Abstract
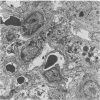
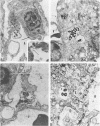
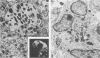
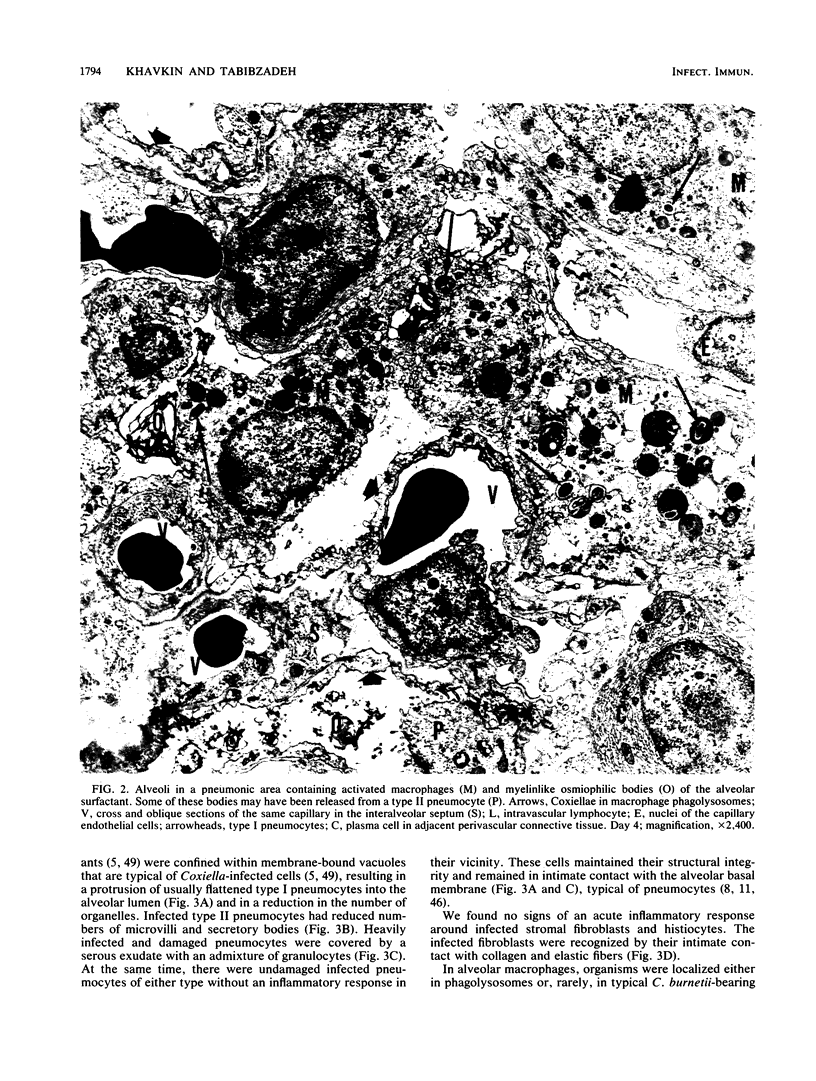
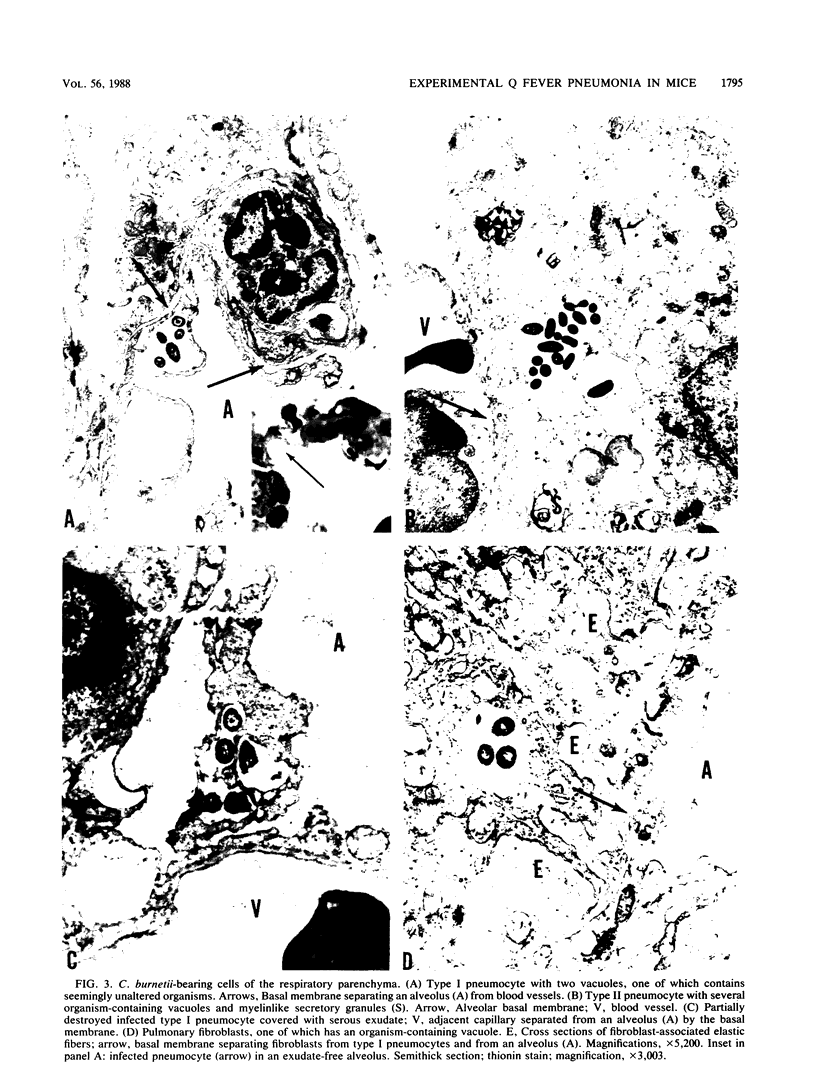
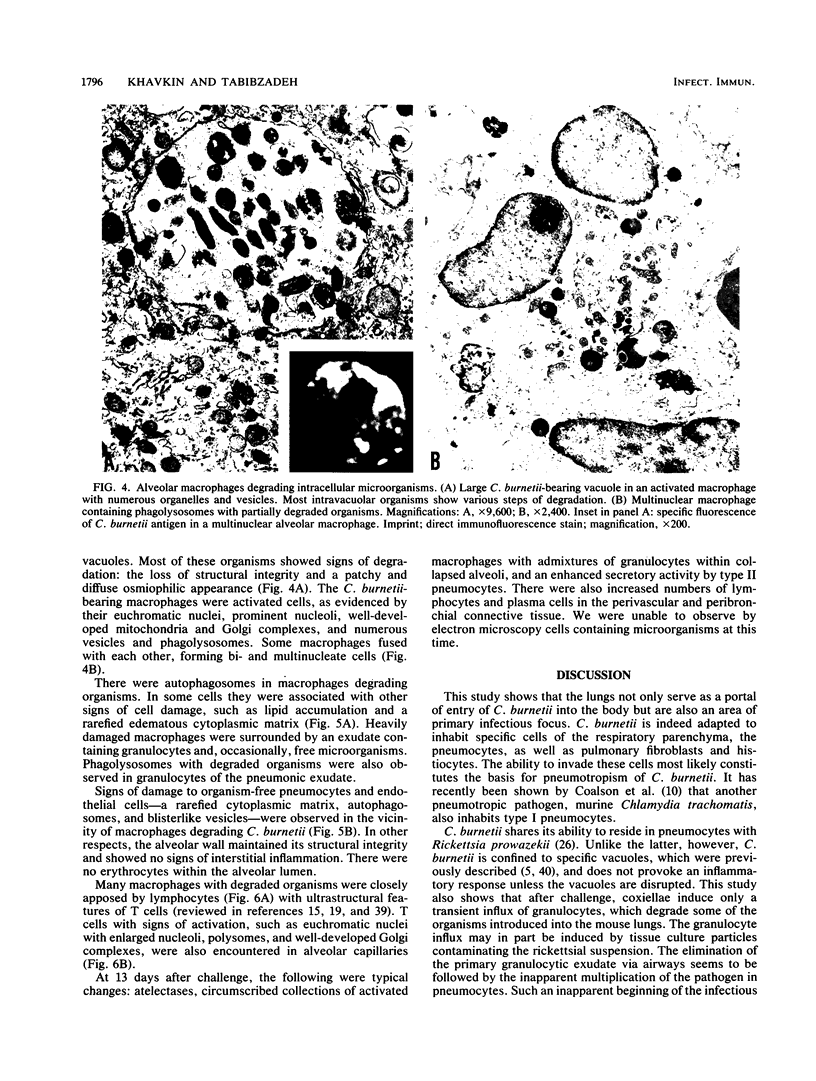
A histologic, immunofluorescence, and electron microscopic study of the intracellular parasitism of Coxiella burnetii (the Q fever agent) in mouse lungs after intranasal challenge was undertaken. It was shown that this microorganism invades type I and, rarely, type II pneumocytes as well as pulmonary fibroblasts and histiocytes. The infectious process can be described as a focal intra-alveolar inflammation with the macrophages prevailing in the exudate. It is self-limited, with a complete resolution. The inflammation is associated with atelectases and with increased secretory activity by type II pneumocytes. Alveolar macrophages and granulocytes degrade C. burnetii. This degradation is followed by damage to and eventual disintegration of some macrophages and by damage to some bacterium-free pneumocytes and vascular endothelial cells in the vicinity of macrophages degrading organisms. The cell damage might be caused by lipopolysaccharide released from degraded organisms. The infectious process is also associated with the influx of T cells in the pneumonic foci, T-cell attachment to the macrophages degrading organisms, and fusion of some macrophages. These are considered a morphologic expression of cell-mediated immunity involved in the infectious process.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen A. C., Spitz S. A Comparative Study of the Pathology of Scrub Typhus (Tsutsugamushi Disease) and Other Rickettsial Diseases. Am J Pathol. 1945 Jul;21(4):603–681. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amosenkova N. I., Khavkin T. N. O techenii éksperimental'noi Ku-rikketsial'noi pnevmonii u belykh myshei (opyty s intranazal'nym zarazheniem) Tr Leningr Inst Epidemiol Mikrobiol. 1963;25:154–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ariel B. M., Khavkin T. N., Amosenkova N. I. Interaction between Coxiellae burnetii and the cells in experimental Q-rickettsiosis. Histologic and electron microscope studies. Pathol Microbiol (Basel) 1973;39(6):412–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENENSON A. S., TIGERTT W. D. Studies on Q fever in man. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1956;69:98–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baca O. G., Paretsky D. Q fever and Coxiella burnetii: a model for host-parasite interactions. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Jun;47(2):127–149. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.2.127-149.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berke G. Cytotoxic T-lymphocytes. How do they function? Immunol Rev. 1983;72:5–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb01071.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertalanffy F. D. Respiratory tissue: structure, histophysiology, cytodynamics. II. New approaches and interpretations. Int Rev Cytol. 1964;17:213–297. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60408-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantin A., Crystal R. G. "Interstitial pathology': an overview of the chronic interstitial lung disorders. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1985;76 (Suppl 1):83–91. doi: 10.1159/000233738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coalson J. J., Winter V. T., Bass L. B., Schachter J., Grubbs B. G., Williams D. M. Chlamydia trachomatis pneumonia in the immune, athymic and normal BALB mouse. Br J Exp Pathol. 1987 Jun;68(3):399–411. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crystal R. G., Gadek J. E., Ferrans V. J., Fulmer J. D., Line B. R., Hunninghake G. W. Interstitial lung disease: current concepts of pathogenesis, staging and therapy. Am J Med. 1981 Mar;70(3):542–568. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90577-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossi C. E., Zicca A., Cadoni A., Mingari M. C., Moretta A., Moretta L. Ultrastructural characteristics of human T cell clones with various cytolytic activities. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Aug;13(8):670–677. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackstadt T., Williams J. C. Biochemical stratagem for obligate parasitism of eukaryotic cells by Coxiella burnetii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3240–3244. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall W. C., White J. D., Kishimoto R. A., Whitmire R. E. Aerosol Q fever infection of the nude mouse. Vet Pathol. 1981 Sep;18(5):672–683. doi: 10.1177/030098588101800512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M., Larsen G. L., Henson J. E., Newman S. L., Musson R. A., Leslie C. C. Resolution of pulmonary inflammation. Fed Proc. 1984 Oct;43(13):2799–2806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang Y. H., Carl M., Grimley P. M., Serrate S., Yaffe L. Immunoultrastructural studies of human NK cells: I. Ultracytochemistry and comparison with T cell subsets. Anat Rec. 1987 Mar;217(3):274–289. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092170308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang Y. H., Carl M., Watson L. P., Yaffe L. Immunoultrastructural studies of human NK cells: II. Effector-target cell binding and phagocytosis. Anat Rec. 1987 Mar;217(3):290–304. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092170309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khavkin T. N., Amosenkova N. I., Krasnik F. I. Infectious process in the lungs after intranasal challenge of white mice with Rickettsia prowazekii. A histologic immunoluminescent and electron microscopic study. Am J Pathol. 1974 Aug;76(2):213–224. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khavkin T. N., Ariel B. M., Amosenkova N. I., Kransnik F. I. Interaction of Rickettsia Prowazekii with phagocytes in the course of infectious process. A histological, immuno-luminescent and electron microscopic study of the mouse lung. Exp Mol Pathol. 1975 Jun;22(3):417–429. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(75)90085-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khavkin T. N. Porazheniia legkikh pri éksperimental'nom ku-rikketsioze. Arkh Patol. 1970;32(11):33–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khavkin T., Sukhinin V., Amosenkova N. Host-parasite interaction and development of infraforms in chicken embryos infected with Coxiella burnetii via the yolk sac. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):1281–1291. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.1281-1291.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto R. A., Veltri B. J., Shirey F. G., Canonico P. G., Walker J. S. Fat of Coxiella burnetti in macrophages from immune guinea pigs. Infect Immun. 1977 Feb;15(2):601–607. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.2.601-607.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullbacher A., Ada G. L. How do cytotoxic T lymphocytes work in vivo? Microb Pathog. 1987 Nov;3(5):315–318. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90001-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PULVER W., FELLMANN N. Uber tödlich verlaufene Q-Fieber-Erkrankungen. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1957 Jan 26;87(4):73–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peirce T. H., Yucht S. C., Gorin A. B., Jordan G. W., Tesluk H., Lillington G. A. Q fever pneumonitis. Diagnosis by transbronchoscopic lung biopsy. West J Med. 1979 May;130(5):453–455. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasthofer E. F., Barton J. C., Zarcone D., Grossi C. E. Ultrastructural morphology of granular lymphocytes (GL) from patients with immunophenotypically homogeneous expansions of GL populations (GLE). J Submicrosc Cytol. 