Abstract
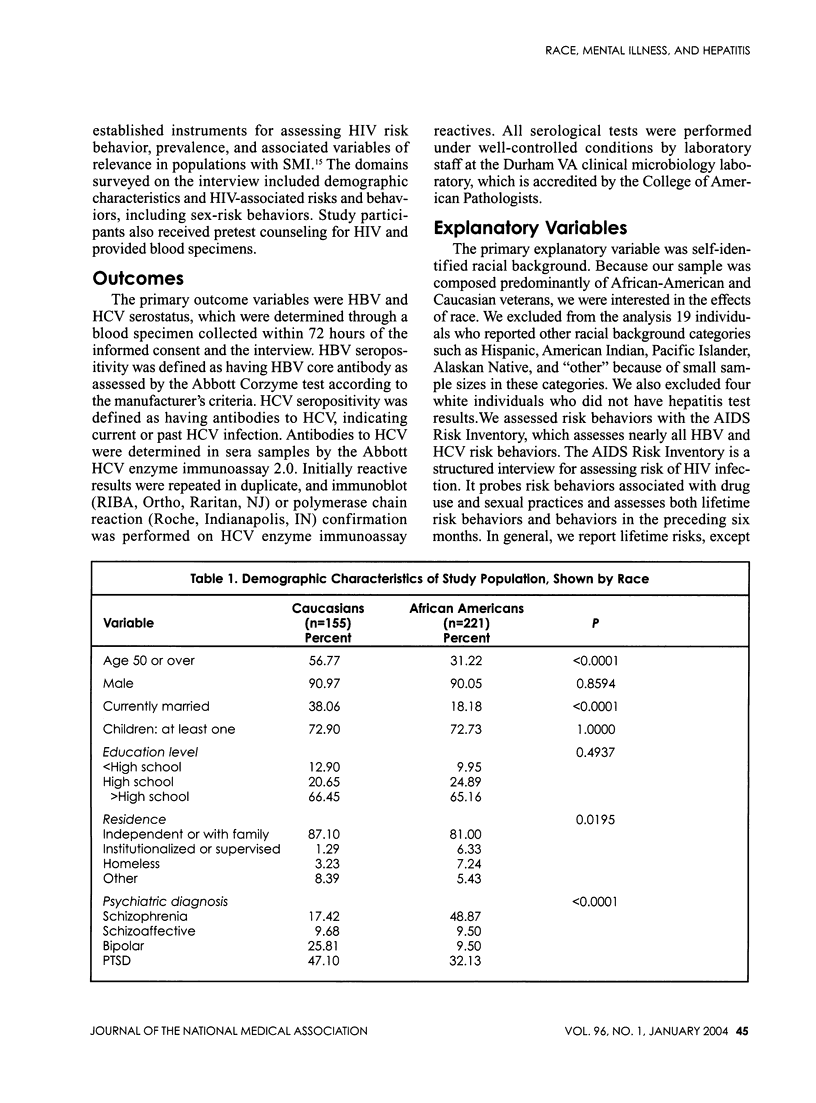
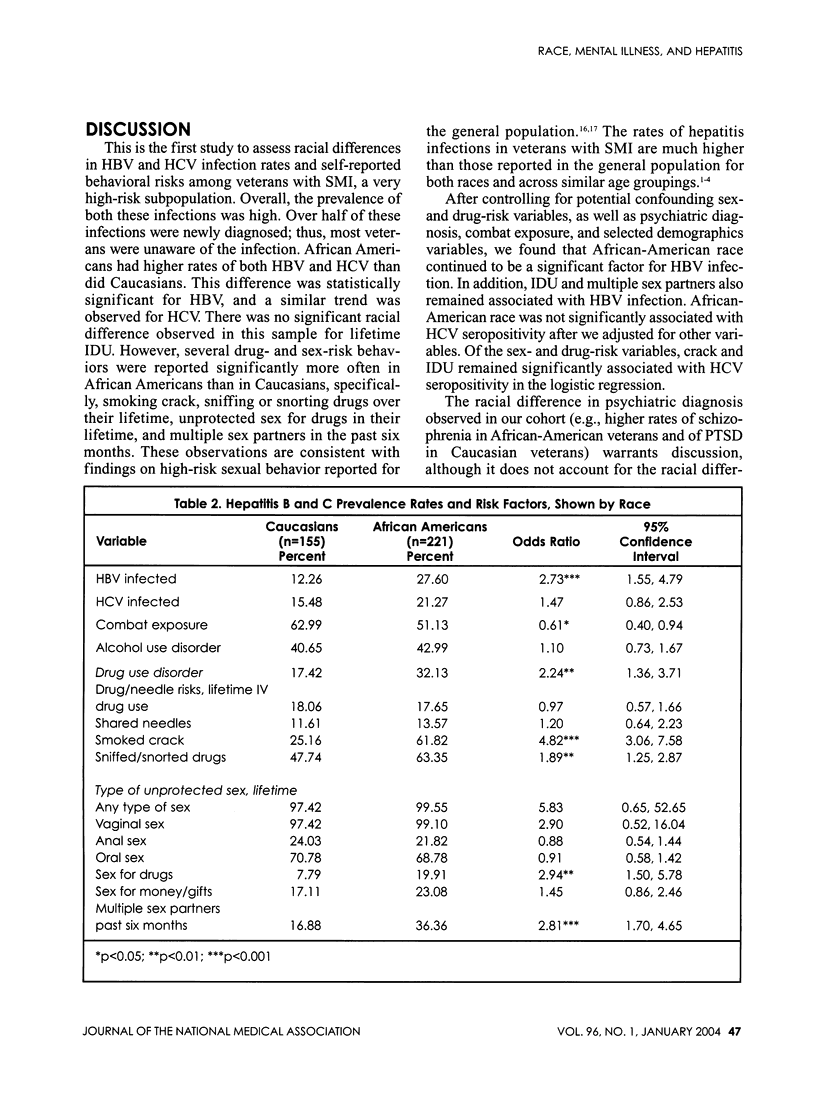
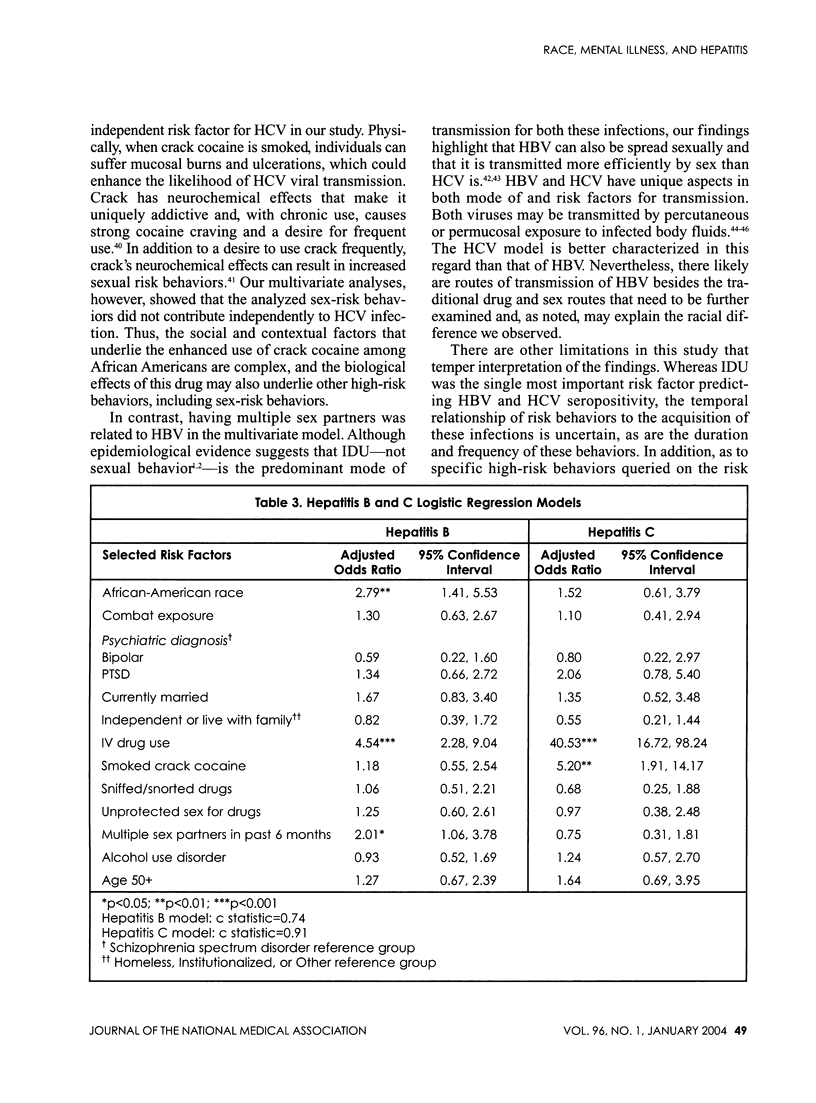
Racial differences in the seroprevalence of and risks for hepatitis B (HBV) and hepatitis C (HCV) were examined in military veterans with severe mental illnesses (SMI). Participants (376; 155 Caucasian, 221 African American) were inpatients at a Veterans Affairs (VA) psychiatric unit in Durham, N.C., from 1998 to 2000. Prevalence rates of HBV and HCV were 21.3% and 18.9%, respectively. African Americans had a higher HBV seroprevalence than did Caucasians: 27.6% versus 12.3%; odds ratio (OR) 2.73; 95% confidence interval (CI)=1.55, 4.79. Although not statistically significant, HCV seroprevalence was also higher for African Americans than it was for Caucasians: 21.3% versus 15.5%; OR=1.47; 95% CI=0.86, 2.53. No racial difference was observed for injection drug use (IDU), the strongest risk indicator for both HBV and HCV. Multivariable analyses indicated that African-American race, IDU, and multiple sex partners in the past six months were related to an increased risk of HBV, whereas IDU and smoking crack cocaine were both independently related to an increased risk of HCV. Thus, veterans with SMI--particularly African-American veterans--have high rates of HBV and HCV infection. African-American veterans have significantly higher rates of HBV than do Caucasian veterans, which persist after controlling for prominent risk behaviors.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adebimpe V. R., Klein H. E., Fried J. Hallucinations and delusions in black psychiatric patients. J Natl Med Assoc. 1981 Jun;73(6):517–520. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ademmer K., Beutel M., Bretzel R., Jaeger C., Reimer C., Clemens J. Suicidal ideation with IFN-alpha and ribavirin in a patient with hepatitis C. Psychosomatics. 2001 Jul-Aug;42(4):365–367. doi: 10.1176/appi.psy.42.4.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alter M. J., Kruszon-Moran D., Nainan O. V., McQuillan G. M., Gao F., Moyer L. A., Kaslow R. A., Margolis H. S. The prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection in the United States, 1988 through 1994. N Engl J Med. 1999 Aug 19;341(8):556–562. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199908193410802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. E., Dahlberg L. L. High-risk sexual behavior in the general population. Results from a national survey, 1988-1990. Sex Transm Dis. 1992 Nov-Dec;19(6):320–325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell C. C., Mehta H. The misdiagnosis of black patients with manic depressive illness. J Natl Med Assoc. 1980 Feb;72(2):141–145. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard E. B., Jones-Alexander J., Buckley T. C., Forneris C. A. Psychometric properties of the PTSD Checklist (PCL). Behav Res Ther. 1996 Aug;34(8):669–673. doi: 10.1016/0005-7967(96)00033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonaccorso Stefania, Marino Valentina, Puzella Antonella, Pasquini Massimo, Biondi Massimo, Artini Marco, Almerighi Cristiana, Verkerk Robert, Meltzer Herbert, Maes Michael. Increased depressive ratings in patients with hepatitis C receiving interferon-alpha-based immunotherapy are related to interferon-alpha-induced changes in the serotonergic system. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2002 Feb;22(1):86–90. doi: 10.1097/00004714-200202000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun B. L., Murray D., Hannan P., Sidney S., Le C. Cocaine use and characteristics of young adult users from 1987 to 1992: the CARDIA Study. Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults. Am J Public Health. 1996 Dec;86(12):1736–1741. doi: 10.2105/ajph.86.12.1736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs M. E., Baker C., Hall R., Gaziano J. M., Gagnon D., Bzowej N., Wright T. L. Prevalence and risk factors for hepatitis C virus infection at an urban Veterans Administration medical center. Hepatology. 2001 Dec;34(6):1200–1205. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2001.29303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bräu Norbert, Bini Edmund J., Shahidi Azra, Aytaman Ayse, Xiao Peiying, Stancic Saray, Eng Robert, Brown Sheldon T., Paronetto Fiorenzo. Prevalence of hepatitis C and coinfection with HIV among United States veterans in the New York City metropolitan area. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002 Aug;97(8):2071–2078. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2002.05924.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterfield Marian I., Bosworth Hayden B., Meador Keith G., Stechuchak Karen M., Essock Susan M., Osher Fred C., Goodman Lisa A., Swanson Jeffrey W., Bastian Lori A., Horner Ronnie D. Gender differences in hepatitis C infection and risks among persons with severe mental illness. Psychiatr Serv. 2003 Jun;54(6):848–853. doi: 10.1176/appi.ps.54.6.848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carvajal García-Pando Alfonso, García del Pozo Javier, Sánchez Ana Sánchez, Velasco Martín Alfonso, Rueda de Castro Ana María, Lucena M. Isabel. Hepatotoxicity associated with the new antidepressants. J Clin Psychiatry. 2002 Feb;63(2):135–137. doi: 10.4088/jcp.v63n0208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chawarski M. C., Pakes J., Schottenfeld R. S. Assessment of HIV risk. J Addict Dis. 1998;17(4):49–59. doi: 10.1300/J069v17n04_05. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung R. C. Epidemiology of hepatitis C virus infection in American veterans. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000 Mar;95(3):740–747. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2000.01854.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman D., Baker F. M. Misdiagnosis of schizophrenia in older, black veterans. J Nerv Ment Dis. 1994 Sep;182(9):527–528. doi: 10.1097/00005053-199409000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwight M. M., Kowdley K. V., Russo J. E., Ciechanowski P. S., Larson A. M., Katon W. J. Depression, fatigue, and functional disability in patients with chronic hepatitis C. J Psychosom Res. 2000 Nov;49(5):311–317. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3999(00)00155-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiscus S. A., Kelly W. F., Battigelli D. A., Weber D. J., Schoenbach V. J., Landis S. E., Wilber J. C., Van der Horst C. M. Hepatitis C virus seroprevalence in clients of sexually transmitted disease clinics in North Carolina. Sex Transm Dis. 1994 May-Jun;21(3):155–160. doi: 10.1097/00007435-199405000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana Robert J., Hussain Khozema B., Schwartz Steven M., Moyer Cheryl A., Su Grace L., Lok Anna S. F. Emotional distress in chronic hepatitis C patients not receiving antiviral therapy. J Hepatol. 2002 Mar;36(3):401–407. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(01)00280-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forton Daniel M., Thomas Howard C., Murphy Christine A., Allsop Joanna M., Foster Graham R., Main Janice, Wesnes Keith A., Taylor-Robinson Simon D. Hepatitis C and cognitive impairment in a cohort of patients with mild liver disease. Hepatology. 2002 Feb;35(2):433–439. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2002.30688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried Michael W., Shiffman Mitchell L., Reddy K. Rajender, Smith Coleman, Marinos George, Gonçales Fernando L., Jr, Häussinger Dieter, Diago Moises, Carosi Giampiero, Dhumeaux Daniel. Peginterferon alfa-2a plus ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med. 2002 Sep 26;347(13):975–982. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa020047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frueh B. Christopher, Hamner Mark B., Bernat Jeffrey A., Turner Samuel M., Keane Terence M., Arana George W. Racial differences in psychotic symptoms among combat veterans with PTSD. Depress Anxiety. 2002;16(4):157–161. doi: 10.1002/da.10068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelberg L., Robertson M. J., Leake B., Wenzel S. L., Bakhtiar L., Hardie E. A., Sadler N., Getzug T. Hepatitis B among homeless and other impoverished US military veterans in residential care in Los Angeles. Public Health. 