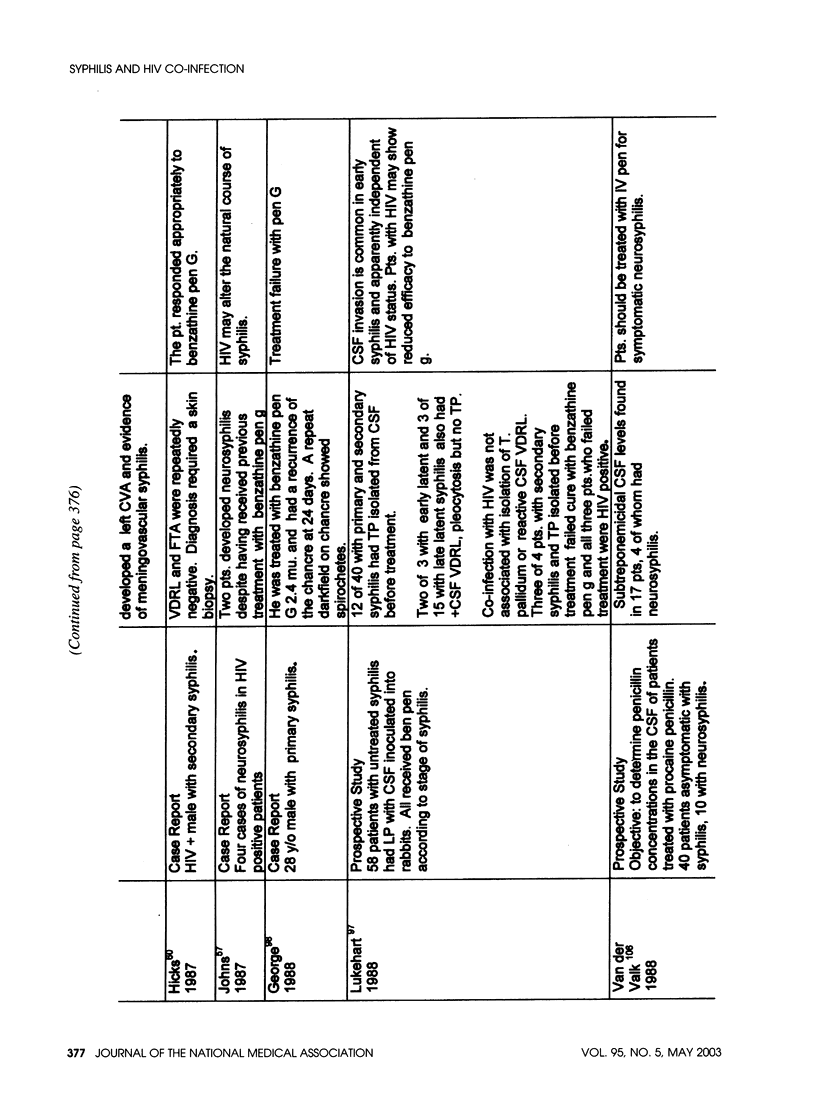
- George D., Alexander W. J. Possible penicillin treatment failure in primary syphilis. Ala J Med Sci. 1988 Oct;25(4):427–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold J., Dwyer J. A short history of AIDS. Med J Aust. 1994 Mar 7;160(5):251–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt R. M., Lukehart S. A., Plummer F. A., Quinn T. C., Critchlow C. W., Ashley R. L., D'Costa L. J., Ndinya-Achola J. O., Corey L., Ronald A. R. Genital ulceration as a risk factor for human immunodeficiency virus infection. AIDS. 1988 Feb;2(1):47–50. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198802000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene B. M., Miller N. R., Bynum T. E. Failure of penicillin G benzathine in the treatment of neurosyphilis. Arch Intern Med. 1980 Aug;140(8):1117–1118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosskurth H., Gray R., Hayes R., Mabey D., Wawer M. Control of sexually transmitted diseases for HIV-1 prevention: understanding the implications of the Mwanza and Rakai trials. Lancet. 2000 Jun 3;355(9219):1981–1987. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)02336-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosskurth H., Mosha F., Todd J., Mwijarubi E., Klokke A., Senkoro K., Mayaud P., Changalucha J., Nicoll A., ka-Gina G. Impact of improved treatment of sexually transmitted diseases on HIV infection in rural Tanzania: randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 1995 Aug 26;346(8974):530–536. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(95)91380-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gwanzura L., Latif A., Bassett M., Machekano R., Katzenstein D. A., Mason P. R. Syphilis serology and HIV infection in Harare, Zimbabwe. Sex Transm Infect. 1999 Dec;75(6):426–430. doi: 10.1136/sti.75.6.426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastings G. E., Weber R. J. Inflammatory bowel disease: Part I. Clinical features and diagnosis. Am Fam Physician. 1993 Feb 15;47(3):598–608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera G. A., Lackritz E. M., Janssen R. S., Raimondi V. P., Dodd R. Y., Aberle-Grasse J., Petersen L. R. Serologic test for syphilis as a surrogate marker for human immunodeficiency virus infection among United States blood donors. Transfusion. 1997 Aug;37(8):836–840. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1997.37897424407.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hicks C. B., Benson P. M., Lupton G. P., Tramont E. C. Seronegative secondary syphilis in a patient infected with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) with Kaposi sarcoma. A diagnostic dilemma. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Oct;107(4):492–495. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-107-4-492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. D., Neumann A. U., Perelson A. S., Chen W., Leonard J. M., Markowitz M. Rapid turnover of plasma virions and CD4 lymphocytes in HIV-1 infection. Nature. 1995 Jan 12;373(6510):123–126. doi: 10.1038/373123a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. D. Time to hit HIV, early and hard. N Engl J Med. 1995 Aug 17;333(7):450–451. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199508173330710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hook E. W., 3rd Syphilis and HIV infection. J Infect Dis. 1989 Sep;160(3):530–534. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.3.530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson M. M., Morton R. S. Fracastoro and syphilis: 500 years on. Lancet. 1996 Nov 30;348(9040):1495–1496. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(96)08170-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns D. R., Tierney M., Felsenstein D. Alteration in the natural history of neurosyphilis by concurrent infection with the human immunodeficiency virus. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jun 18;316(25):1569–1572. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198706183162503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalichman S. C., Rompa D., Cage M. Sexually transmitted infections among HIV seropositive men and women. Sex Transm Infect. 2000 Oct;76(5):350–354. doi: 10.1136/sti.76.5.350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koplan J. From the CDC: Syphilis elimination: history in the making--opening remarks. Sex Transm Dis. 2000 Feb;27(2):63–65. doi: 10.1097/00007435-200002000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenromp E. L., de Vlas S. J., Nagelkerke N. J., Habbema J. D. Estimating the magnitude of STD cofactor effects on HIV transmission: how well can it be done? Sex Transm Dis. 2001 Nov;28(11):613–621. doi: 10.1097/00007435-200111000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krech T. Syphilis und AIDS. Eine historische Parallele. Fortschr Med. 1988 Jul 20;106(21):439–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane H. C., Masur H., Edgar L. C., Whalen G., Rook A. H., Fauci A. S. Abnormalities of B-cell activation and immunoregulation in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1983 Aug 25;309(8):453–458. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198308253090803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langtry J. A., Copeman P. W. Late secondary syphilis altered by systemic corticosteroids in a human immunodeficiency virus antibody positive man. J R Soc Med. 1990 Jan;83(1):49–49. doi: 10.1177/014107689008300120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent R. Syphilis acquise et infection par le VIH. Presse Med. 1994 Nov 12;23(35):1621–1626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukehart S. A., Hook E. W., 3rd, Baker-Zander S. A., Collier A. C., Critchlow C. W., Handsfield H. H. Invasion of the central nervous system by Treponema pallidum: implications for diagnosis and treatment. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Dec 1;109(11):855–862. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-109-11-855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Zetina J., Ford W., Weber M., Barna S., Woerhle T., Kerndt P., Monterroso E. Predictors of syphilis seroreactivity and prevalence of HIV among street recruited injection drug users in Los Angeles County, 1994-6. Sex Transm Infect. 2000 Dec;76(6):462–469. doi: 10.1136/sti.76.6.462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER W. R. A SYSTEM TO PROVIDE AND TEACH COMPREHENSIVE MEDICAL CARE. JAMA. 1964 Jul 6;189:1–5. doi: 10.1001/jama.1964.03070010007001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCune J. M. The dynamics of CD4+ T-cell depletion in HIV disease. Nature. 2001 Apr 19;410(6831):974–979. doi: 10.1038/35073648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDaniel W. E. Unusual manifestations of syphilis with human immunodeficiency virus infection. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1988 Sep;19(3):578–578. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(88)80335-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohr J. A., Griffiths W., Jackson R., Saadah H., Bird P., Riddle J. Neurosyphilis and penicillin levels in cerebrospinal fluid. JAMA. 1976 Nov 8;236(19):2208–2209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musher D. M., Hague-Park M., Gyorkey F., Anderson D. C., Baughn R. E. The interaction between Treponema pallidum and human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jan;147(1):77–86. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.1.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musher D. M. How much penicillin cures early syphilis? Ann Intern Med. 1988 Dec 1;109(11):849–851. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-109-11-849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll A., Johnson A. M., Adler M. W., Laga M. Preventing HIV-1: lessons from Mwanza and Rakai. Lancet. 1999 May 1;353(9163):1522–1524. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(99)00078-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuttbrock L., Rosenblum A., Magura S., McQuistion H. L., Joseph H. The association between cocaine use and HIV/STDs among soup kitchen attendees in New York City. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2000 Sep 1;25(1):86–91. doi: 10.1097/00042560-200009010-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Keefe R., Marcus P., Townsend J., Gold M. Use of the term 'gay bowel syndrome'. Am Fam Physician. 1994 Feb 15;49(3):580–582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavis C. S., Folds J. D., Baseman J. B. Cell-mediated immunity during syphilis. Br J Vener Dis. 1978 Jun;54(3):144–150. doi: 10.1136/sti.54.3.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce J. M. A note on the origins of syphilis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1998 Apr;64(4):542–547. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.64.4.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROCKWELL D. H., YOBS A. R., MOORE M. B., Jr THE TUSKEGEE STUDY OF UNTREATED SYPHILIS; THE 30TH YEAR OF OBSERVATION. Arch Intern Med. 1964 Dec;114:792–798. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1964.03860120104011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahlenbeck S. I., Yohannes G., Molla K., Reifen R., Assefa A. Infection with HIV, syphilis and hepatitis B in Ethiopia: a survey in blood donors. Int J STD AIDS. 1997 Apr;8(4):261–264. doi: 10.1258/0956462971919886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Røttingen J. A., Cameron D. W., Garnett G. P. A systematic review of the epidemiologic interactions between classic sexually transmitted diseases and HIV: how much really is known? Sex Transm Dis. 2001 Oct;28(10):579–597. doi: 10.1097/00007435-200110000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
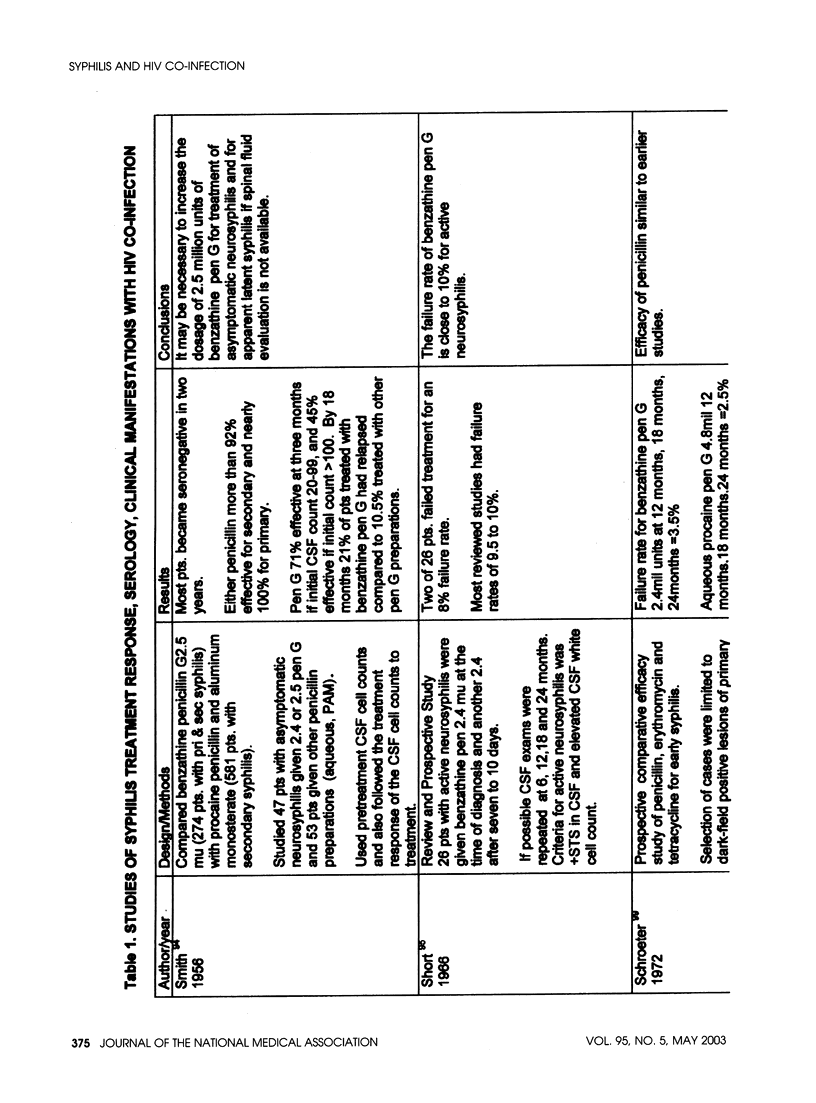
- SMITH C. A., KAMP M., OLANSKY S., PRICE E. V. Benzathine penicillin G in the treatment of syphilis. Bull World Health Organ. 1956;15(6):1087–1096. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satcher D. From the CDC: Syphilis elimination: history in the making--closing remarks. Sex Transm Dis. 2000 Feb;27(2):66–67. doi: 10.1097/00007435-200002000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeter A. L., Lucas J. B., Price E. V., Falcone V. H. Treatment for early syphilis and reactivity of serologic tests. JAMA. 1972 Jul 31;221(5):471–476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selik R. M., Haverkos H. W., Curran J. W. Acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) trends in the United States, 1978-1982. Am J Med. 1984 Mar;76(3):493–500. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90669-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellati T. J., Wilkinson D. A., Sheffield J. S., Koup R. A., Radolf J. D., Norgard M. V. Virulent Treponema pallidum, lipoprotein, and synthetic lipopeptides induce CCR5 on human monocytes and enhance their susceptibility to infection by human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Infect Dis. 2000 Jan;181(1):283–293. doi: 10.1086/315209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sepkowitz K. A. AIDS--the first 20 years. N Engl J Med. 2001 Jun 7;344(23):1764–1772. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200106073442306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short D. H., Knox J. M., Glicksman J. Neurosyphilis, the search for adequate treatment. A review and report of a study using benzathine penicillin G. Arch Dermatol. 