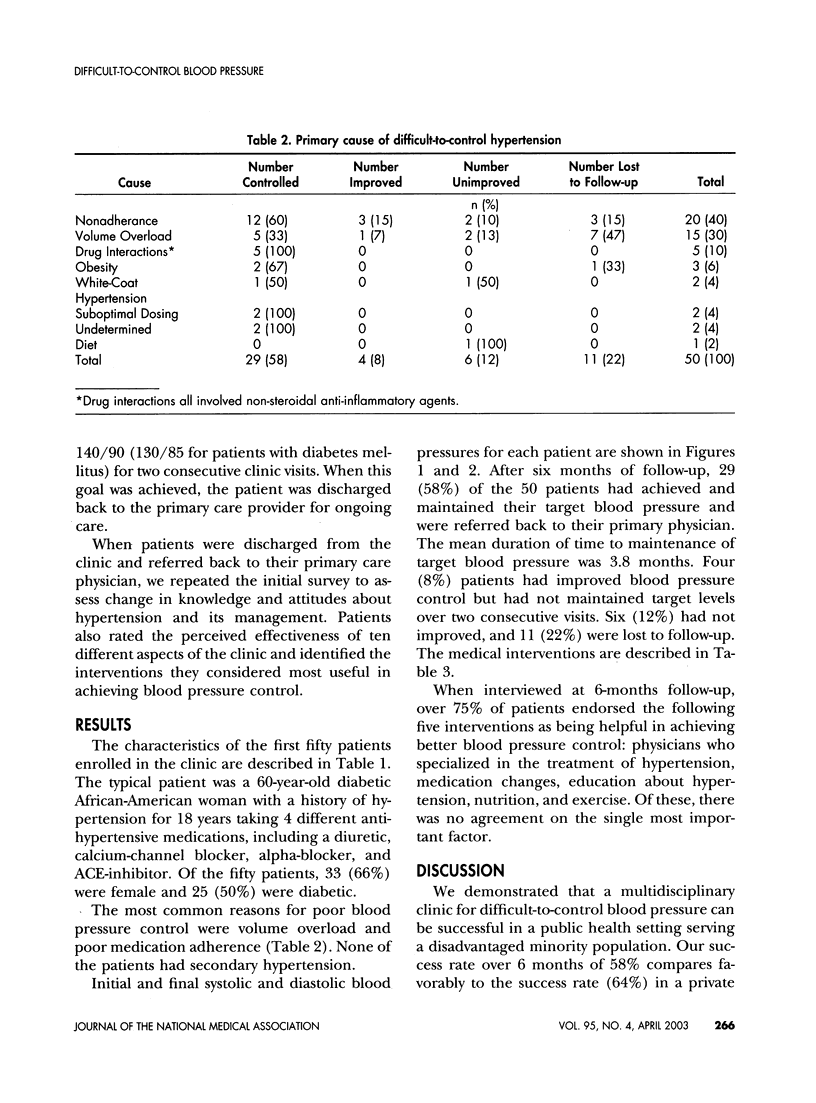
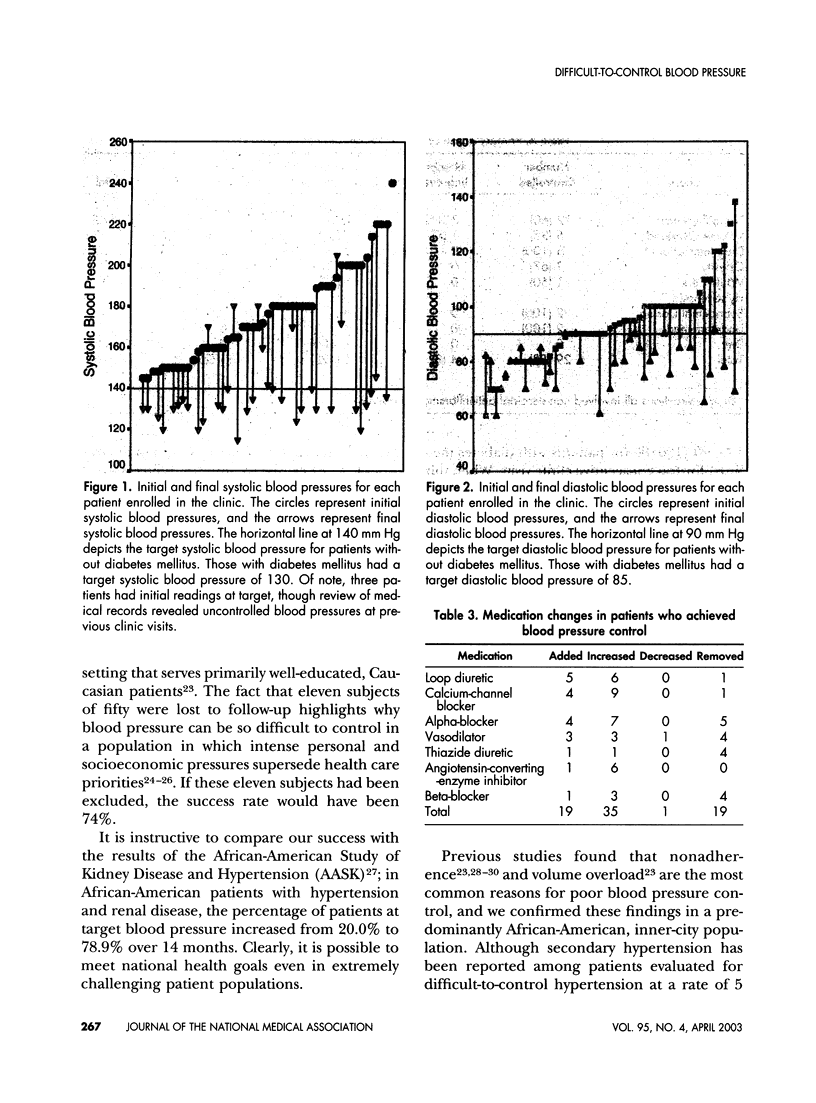
Abstract
Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in disadvantaged populations remains high. Few innovative strategies or services to treat chronic diseases have been critically analyzed in these patients. We evaluated our initial experiences with a newly established multidisciplinary clinic For the treatment of difficult-to-control hypertension and describe reasons for poor blood pressure control as well as treatment strategies. Patients with blood pressures greater than 140/90 despite concurrent treatment with three or more medications for at least three months were referred to our clinic. Data regarding sociodemographic characteristics, health beliefs and behaviors were collected. Two physicians jointly proposed an explanation for lack of blood pressure control. A multidisciplinary team of physicians, nurses, pharmacists, and nutritionists aggressively assessed and reinforced educational objectives tailored to individual needs. 58% of patients achieved target blood pressure at six months, but 22% were lost to follow-up. The most common reasons for previous treatment failure were volume overload and poor medication adherence. We conclude that a multidisciplinary clinic for difficult-to-control blood pressure can be successful in a large, urban hospital serving a disadvantaged minority population. However, more study is needed to delineate the specific reasons for success and further refine treatment strategies.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahluwalia J. S., McNagny S. E., Rask K. J. Correlates of controlled hypertension in indigent, inner-city hypertensive patients. J Gen Intern Med. 1997 Jan;12(1):7–14. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1497.1997.12107.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlowitz D. R., Ash A. S., Hickey E. C., Friedman R. H., Glickman M., Kader B., Moskowitz M. A. Inadequate management of blood pressure in a hypertensive population. N Engl J Med. 1998 Dec 31;339(27):1957–1963. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199812313392701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betancourt J. R., Carrillo J. E., Green A. R. Hypertension in multicultural and minority populations: linking communication to compliance. Curr Hypertens Rep. 1999 Dec;1(6):482–488. doi: 10.1007/BF03215777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burt V. L., Cutler J. A., Higgins M., Horan M. J., Labarthe D., Whelton P., Brown C., Roccella E. J. Trends in the prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in the adult US population. Data from the health examination surveys, 1960 to 1991. Hypertension. 1995 Jul;26(1):60–69. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.26.1.