2001 Jul;115(4):286–291. doi: 10.1038/sj/ph/1900783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleason Ondria C., Yates William R., Isbell M. Daniel, Philipsen Michelle A. An open-label trial of citalopram for major depression in patients with hepatitis C. J Clin Psychiatry. 2002 Mar;63(3):194–198. doi: 10.4088/jcp.v63n0304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harsch H. H., Pankiewicz J., Bloom A. S., Rainey C., Cho J. K., Sperry L., Stein E. A. Hepatitis C virus infection in cocaine users--a silent epidemic. Community Ment Health J. 2000 Jun;36(3):225–233. doi: 10.1023/a:1001988613235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland C. A., Ma Y., Moscicki B., Durako S. J., Levin L., Wilson C. M. Seroprevalence and risk factors of hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and human cytomegalovirus among HIV-infected and high-risk uninfected adolescents: findings of the REACH Study. Adolescent Medicine HIV/AIDS Research Network. Sex Transm Dis. 2000 May;27(5):296–303. doi: 10.1097/00007435-200005000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang L. Y., Ross M. W., Zack C., Bull L., Rickman K., Holleman M. Prevalence of sexually transmitted infections and associated risk factors among populations of drug abusers. Clin Infect Dis. 2000 Oct 25;31(4):920–926. doi: 10.1086/318131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanno A., Yamada M., Abe M., Okamoto Y. A case of interferon alpha-induced manic psychosis in chronic hepatitis C. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1999 Jan;187(1):79–82. doi: 10.1620/tjem.187.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelen G. D., Green G. B., Purcell R. H., Chan D. W., Qaqish B. F., Sivertson K. T., Quinn T. C. Hepatitis B and hepatitis C in emergency department patients. N Engl J Med. 1992 May 21;326(21):1399–1404. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199205213262105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim A., Galanter M., Castaneda R., Lifshutz H., Franco H. Crack cocaine use and sexual behavior among psychiatric inpatients. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 1992;18(3):235–246. doi: 10.3109/00952999209026064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraus M. R., Schäfer A., Faller H., Csef H., Scheurlen M. Paroxetine for the treatment of interferon-alpha-induced depression in chronic hepatitis C. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2002 Jun;16(6):1091–1099. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2036.2002.01265.