1987 Apr;19(2):345–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYCHLO A., POSPISIL R. [On the morphology and pathogenesis of experimental Q-fever in the guinea pig]. Pathol Microbiol (Basel) 1960;23:489–503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rikihisa Y. Glycogen autophagosomes in polymorphonuclear leukocytes induced by rickettsiae. Anat Rec. 1984 Mar;208(3):319–327. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092080302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollwagen F. M., Bakun A. J., Dorsey C. H., Dasch G. A. Mechanisms of immunity to infection with typhus rickettsiae: infected fibroblasts bear rickettsial antigens on their surfaces. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):911–916. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.911-916.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman D. J. Infection and injury of human endothelial cells by Rickettsia rickettsii. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 May-Jun;137A(3):336–341. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(86)80045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TIGERTT W. D., BENENSON A. S., GOCHENOUR W. S. Airborne Q fever. Bacteriol Rev. 1961 Sep;25:285–293. doi: 10.1128/br.25.3.285-293.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITTICK J. W. Necropsy findings in a case of Q fever in Britain. Br Med J. 1950 Apr 29;1(4660):979–980. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.4660.979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E., Dobson M. E., Dasch G. A. Biochemistry of rickettsiae: recent advances. Acta Virol. 1987 May;31(3):271–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. Growth and physiology of rickettsiae. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Sep;37(3):259–283. doi: 10.1128/br.37.3.259-283.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. The biology of rickettsiae. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1982;36:345–370. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.36.100182.002021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H. Early events in the interaction of the obligate intracytoplasmic parasite, Rickettsia prowazekii, with eucaryotic cells: entry and lysis. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 May-Jun;137A(3):333–336. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(86)80044-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ten Have-Opbroek A. A. The structural composition of the pulmonary acinus in the mouse. A scanning electron microscopical and developmental-biological analysis. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1986;174(1):49–57. doi: 10.1007/BF00318335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]