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burt V. L., Whelton P., Roccella E. J., Brown C., Cutler J. A., Higgins M., Horan M. J., Labarthe D. Prevalence of hypertension in the US adult population. Results from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988-1991. Hypertension. 1995 Mar;25(3):305–313. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.25.3.305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark L. T. Improving compliance and increasing control of hypertension: needs of special hypertensive populations. Am Heart J. 1991 Feb;121(2 Pt 2):664–669. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(91)90443-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dressler W. W. Hypertension in the African American community: social, cultural, and psychological factors. Semin Nephrol. 1996 Mar;16(2):71–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds D., Foerster E., Groth H., Greminger P., Siegenthaler W., Vetter W. Does self-measurement of blood pressure improve patient compliance in hypertension? J Hypertens Suppl. 1985 Apr;3(1):S31–S34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freis E. D. Improving treatment effectiveness in hypertension. Arch Intern Med. 1999 Nov 22;159(21):2517–2521. doi: 10.1001/archinte.159.21.2517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gornick M. E., Eggers P. W., Reilly T. W., Mentnech R. M., Fitterman L. K., Kucken L. E., Vladeck B. C. Effects of race and income on mortality and use of services among Medicare beneficiaries. N Engl J Med. 1996 Sep 12;335(11):791–799. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199609123351106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves J. W. Management of difficult-to-control hypertension. Mayo Clin Proc. 2000 Mar;75(3):278–284. doi: 10.4065/75.3.278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He Jiang, Muntner Paul, Chen Jing, Roccella Edward J., Streiffer Richard H., Whelton Paul K. Factors associated with hypertension control in the general population of the United States. Arch Intern Med. 2002 May 13;162(9):1051–1058. doi: 10.1001/archinte.162.9.1051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan N. M. Ethnic aspects of hypertension. Lancet. 1994 Aug 13;344(8920):450–452. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)91774-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller N. H., Hill M., Kottke T., Ockene I. S. The multilevel compliance challenge: recommendations for a call to action. A statement for healthcare professionals. Circulation. 1997 Feb 18;95(4):1085–1090. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.95.4.1085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moorman P. G., Hames C. G., Tyroler H. A. Socioeconomic status and morbidity and mortality in hypertensive blacks. Cardiovasc Clin. 1991;21(3):179–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachter L. M., Weller S. C. Acculturation and compliance with medical therapy. J Dev Behav Pediatr. 