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno Eri, Rothbard Aileen B. Racial disparities in antipsychotic prescription patterns for patients with schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 2002 Apr;159(4):567–572. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.159.4.567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski D. Genetic susceptibility to malaria getting complex. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2000 Jun;10(3):320–324. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(00)00087-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leigh B. C., Temple M. T., Trocki K. F. The sexual behavior of US adults: results from a national survey. Am J Public Health. 1993 Oct;83(10):1400–1408. doi: 10.2105/ajph.83.10.1400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie-Blanton M., Anthony J. C., Schuster C. R. Probing the meaning of racial/ethnic group comparisons in crack cocaine smoking. JAMA. 1993 Feb 24;269(8):993–997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQuillan G. M., Coleman P. J., Kruszon-Moran D., Moyer L. A., Lambert S. B., Margolis H. S. Prevalence of hepatitis B virus infection in the United States: the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys, 1976 through 1994. Am J Public Health. 1999 Jan;89(1):14–18. doi: 10.2105/ajph.89.1.14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murdoch Maureen, Hodges James, Cowper Diane, Fortier Larry, van Ryn Michelle. Racial disparities in VA service connection for posttraumatic stress disorder disability. Med Care. 2003 Apr;41(4):536–549. doi: 10.1097/01.MLR.0000053232.67079.A5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy E. L., Bryzman S. M., Glynn S. A., Ameti D. I., Thomson R. A., Williams A. E., Nass C. C., Ownby H. E., Schreiber G. B., Kong F. Risk factors for hepatitis C virus infection in United States blood donors. NHLBI Retrovirus Epidemiology Donor Study (REDS) Hepatology. 2000 Mar;31(3):756–762. doi: 10.1002/hep.510310329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neighbors H. W. Socioeconomic status and psychologic distress in adult blacks. Am J Epidemiol. 1986 Nov;124(5):779–793. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osher Fred C., Goldberg Richard W., McNary Scot W., Swartz Marvin S., Essock Susan M., Butterfield Marian I., Rosenberg Stanley D., Five-Site Health and Risk Study Research Committee Substance abuse and the transmission of hepatitis C among persons with severe mental illness. Psychiatr Serv. 2003 Jun;54(6):842–847. doi: 10.1176/appi.ps.54.6.842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. D., Goodman L. A., Osher F. C., Swartz M. S., Essock S. M., Butterfield M. I., Constantine N. T., Wolford G. L., Salyers M. P. Prevalence of HIV, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C in people with severe mental illness. Am J Public Health. 