1966 Jan;93(1):87–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegal F. P., Lopez C., Hammer G. S., Brown A. E., Kornfeld S. J., Gold J., Hassett J., Hirschman S. Z., Cunningham-Rundles C., Adelsberg B. R. Severe acquired immunodeficiency in male homosexuals, manifested by chronic perianal ulcerative herpes simplex lesions. N Engl J Med. 1981 Dec 10;305(24):1439–1444. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198112103052403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonsen J. N., Cameron D. W., Gakinya M. N., Ndinya-Achola J. O., D'Costa L. J., Karasira P., Cheang M., Ronald A. R., Piot P., Plummer F. A. Human immunodeficiency virus infection among men with sexually transmitted diseases. Experience from a center in Africa. N Engl J Med. 1988 Aug 4;319(5):274–278. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198808043190504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh A. E., Romanowski B. Syphilis: review with emphasis on clinical, epidemiologic, and some biologic features. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1999 Apr;12(2):187–209. doi: 10.1128/cmr.12.2.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sopelak V. M., Williams R. F., Aso T., Marut E. L., Hodgen G. D. A mechanical 'hypothalamus' for ovulation induction therapy. JAMA. 1984 Mar 16;251(11):1477–1477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torian Lucia V., Makki Hadi A., Menzies Isaura B., Murrill Christopher S., Weisfuse Isaac B. HIV infection in men who have sex with men, New York City Department of Health sexually transmitted disease clinics, 1990-1999: a decade of serosurveillance finds that racial disparities and associations between HIV and gonorrhea persist. Sex Transm Dis. 2002 Feb;29(2):73–78. doi: 10.1097/00007435-200202000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramont E. C. Persistence of Treponema pallidum following penicillin G therapy. Report of two cases. JAMA. 1976 Nov 8;236(19):2206–2207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramont E. C. Syphilis in the AIDS era. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jun 18;316(25):1600–1601. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198706183162510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanham G., Penne L., Allemeersch H., Kestens L., Willems B., van der Groen G., Jeang K. T., Toossi Z., Rich E. Modeling HIV transfer between dendritic cells and T cells: importance of HIV phenotype, dendritic cell-T cell contact and T-cell activation. AIDS. 2000 Oct 20;14(15):2299–2311. doi: 10.1097/00002030-200010200-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei X., Ghosh S. K., Taylor M. E., Johnson V. A., Emini E. A., Deutsch P., Lifson J. D., Bonhoeffer S., Nowak M. A., Hahn B. H. Viral dynamics in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. Nature. 1995 Jan 12;373(6510):117–122. doi: 10.1038/373117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. M. Unraveling the Tuskegee Study of Untreated Syphilis. Arch Intern Med. 2000 Mar 13;160(5):585–598. doi: 10.1001/archinte.160.5.585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yinnon A. M., Coury-Doniger P., Polito R., Reichman R. C. Serologic response to treatment of syphilis in patients with HIV infection. Arch Intern Med. 1996 Feb 12;156(3):321–325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Hoek A., Yuliang F., Dukers N. H., Zhiheng C., Jiangting F., Lina Z., Xiuxing Z. High prevalence of syphilis and other sexually transmitted diseases among sex workers in China: potential for fast spread of HIV. AIDS. 2001 Apr 13;15(6):753–759. doi: 10.1097/00002030-200104130-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Valk P. G., Kraai E. J., van Voorst Vader P. C., Haaxma-Reiche H., Snijder J. A. Penicillin concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) during repository treatment regimen for syphilis. Genitourin Med. 1988 Aug;64(4):223–225. doi: 10.1136/sti.64.4.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