1993 Jun;14(3):163–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose L. E., Kim M. T., Dennison C. R., Hill M. N. The contexts of adherence for African Americans with high blood pressure. J Adv Nurs. 2000 Sep;32(3):587–594. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2648.2000.01538.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sackett D. L., Haynes R. B., Gibson E. S., Hackett B. C., Taylor D. W., Roberts R. S., Johnson A. L. Randomised clinical trial of strategies for improving medication compliance in primary hypertension. Lancet. 1975 May 31;1(7918):1205–1207. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92192-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz J. F., Sheps S. G. Management of patients with hypertension: a hypertension clinic model. Mayo Clin Proc. 1994 Oct;69(10):997–999. doi: 10.1016/s0025-6196(12)61829-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setaro J. F., Black H. R. Refractory hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1992 Aug 20;327(8):543–547. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199208203270808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shea S., Misra D., Ehrlich M. H., Field L., Francis C. K. Predisposing factors for severe, uncontrolled hypertension in an inner-city minority population. N Engl J Med. 1992 Sep 10;327(11):776–781. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199209103271107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whelton Paul K., He Jiang, Appel Lawrence J., Cutler Jeffrey A., Havas Stephen, Kotchen Theodore A., Roccella Edward J., Stout Ron, Vallbona Carlos, Winston Mary C. Primary prevention of hypertension: clinical and public health advisory from The National High Blood Pressure Education Program. JAMA. 2002 Oct 16;288(15):1882–1888. doi: 10.1001/jama.288.15.1882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winickoff R. N., Murphy P. K. The persistent problem of poor blood pressure control. Arch Intern Med. 1987 Aug;147(8):1393–1396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright Jackson T., Jr, Agodoa Lawrence, Contreras Gabriel, Greene Tom, Douglas Janice G., Lash James, Randall Otelio, Rogers Nancy, Smith Michael C., Massry Shaul. Successful blood pressure control in the African American Study of Kidney Disease and Hypertension. Arch Intern Med. 2002 Jul 22;162(14):1636–1643. doi: 10.1001/archinte.162.14.1636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yakovlevitch M., Black H. R. Resistant hypertension in a tertiary care clinic. Arch Intern Med. 1991 Sep;151(9):1786–1792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