2001 Jan;91(1):31–37. doi: 10.2105/ajph.91.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenheck R., Seibyl C. L. Homelessness: health service use and related costs. Med Care. 1998 Aug;36(8):1256–1264. doi: 10.1097/00005650-199808000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stead W. W., Senner J. W., Reddick W. T., Lofgren J. P. Racial differences in susceptibility to infection by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. N Engl J Med. 1990 Feb 15;322(7):422–427. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199002153220702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strakowski S. M., Flaum M., Amador X., Bracha H. S., Pandurangi A. K., Robinson D., Tohen M. Racial differences in the diagnosis of psychosis. Schizophr Res. 1996 Aug 23;21(2):117–124. doi: 10.1016/0920-9964(96)00041-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thio C. L., Thomas D. L., Goedert J. J., Vlahov D., Nelson K. E., Hilgartner M. W., O'Brien S. J., Karacki P., Marti D., Astemborski J. Racial differences in HLA class II associations with hepatitis C virus outcomes. J Infect Dis. 2001 May 30;184(1):16–21. doi: 10.1086/321005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorpe L. E., Ouellet L. J., Levy J. R., Williams I. T., Monterroso E. R. Hepatitis C virus infection: prevalence, risk factors, and prevention opportunities among young injection drug users in Chicago, 1997-1999. J Infect Dis. 2000 Nov 2;182(6):1588–1594. doi: 10.1086/317607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trierweiler S. J., Neighbors H. W., Munday C., Thompson E. E., Binion V. J., Gomez J. P. Clinician attributions associated with the diagnosis of schizophrenia in African American and non-African American patients. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2000 Feb;68(1):171–175. doi: 10.1037//0022-006x.68.1.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vamvakas E. C., Taswell H. F. Epidemiology of blood transfusion. Transfusion. 1994 Jun;34(6):464–470. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1994.34694295059.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace B. C. Treating crack cocaine dependence: the critical role of relapse prevention. J Psychoactive Drugs. 1992 Apr-Jun;24(2):213–222. doi: 10.1080/02791072.1992.10471641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Serag Hashem B., Kunik Mark, Richardson Peter, Rabeneck Linda. Psychiatric disorders among veterans with hepatitis C infection. Gastroenterology. 2002 Aug;123(2):476–482. doi: 10.1053/gast.2002.34750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


